Solid C58 films
Abstract
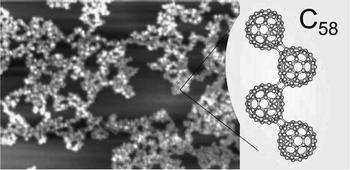
A new solid material has been created in ultra high vacuum by utilizing the aggregation process of C58 molecules deposited onto highly oriented pyrolytic graphite from a mass selected low-energy ion beam comprising C58+. Cluster fluxes of up to 3 × 1011 ions s−1 cm−2 with impinging kinetic energies of 6 ± 0.5 eV were typically applied. Growth of the solid C58 phase proceeds according to the cluster-aggregation-based Volmer–Weber scenario where initially ramified 2D islands transform into 3D pyramid-like structures at higher coverages. The C58 films created exhibit much higher thermal stability than the C60 solid phase.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...