Anti-microbial activities of protic ionic liquids with lactate anion
Abstract
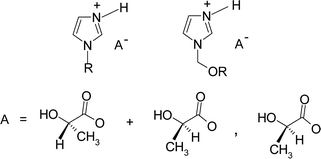
Minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) and minimum biocidal concentrations (MBC) were established for 1-alkylimidazolium and 1-alkoxymethylimidazolium lactates tested against rods, cocci and fungi. We found that anti-microbial activities of the protic ionic liquids are strongly related to the length of the substituent and to the DL- or L-type anion. Lactates with short substituents up to pentyl or pentyloxymethyl remain inactive toward microorganisms. In addition physical properties and thermal stability of protic ionic liquids have been described. We found them to readily undergo decomposition under the effect of ozone in aqueous solution.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...