Multidimensional HRMASNMR: a platform for in vivo studies using intact bacterial cells
Abstract
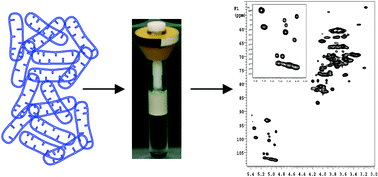
In vivo analysis in whole cell bacteria, especially the native tertiary structures of the bacterial cell wall, remains an unconquered frontier. The current understanding of bacterial cell wall structures has been based on destructive analysis of individual components. These in vitro results may not faithfully reflect the native structural and conformational information. Multidimensional High Resolution

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...