Conformational control of HCl co-transporter: imidazole functionalised isophthalamidevs. 2,6-dicarboxamidopyridine†
Abstract
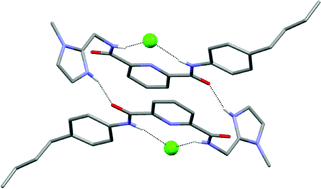
Replacement of the central isophthalamide core in a synthetic HCl receptor, with a 2,6-dicarboxamidopyridine, leads to a more preorganised molecular structure that exhibits higher chloride affinity and membrane transport flux.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...