The participation of biological agents in pulp bleaching systems has received a lot of attention from research teams around the world, driven by the environmental benefits that biobleaching could bring. Nature showed us the ability of some of its agents, such as wood-decaying fungi, to delignify and bleach wood and wood pulp. What we need to do is to enhance the efficiency of such agents to make them cope with the fast pace of our modern pulp mills. To do so, a profound understanding of the biobleaching system is required. Our efforts to discover new efficient mediators for the laccase-mediator system (LMS) brought us to use several techniques to analyse the reactions involved in mediated enzymatic delignification. Mostly based on electrochemistry, these techniques are reviewed in this paper, along with key results. Cyclic voltammetry was used to characterize electron transfer rates between each element of the LMS. We found, along with other authors, that the mediator redox potential has a great influence on its efficiency. We used bulk electrolysis to simulate the oxidative action of laccase on mediators and model compounds of lignin. Such electrolysis techniques allowed us to study mediated lignin oxidation outside of normal laccase working conditions. Finally, an electrolysis-based method for mediated pulp delignification that we developed, based upon our research on biobleaching, is presented.
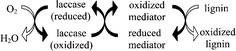
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
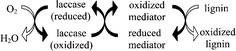

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...