Structural evolution of SiO2–ZrO2 nano-sol intercalated clays upon pillaring reaction†
Abstract
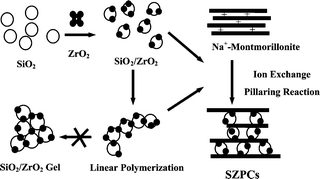
A two-dimensional layered nanohybrid with a high specific surface area has been prepared by ion exchange reactions between the sodium ions in montmorillonite and the positively charged Zr-coated SiO2 sol particles. The basal spacing increases from 12.5 Å to 26 Å upon intercalation due to the insertion of a SiO2–ZrO2 nano-sol into the interlayer space of montmorillonite. Upon

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...