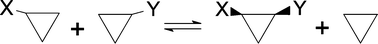
Several possible scales of steric effects of the alkyl groups were suggested on the basis of isodesmic model reactions, in which a sterically crowded compound is formally synthesized from simpler derivatives. The reaction energies were calculated within the framework of the density functional theory at the level B3LYP/6-311+G(d.p)//B3LYP/6-311+G(d.p) for 6 model systems and 7 various alkyl groups. The most important systems were cis-1,2-dialkylcyclopropanes 1 synthesized from two mono derivatives and sterically crowded derivatives of bicyclo[2.2.2]octane 2 with C3 symmetry. The scales of steric effects evaluated from the two models were rather different: the first scale depended in effect only on the C atoms in the α and β positions and the effects were almost equal for all primary alkyls. The second scale depended also on the γ position and the effect of the CH2–t-Bu group was much greater than that of the