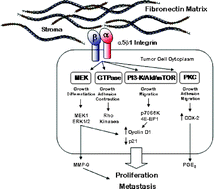
Throughout many countries, lung cancer will kill more people this year than malignancies related to breast, prostate, colon, liver, kidney and melanoma combined. Despite recent advances in understanding the molecular biology of lung carcinoma and the introduction of multiple new chemotherapeutic agents for its treatment, its dismal five-year survival rate (<15%) has not changed substantially. The lack of advancement in this area reflects the limited knowledge available concerning the factors that promote oncogenic transformation and proliferation of carcinoma cells in the lung. Malignant transformation plays a key role in tumor growth and invasion; however, other factors such as the surrounding stroma, local growth factors, vascularity, and systemic hormones are important contributors as well. We believe that the composition of the lung extracellular matrix is also important due to its ability to affect malignant cell behavior in vitro. The matrix glycoprotein fibronectin, for example, is highly expressed in chronic lung disorders where most lung carcinomas are identified. This document reviews information that implicates fibronectin in the stimulation of lung carcinoma cell growth. Data available to date indicate that by binding to specific integrin receptors expressed on the surface of tumor cells, fibronectin stimulates intracellular signals implicated in the pathobiology of lung carcinogenesis and lung tumor chemoresistance including mitogen-activated protein kinases, GTPases, and the PI3-kinase/Akt/mTOR pathway. Thus, integrin-mediated signals triggered by fibronectin in tumor cells represent promising targets for the development of novel anti-cancer strategies.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...