Polymer sensors for nitroaromatic explosives detection
Abstract
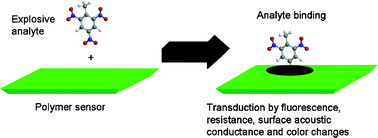
Several polymers have been used to detect nitroaromatic explosives by a variety of transduction schemes. Detection relies on both electronic and structural interactions between the sensing material and the analyte. Quenching of luminescent polymers by electron deficient nitroaromatic explosives, such as trinitrotoluene, may be monitored to detect explosives. Resistive sensing using carbon black particles that have been coated with different organic polymers and deposited across metallic leads can also be used to detect nitroaromatic vapors in an electronic nose approach. Frequency changes in surface acoustic wave devices may be monitored to detect nitroaromatics after their adsorption into polymer coatings. Luminescent polymetalloles have recently been investigated for sensing explosives in aqueous-based solutions and for improved visual detection of trace particulates on surfaces.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...