Highly efficient supramolecular photocatalysts for CO2 reduction using visible light†
Abstract
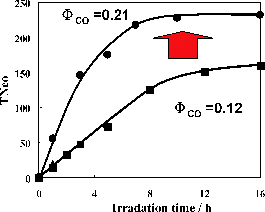
We report the most efficient homogeneous photocatalyst yet for CO2 reduction using a wide range of visible-light wavelength. We synthesized new Ru(II)–Re(I) binuclear complexes with 1,3-bis(4′-methyl-[2,2′]bipyridinyl-4-yl)-propan-2-ol (bpyC3bpy) as a bridge ligand, specifically [Ru-ReP(OEt)3]3+ and [Ru-Repy]3+ where a P(OEt)3 or pyridine ligand coordinates on the Re site. Their photocatalytic activities were compared with [Ru-ReCl]2+, which has a Cl− ligand on the Re site and has recently been reported as a much better photocatalyst (Φ = 0.12, TNCO = 160) than a 1 : 1 mixed system of the corresponding Ru(II) and Re(I) mononuclear complexes. The best photocatalyst was [Ru-ReP(OEt)3]3+, for which Φ = 0.21 and TNCO = 232. A mechanistic study clearly showed that [Ru-ReP(OEt)3]3+ is rapidly converted into the solvento complex [Ru-ReSol]3+, (Sol = DMF or TEOA) which is the actual photocatalyst. Although similar rapid ligand substitution occurs with other supramolecules, the pyridine and Cl− anions accelerate the decomposition of the supramolecular photocatalysts.
- This article is part of the themed collection: In honour of Vincenzo Balzani

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...