Evaluation of the extraction methods for arsenic speciation in rice straw, Oryza sativa L., and analysis by HPLC-HG-AFS
Abstract
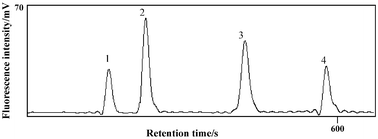
The most important and difficult step during arsenic speciation analysis is to extract the various arsenic species in the original forms from the samples. In this work, a study has been carried out to compare the different extraction methods by using different extraction solvents including water, methanol, water–methanol, water–ethanol and water–acetonitrile. Different techniques (shaking, ultrasonic, Soxhlet and microwave-assisted extraction) were applied during the procedure. A new, nontoxic and effective extraction method for arsenic speciation in the terrestrial plant material, rice straw, with water–ethanol mixture as extraction solvent using microwave-assisted extraction was found to provide good extraction efficiency without internal species conversion. The extraction of arsenic from the rice straw and subsequent determination of individual arsenic species by high performance liquid chromatography-hydride generation-atomic fluorescence spectrometry (HPLC-HG-AFS) is described. By using the proposed extraction method, the total arsenic extraction efficiency was 90.3%. The arsenic species in rice straw were analyzed and four normal chemical forms, AsIII, AsV, MMAV and DMAV, in straw shoots were found, but no MMAV was found in the straw roots.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...