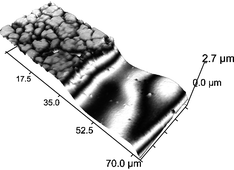
Electropolishing of stainless steels in a choline chloride based ionic liquid: an electrochemical study with surface characterisation using SEM and atomic force microscopy
Abstract
We have studied the anodic dissolution (electropolishing) of various stainless steel alloys in an

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...