A new strategy for the synthesis of taurine derivatives using the ‘safety-catch’ principle for the protection of sulfonic acids
Abstract
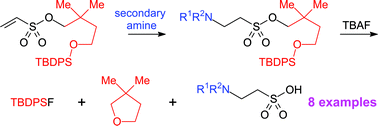
The safety-catch principle has been applied for the development of a new method for protecting sulfonic acids. 2,2-Dimethylsuccinic acid was reduced to 2,2-dimethylbutane-1,4-diol, which was selectively silylated to give 4-(tert-butyldiphenylsilanyloxy)-2,2-dimethylbutan-1-ol. Reaction of the latter compound with 2-chloroethanesulfonyl chloride in the presence of triethylamine afforded 4-(tert-butyldiphenylsilyloxy)-2,2-dimethylbutyl ethenesulfonate directly. The ethenesulfonate underwent Michael-type addition with secondary amines to give protected derivatives of taurine (2-aminoethanesulfonic acid). Deprotection was achieved on treatment with tetrabutylammonium fluoride, whereby cleavage of the silicon–oxygen bond led to an intermediate alkoxide that immediately cyclised to 2,2-dimethyltetrahydrofuran with liberation of a sulfonate. Pure sulfonic acids were obtained from the crude product by ion exchange chromatography on a strongly basic resin, which was eluted with aqueous acetic acid. The method developed should be generally applicable to the protection of sulfonic acids and is amenable to a multiparallel format.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...