Charge-transfer phase transition and zero thermal expansion in caesium manganese hexacyanoferrates†
Abstract
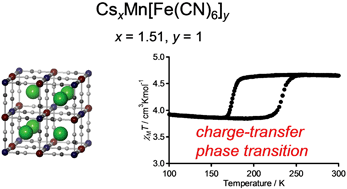
A series of caesium manganese hexacyanoferrates is prepared; CsI1.78MnII[FeII(CN)6]0.78[FeIII(CN)6]0.22 (1), CsI1.57MnII[FeII(CN)6]0.57[FeIII(CN)6]0.43 (2), CsI1.51MnII[FeII(CN)6]0.51[FeIII(CN)6]0.49 (3), and CsI0.94MnII[FeII(CN)6]0.21[FeIII(CN)6]0.70·0.8H2O (4). 1–3 show charge-transfer phase transitions between the high-temperature (HT) and low-temperature (LT) phases with transition temperatures (T1/2↓, T1/2↑) of (207 K, 225 K) (1), (190 K, 231 K) (2), and (175 K, 233 K) (3) at a cooling and warming rates of 0.5 K min−1. Variable temperature ![[3 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0033_0304.gif) m), but the lattice constants decrease from the HT phase to the LT phase; a = 10.5446(17) → 10.4280(7) Å (1), 10.5589(17) → 10.3421(24) Å (2), and 10.5627(11) → 10.3268(23) Å (3). The magnetization vs. temperature curves and the magnetization vs. external magnetic field curves show that the LT phases are ferromagnetic with Curie temperatures of 4.3 (1), 5.0 (2), and 5.6 K (3). At a cooling rate of −0.5 K min−1, 4 does not show the charge-transfer phase transition, but does show a behavior of zero thermal expansion with a thermal expansivity of +0.2 × 10−6 K−1 throughout the temperature range 300 and 20 K.
m), but the lattice constants decrease from the HT phase to the LT phase; a = 10.5446(17) → 10.4280(7) Å (1), 10.5589(17) → 10.3421(24) Å (2), and 10.5627(11) → 10.3268(23) Å (3). The magnetization vs. temperature curves and the magnetization vs. external magnetic field curves show that the LT phases are ferromagnetic with Curie temperatures of 4.3 (1), 5.0 (2), and 5.6 K (3). At a cooling rate of −0.5 K min−1, 4 does not show the charge-transfer phase transition, but does show a behavior of zero thermal expansion with a thermal expansivity of +0.2 × 10−6 K−1 throughout the temperature range 300 and 20 K.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...