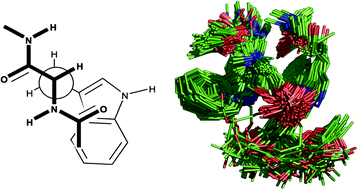
A series of molecular models of the adducts formed between N-acetyl-L-tryptophan ethylamide and diacetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine have been generated. Using rOesy data that enabled us to place restrictions on the proximity of a number of key protons in the amino acid/phosphocholine pairs, a series of structures were generated following molecular dynamics and mechanics experiments using the CHARMM27 force field. These structures were then subjected to a series of clustering algorithms in order to classify the tight binding interactions between a single tryptophan and a phosphocholine. From these analyses, it is evident that: (i) binding is characterised by hydrogen bonding between the indole NH as donor and phosphate oxygen as acceptor, cation–carbonyl interactions between the cholineammonium and amide carbonyl groups and cation–π interactions; (ii) cation–π interactions are not always observed, particularly when their formation is at the expense of cation–carbonyl and hydrogen bonding interactions; (iii) on the basis of amino acid torsional parameters, it is possible to predict whether the phosphocholine headgroup will bind in a compact or elongated conformation. Extension of the procedures to characterise 2 : 1 Trp–PC binding revealed that the same intermolecular interactions are predominant; however, combinations of all three intermolecular interactions within the same adduct occur much more frequently due to the availability of donor/acceptor groups from both tryptophans in the 2 : 1 system.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...