Microwave enhanced electroanalysis of formulations: processes in micellar media at glassy carbon and at platinum electrodes
Abstract
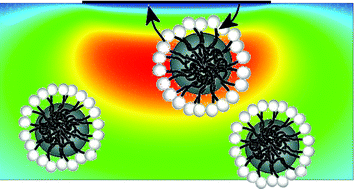
The direct electroanalysis of complex formulations containing α-tocopherol (
* Corresponding authors
a
Department of Chemistry, University of Bath, Bath, UK
E-mail:
f.marken@bath.ac.uk
b Physical and Theoretical Chemistry Laboratory, Oxford University, South Parks Road, Oxford, UK
c Departamento de Química Analítica, Nutrición y Bromatología, Universidad de Alicante, PO Box 99, 03080 Alicante, Spain
The direct electroanalysis of complex formulations containing α-tocopherol (

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
M. A. Ghanem, R. G. Compton, B. A. Coles, A. Canals and F. Marken, Analyst, 2005, 130, 1425 DOI: 10.1039/B507167D
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
