Carbon-based hydrogels: synthesis and their recent energy applications
Abstract
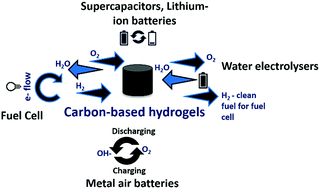
Hydrogels are a class of materials with large amounts of water in their three-dimensional hierarchical structures. The ability to fine-tune the structures of hydrogels and the prospects of building various microcosms within a large framework are a few of the many characteristics which make hydrogels quite superior in the list of materials developed so far for various applications. This review introduces the strategies of synthesising various types of carbon-based hydrogels and the various mechanisms and ideas which were instrumental in their formation. It also critically brings out the important concepts, latest developments and perspectives associated with the use of hydrogels for recent energy applications. Based on the most recent papers and the most impactful findings, we have described the synthesis of carbon-based hydrogels by broadly dividing them into three categories: graphene-based hydrogels, polymer-based hydrogels and biomass-derived hydrogels. Among these, hydrogels which are conductive in nature are predominantly used in the field of energy applications like supercapacitors, lithium batteries, metal–air batteries, fuel cells and water electrolysers. The flexibility in using sustainable materials and the ability to incorporate tailor-made, non-toxic, cheap, electrochemically active functional moieties during their synthesis make them the frontrunners in the field of green chemistry and energy applications.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...