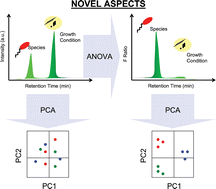
Four bacteria, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus warneri, and Micrococcus luteus, were grown at temperatures of 23, 30, and 37 °C and were characterized by pyrolysis-gas chromatography/differential mobility spectrometry (Py-GC/DMS) providing, with replicates, 120 data sets of retention time, compensation voltage, and ion intensity, each for negative and positive polarity. Principal component analysis (PCA) for 96 of these data sets exhibited clusters by temperature of culture growth and not by genus. Analysis of variance was used to isolate the constituents with dependences on growth temperature. When these were subtracted from the data sets, Fisher ratios with PCA resulted in four clusters according to genus at all temperatures for ions in each polarity. Comparable results were obtained from unsupervised PCA with 24 of the original data sets. The ions with taxonomic features were reconstructed into 3D plots of retention time, compensation voltage, and Fisher ratio and were matched, through GC-mass spectrometry (MS), with chemical standards attributed to the thermal decomposition of proteins and lipid A. Results for negative ions provided simpler data sets than from positive ions, as anticipated from selectivity of gas phase ion-molecule reactions in air at ambient pressure.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...