Synthesis, characterisation, reactivity and in vitro antiamoebic activity of hydrazone based oxovanadium(iv), oxovanadium(v) and µ-bis(oxo)bis{oxovanadium(v)} complexes
Abstract
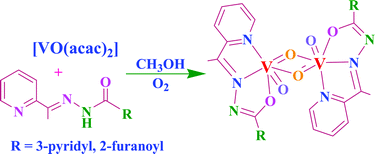
Binuclear, µ-bis(oxo)bis{oxovanadium(V)} complexes [(VOL)2(µ-O)2] (2 and 7) (where HL are the hydrazones Hacpy-nah I or Hacpy-fah II; acpy = 2-acetylpyridine, nah = nicotinic acid hydrazide and fah = 2-furoic acid hydrazide) were prepared by the reaction of [VO(acac)2] and the ligands in methanol followed by aerial oxidation. The paramagnetic intermediate complexes [VO(acac)(acpy-nah)] (1) and [VO(acac)(acpy-fah)] (6) have also been isolated. Treatment of [VO(acac)(acpy-nah)] and [VO(acac)(acpy-fah)] with aqueous H2O2 yields the oxoperoxovanadium(V) complexes [VO(O2)(acpy-nah)] (3) and [VO(O2)(acpy-fah)] (8). In the presence of catechol (H2cat) or benzohydroxamic acid (H2bha), 1 and 6 give the mixed chelate complexes [VO(cat)L] (HL = I: 4, HL = II: 9) or [VO(bha)L] (HL = I: 5, HL = II: 10). Complexes 4, 5, 9 and 10 slowly convert to the corresponding oxo-µ-oxo species 2 and 7 in DMF solution. Ascorbic acid enhances this conversion under aerobic conditions, possibly through reduction of these complexes with concomitant removal of coordinated catecholate or benzohydroxamate. Acidification of 7 with HCl dissolved in methanol afforded a hydroxo(oxo) complex. The crystal and molecular structure of 2·1.5H2O has been determined, and the structure of 7 re-determined, by single crystal X-ray diffraction. Both of these binuclear complexes contain the uncommon asymmetrical {VO(µ-O)}2 diamond core. The in vitro tests of the antiamoebic activity of ligands I and II and their binuclear complexes 2 and 7 against the protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica show that the ligands have no amoebicidal activity while their vanadium complexes 2 and 7 display more effective amoebicidal activity than the most commonly used drug metronidazole (IC50 values are 1.68 and 0.45 µM, respectively vs 1.81 µM for metronidazole). Complexes 2 and 7 catalyse the oxidation of styrene and ethyl benzene effectively. Oxidation of styrene, using H2O2 as an oxidant, gives styrene epoxide, 2-phenylacetaldehyde, benzaldehyde, benzoic acid and 1-phenyl-ethane-1,2-diol, while ethyl benzene yields benzyl alcohol, benzaldehyde and 1-phenyl-ethane-1,2-diol.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...