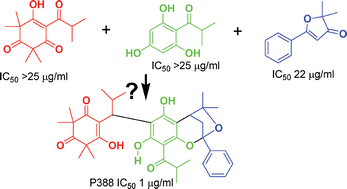
Cytotoxic activity against the P388 cell line was seen in a crude extract of the New Zealand shrub Lophomyrtus bullata
(Myrtaceae). Bioactivity-guided isolation led to a compound with NMR spectra complicated by the presence of two isomers. These crystallised together and an X-ray structure showed them to be stereoisomeric hybrids of triketone, phloroglucinol and bullatenone units. NMR measurements on the mixed isomers, as well as a cyclic ether produced from them by acid catalysed dehydration, were consistent with these structures. The natural products, named bullataketals A and B, have cytotoxic activity against the P388 cell line (IC50 1 µg ml−1), and antimicrobial activity against Bacillus subtilis.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...