Probing carboxylate Gibbs transfer energies via liquid|liquid transfer at triple phase boundary electrodes: ion-transfer voltammetryversus COSMO-RS predictions
Abstract
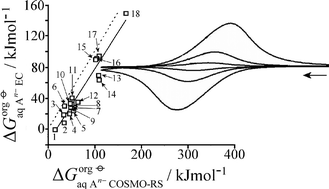
Understanding liquid|liquid ion transfer processes is important in particular for naturally occurring species such as carboxylates. In this study electrochemically driven mono-, di-, and tri-carboxylate anion transfer at the 4-(3-phenylpropyl)pyridine|aqueous electrolyte interface is investigated experimentally for a triple phase boundary system at graphite electrodes. The tetraphenylporphyrinato-Mn(III/II) redox system (Mn(III/II)TPP) dissolved in the water-immiscible organic phase (

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...