Mechanistic studies on oxidation of nitrite by a {Mn3O4}4+ core in aqueous acidic media†
Abstract
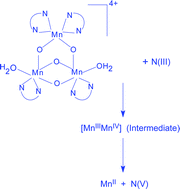
[MnIV3(µ-O)4(phen)4(H2O)2]4+ (1, phen = 1,10-phenanthroline) equilibrates with its conjugate base [Mn3(µ-O)4(phen)4(H2O)(OH)]3+ (2) in aqueous solution. Among the several synthetic multinuclear oxo- and/or carboxylato bridged manganese complexes known to date containing metal-bound water, to the best of our knowledge, only 1 deprotonates (1 ⇌ 2 + H+, pKa = 4.00 (±0.15) at 25.0 °C, I = 1.0 M, maintained with NaNO3) at physiological pH. An aqueous solution of 1 quantitatively oxidises N(III) (HNO2 and NO2−) to NO3− within pH 2.3–4.1, the end manganese state being MnII. Both 1 and 2 are reactive oxidants in the title redox. In contrast to a common observation that anions react quicker than their conjugate acids in reducing metal centred oxidants, HNO2 reacts faster than NO2− in reducing 1 or 2. The observed rates of nitrite oxidation do not depend on the variation of 1,10-phenanthroline content of the solution indicating that the MnIV-bound phen ligands do not dissociate in solution under experimental conditions. Also, there was no kinetic evidence for any kind of pre-equilibrium replacement of MnIV-bound water by nitrite prior to electron transfer which indicates the substitution-inert nature of the MnIV-bound waters and the 1,10-phenanthroline ligands. The MnIV3 to MnII transition in the present observation proceeds through the intermediate generation of the spectrally characterised mixed-valent MnIIIMnIV dimer that quickly produces MnII. The reaction rates are substantially lowered when solvent H2O is replaced by D2O and a rate determining 1e, 1H+ electroprotic mechanism is proposed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...