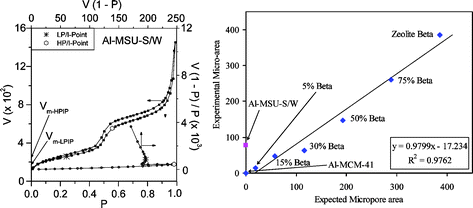
In this work we provide evidence of microporosity in the nanostructured mesoporous aluminosilicates MSU-S/W(BEA) synthesized from zeolite BEA seeds, based on the so called I-point plots (refs. 18–20) of the BET equation. Seventeen solids were characterized for their porous characteristics as follows: (i) one mesoporous aluminosilicate 2%Al-MSU-S/W(BEA), (ii) two typical mesoporous MCM-41 materials, one pure silica and one aluminosilicate 2%Al-MCM-41, (iii) three typical microporous zeolites, i.e., zeolites Y, ZSM-5 and beta, (iv) two typical amorphous silica–alumina (ASA) samples, (v) five mechanical mixtures of mesoporous Al-MCM-41 with zeolite beta at different addition percentages, and (vi) four amorphous or partially crystalline ZSM-5 based aluminosilicates. The P,V data from the nitrogen-adsorption isotherms of those porous solids were plotted according to the I-point modification of the BET equation in the form V[1 − (P/P0)]/(P/P0) = CVm
− (C
− 1)V[1 − (P/P0)]. Plots of V[1 − (P/P0)]/(P/P0) vs. V[1 − (P/P0)] provided lines which have the shape of an inclined V, i.e. >, and variable slopes corresponding to (C
− 1) from which the values of the C parameter were determined for the whole range of partial pressures 0 < P/P0 < 1. The inversion point of the above plots, called the I-point, projected onto the V[1 − (P/P0)] axis corresponds exactly to the volume of the monolayer Vm = VI[1 − (PI/P0)], from which the value of the specific surface area SI (m2 g−1) was determined. The shape of the I-plots depended strongly on the type of porous solids, i.e. microporous/zeolitic and partially crystalline zeolitic materials with combined micro- and meso/macroporosity; ordered mesoporous MCM-type materials; ASA materials with random mesoporosity; and mechanical mixtures of zeolite beta with MCM-41. The I-plot for the MSU-S/W(BEA) solid exhibited the combined characteristics of the plots of ordered mesoporous MCM-41 samples and of partially crystalline zeolitic materials, thus proving the presence of microporous domains within the homogeneous mesoporous structure of the MSU-S material. The I-plot result supports the proposed presence of protozeolitic subunits in the framework walls, of MSU-S, even though XRD and electron diffraction TEM studies have shown the material to be free of any zeolitic crystalline phase. The surface areas estimated by the I-method were similar to those provided by the BET model for the zeolitic and the ASA samples, while in the case of the ordered MCM-41 and MSU-S/W(BEA) mesostructures, two surface area values can be estimated based on different interpretations of the I-method, one similar to the value from the BET model and one supported by the modified CPSM model (refs. 31–34).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...