Maximizing the relaxivity of HSA-bound gadolinium complexes by simultaneous optimization of rotation and water exchange†
Abstract
Two new
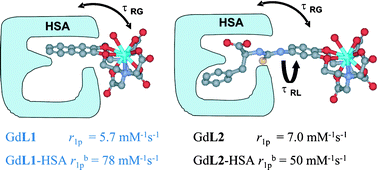
* Corresponding authors
a
Dipartimento di Scienze dell'Ambiente e della Vita, Università del Piemonte Orientale “Amedeo Avogadro”, Via Bellini 25/G, I-15100 Alessandria, Italy
E-mail:
mauro.botta@mfn.unipmn.it
b DiSCAFF & DFB Center, Università degli Studi del Piemonte Orientale “Amedeo Avogadro”, Via Bovio 6, I-28100 Novara, Italy
c
Dipartimento di Chimica IFM, Università degli Studi di Torino, Via P. Giuria 7, I-10125 Torino, Italy
E-mail:
silvio.aime@unito.it
Two new

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
S. Avedano, L. Tei, A. Lombardi, G. B. Giovenzana, S. Aime, D. Longo and M. Botta, Chem. Commun., 2007, 4726 DOI: 10.1039/B714438E
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
