‘Passive’ nanoparticles for organ-selective systemic delivery: design, mechanism and perspective
Abstract
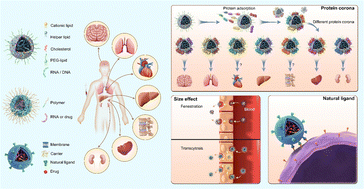
Nanotechnology has shown tremendous success in the drug delivery field for more effective and safer therapy, and has recently enabled the clinical approval of RNA medicine, a new class of therapeutics. Various nanoparticle strategies have been developed to improve the systemic delivery of therapeutics, among which surface modification of targeting ligands on nanoparticles has been widely explored for ‘active’ delivery to a specific organ or diseased tissue. Meanwhile, compelling evidence has recently been reported that organ-selective targeting may also be achievable by systemic administration of nanoparticles without surface ligand modification. In this Review, we highlight this unique set of ‘passive’ nanoparticles and their compositions and mechanisms for organ-selective delivery. In particular, the lipid-based, polymer-based, and biomimetic nanoparticles with tropism to different specific organs after intravenous administration are summarized. The underlying mechanisms (e.g., protein corona and size effect) of these nanosystems for organ selectivity are also extensively discussed. We further provide perspectives on the opportunities and challenges in this exciting area of organ-selective systemic nanoparticle delivery.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...