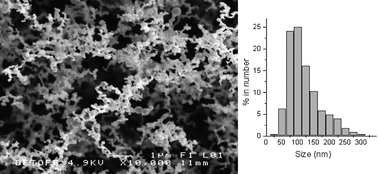
A new chromium oxyselenide solid–solution series Cr2O3−xSex (x = 0, 0.1, 0.15, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.7, 1.5, 2.15) was formed by the atmospheric pressure chemical vapour deposition of chromyl chloride and diethylselenide at 600 °C. The level of selenium incorporation was directly related to the gas-phase molar flows of reagents. There was a crossover in structure type adopted by the chromium oxyselenide with selenium incorporation, at x = 0–0.2 the solid solution crystallises in the Cr2O3 structure type, at x = 0.3–2.15 it adopts the Cr2Se3 structure type. All of the chromium oxyselenides were antiferromagnets. They showed a variation in Néel temperature with composition with a minimum temperature of 11 K observed for x = 0.7.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...