Nucleation–elongation: a mechanism for cooperative supramolecular polymerization
Abstract
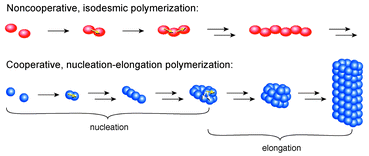
The kinetic and thermodynamic characteristics of polymerizations following a cooperative, nucleation–elongation mechanism are discussed in comparison to those of non-cooperative, isodesmic polymerizations. Nucleation–elongation

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...