Multistate properties of 7-(N,N-diethylamino)-4′-hydroxyflavylium. An example of an unidirectional reaction cycle driven by pH
Abstract
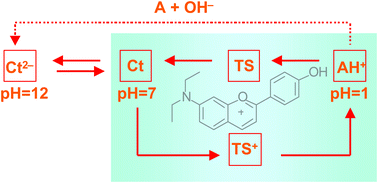
The synthetic flavylium salt 7-(N,N-diethylamino)-4′-hydroxyflavylium tetrafluoroborate gives rise in aqueous solution to a complex network of chemical reactions driven by pH. The system was studied by 1H NMR, single crystal X-ray diffraction, steady state and transient UV-Vis spectrophotometry as well as stopped flow. The crystal structure shows a high degree of coplanarity between the pyrylium system and the phenyl group in position 2. Thermodynamic and kinetic constants for the pH dependent network of chemical reactions were obtained. The introduction of an amino group in position 7 allows formation of protonated species leading, in particular, to a tautomeric form of the protonated cis-chalcone, CcH+, whose absorption spectra is rather red shifted, in comparison with the correspondent protonated trans-chalcone, CtH+. The CcH+ species can be rapidly converted into the flavylium cation through a first order process with lifetime of 0.2 s at pH = 2.35. This new reaction channel confers this compound a peculiar behaviour in acidic media, allowing to define an unidirectional pH driven reaction cycle.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...