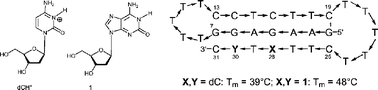
Triplex-forming oligonucleotides (TFOs) containing 2′-deoxyisoguanosine (1), 7-bromo-7-deaza-2′-deoxyisoguanosine (2) as well as the propynylated 9-deazaguanine N7-(2′-deoxyribonucleoside) 3b were prepared. For this the phosphoramidites 9a, b of the nucleoside 1 and, the phosphoramidites 19, 20 of compound 3b were synthesized. They were employed in solid-phase oligonucleotide synthesis to yield the protected 31-mer oligonucleotides. The deblocking of the allyl-protected oligonucleotides containing 1 was carried out by Pd(0)[PPh3]4–PPh3 followed by 25% aq. NH3. Formation of the 31-mer single-stranded intramolecular triplexes was studied by UV-melting curve analysis. In the single-stranded 31-mer oligonucleotides the protonated dC in the dCH+–dG–dC base triad was replaced by 2′-deoxyisoguanosine (1), 7-bromo-7-deaza-2′-deoxyisoguanosine (2) and, 9-deaza-9-propynylguanine N7-(2′-deoxyribonucleoside) (3b). The replacement of protonated dC by compounds 1 and 3b resulted in intramolecular triplexes which are formed pH-independently and are stable under neutral conditions. These triplexes contain “purine” nucleosides in the third pyrimidine rich strand of the oligonucleotide hairpin.