On the nature of metallic nanoparticles obtained from molecular Co3Ru–carbonyl clusters in mesoporous silica matrices†‡
Abstract
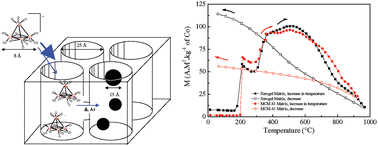
We report on the impregnation of THF solutions of the low-valent heterometallic cluster NEt4[Co3Ru(CO)12] into two mesoporous silica matrices, amorphous xerogels and ordered MCM-41, and a study of its thermal decomposition into metallic nanoparticles by X-ray diffraction, transmission electron microscopy and in situ magnetic measurements under controlled atmospheres. The decomposition of the cluster was monitored as a function of temperature by examining the chemical composition of the particles, their size distributions and their structures as well as their magnetic properties. Treatment under inert atmosphere (i.e. argon) at temperatures below 200 °C resulted in the formation of segregated spherical particles of hcp-ruthenium (2.3 ± 1.0 nm) and hcp-cobalt (3.1 ± 0.9 nm). The latter is transformed to fcc-cobalt (3.2 ± 1.0 nm) above 270 °C. At higher temperatures, Co–Ru alloying takes place and the Ru content of the particles increases with increasing temperature to reach the nominal composition of the molecular precursor, Co3Ru. The particles are more evenly distributed in the MCM-41 framework compared to the disordered xerogel and also show a narrower size distribution. Owing to the different magnetic anisotropy of hcp- and fcc-cobalt, which results in different blocking temperatures, we were able to clearly identify the products formed at the early stages of the thermal decomposition procedure.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...