Structural and melting point characterisation of six chiral ammonium naphthalene carboxylate salts†
Abstract
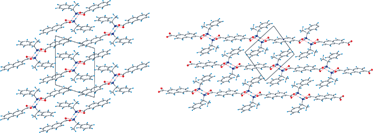
The hydrogen bonded networks of ammonium carboxylate salts formed between naphthalene-2-carboxylate or naphthalene-2,6-dicarboxylate with both optically active and racemic forms of 1-phenylethylammonium are reported. In their solid state form, the ammonium carboxylate salts feature three charge-separated N–H⋯O hydrogen bonds to form two types of 1-D hydrogen bonded columns between naphthalene-2-carboxylate: (naphthalene-2-carboxylate)·((R)-1-phenylethylammonium) (1) and ((naphthalene-2-carboxylate)·((S)-1-phenylethylammonium) (2) form non-centrosymmetric hydrogen bonded columns having a two-fold screw axis, while ((naphthalene-2-carboxylate)·((RS)-1-phenylethylammonium) (3) forms centrosymmetric hydrogen bonded columns having an inversion centre. The melting points of these three salts depend on the type of hydrogen bonded network that is formed. By linking the hydrogen bonded columns through the naphthalene-2,6-dicarboxylate anion, (naphthalene-2,6-dicarboxylate)·((R)-1-phenylethylammonium)2 (4), naphthalene-2,6-dicarboxylate)·((S)-1-phenylethylammonium)2 (5) and ((naphthalene-2,6-dicarboxylate)·((RS)-1-phenylethylammonium)2 (6) form closely related 2-D hydrogen bonded sheets that decompose rather than melt.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...