Activity of surface active substances determined from their surface excess
Abstract
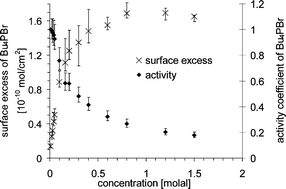
Commonly, the surface excess is determined from surface tension measurements via the Gibbs equation. This equation relates the activity (chemical potential), the surface excess, and the surface tension. When knowing two out of the three quantities, the third one can be calculated. Unfortunately, in the case of surface active components the concentration is in most cases too low to determine the activity from a measurable change in the bulk properties and thus assumptions are made about the activity coefficients. However, if the surface excess is measured directly and the surface tension is known, the activity can be determined making use of the Gibbs equation. The surface excess is the quantity of a

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...