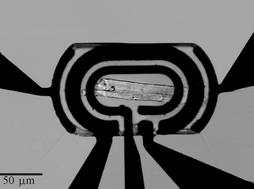
A device based on five individually addressable microelectrodes, fully integrated within a microfluidic system, has been fabricated to enable the real-time measurement of ionic and metabolic fluxes from electrically active, beating single heart cells. The electrode array comprised one pair of pacing microelectrodes, used for field-stimulation of the cell, and three other microelectrodes, configured as an electrochemical lactate microbiosensor, that were used to measure the amounts of lactate produced by the heart cell. The device also allowed simultaneous in-situ microscopy, enabling optical measurements of cell contractility and fluorescence measurements of extracellular pH and cellular Ca2+. Initial experiments aimed to create a metabolic profile of the beating heart cell, and results show well defined excitation-contraction (EC) coupling at different rates. Ca2+ transients and extracellular pH measurements were obtained from continually paced single myocytes, both as a function of the rate of cell contraction. Finally, the relative amounts of intra- and extra-cellular lactate produced during field stimulation were determined, using cell electroporation where necssary.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...