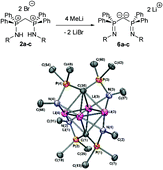
The availability of bis(aminophosphoranes) 2a–c through a straightforward synthesis yielded access to a whole family of N,N ligands via sequential deprotonation. The obtained cationic 3a–c, neutral 4a–c, anionic 5a–c and dianionic 6a–c compounds were fully characterized by NMR and X-ray crystallography. Monocations 3a–c were shown to result from the deprotonation of 2a–c at the bridging methylene carbon. DFT calculations evidenced a substantial negative charge at this carbon. For the neutral bis(iminophosphoranes) 4a–c, two different forms were experimentally observed depending on the nature of the substituent at nitrogen. In the presence of an aryl group, a bis(iminophosphorane) is obtained whereas with alkyl substituent a tautomeric form resulting from a (1,3) hydrogen shift is observed. Theoretical studies were in good agreement with experimental results showing that these two forms are close in energy. The structure obtained for monoanion 5a reveals that a substantial interaction occurs between the anionic carbon and the lithium cation. The X-ray crystal structure of the optically pure dianion 6b has also been recorded.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...