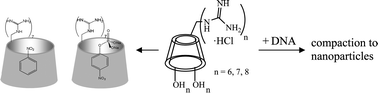
Per(6-guanidino-6-deoxy)-cyclodextrins 4a, 4b and 4c are novel derivatives, resulting from homogeneous introduction of the guanidino group at the primary side of α-, β- and γ-cyclodextrins. The products were obtained from the corresponding amino derivatives, as direct guanidinylation of the known bromo-cyclodextrins provided mixtures. The new compounds were fully characterized by NMR spectroscopy and other analytical methods, and their interaction with guest molecules was studied. Strong complexation with 4-nitrophenyl phosphate (NPP) disodium salt was observed (Kbinding ∼5 × 104 M–1), whereas the non-phosphorylated substrate nitrobenzene (NB) formed a very weak complex. 2D ROESY spectra revealed cavity inclusion in both cases, however the orientation of NPP was opposite to that of NB, such that the phosphate group is oriented toward the primary side facing the guanidine groups. The strong affinity of 4 towards the phosphorylated guest suggested that interaction with DNA was possible. The new compounds were found to completely inhibit the migration of ultra pure calf thymus DNA during agarose gel electrophoresis, whereas no effects were observed with guanidine alone or with the plain cyclodextrins. Further, the condensation of DNA into nanoparticles in the presence of 4b was demonstrated by atomic force microscopy, confirming strong electrostatic interaction between the biopolymer and the multicationic products 4. The strong guanidine–phosphate interactions between 4 and DNA were therefore attributed to the clustering of the guanidine groups in the primary area of the cyclodextrin. Cavity effects could not be assessed.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...