Fluorination of sulfanyl amides using difluoroiodoarene reagents
Abstract
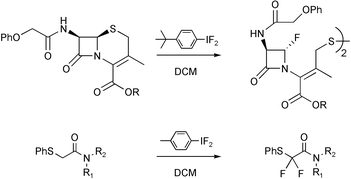
A range of sulfur-containing amides have been fluorinated with the hypervalent iodine difluoride reagents 1, and two principal reaction pathways identified. Cephalosporin esters 2 having a heteroatom in the α-position to sulfur undergo fluorination in DCM with cleavage of the carbon–sulfur bond to form novel fluorinated β-lactams 4. Sulfides with electron-withdrawing groups in the α-position undergo α-fluorination in a process analogous to the classical Pummerer reaction. This Fluoro-Pummerer reaction has been exemplified for a range of simple α-phenylsulfanylacetamides 14–19. When β-hydrogens are present in the substrate a different route is followed, with deprotonation by basic fluoride taking place to yield vinyl sulfides 41–43. When an excess of the fluorinating reagent is used these vinyl sulfides can undergo further reaction in a novel tandem Pummerer-Additive-Pummerer process to yield α,β-difluoro sulfides 45–47.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...