Multi-walled carbon nanotubes for plasmid delivery into Escherichia coli cells
Abstract
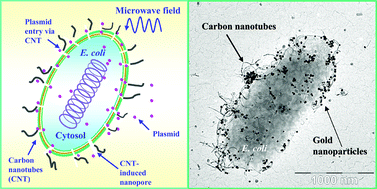
Introduction of foreign genes into bacterial cells (transformation) is used for supplementing defective genes or providing additional biological functions. Transformation can be achieved using either chemical or physical methods, e.g.,

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...