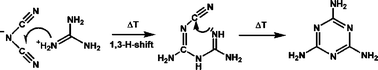
Two modifications of the novel guanidinium dicyanamide have been obtained by means of ion-exchange reaction in aqueous or methanolic solution. The hygroscopic compounds were characterized by solution state NMR, mass spectrometry and vibrational spectroscopy. The crystal structures of the polymorphs were elucidated by means of single-crystal X-ray diffraction at 200 K {β-[C(NH2)3][N(CN)2]: Pna21, Z = 8, a = 1373.1(3), b = 495.5(1), c = 1802.9(4) pm, U = 1226.7(4) × 106 pm3; α-[C(NH2)3][N(CN)2]: P21/c, Z = 8, a = 1924.9(4), b = 496.0(1), c = 1372.4(3) pm, β = 110.46(3)°, U = 1227.5(4) × 106 pm3} and were found to be largely equivalent in terms of the overall assembly of the molecular ions. Thermodynamic and kinetic aspects of the temperature behaviour of the polymorphs, which is characterized by a succession of thermal events in the temperature region between 240 and 440 K, were assessed by means of temperature-dependent X-ray powder diffraction and thermal analysis. Due to the chemical composition of the novel dicyanamide (C3N6H6), which is formally identical with that of melamine C3N3(NH2)3, and its thermal reactivity, which is represented by the facile conversion into melamine around 400 K, guanidinium dicyanamide may be ideally suited as a molecular precursor for chemical approaches toward highly condensed graphitic carbon nitride materials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...