Replacing proline at the apex of heptapeptide-based chloride ion transporters alters their properties and their ionophoretic efficacy
Abstract
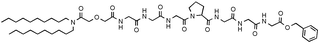
A membrane anchored heptapeptide, (C18H37)2NHCOCH2OCH2CO–NH–Gly–Gly–Gly–Pro–Gly–Gly–Gly–OCH2Ph, has proved to be a selective chloride anion transporter that functions in

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...