A new series of boron substituted cobalt bis(dicarbollide)(1−) ion (1) derivatives of the general formula [(8-CMPO-(CH2-CH2O)2-1,2-C2B9H10)(1′,2′-C2B9H11)-3,3′-Co]−
(CMPO = Ph2P(O)-CH2C(O)NR, R = C4H9
(3b), -C12H25
(4b), -CH2-C6H5
(5b)) was prepared by ring cleavage of the 8-dioxane-cobalt bis(dicarbollide)
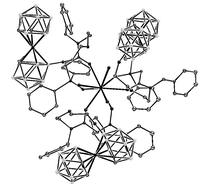
(2) bi-polar compound by the respective primary amines and by subsequent reaction of the resulting amino derivatives (3a–5a) with the nitrophenyl ester of diphenylphosphorylacetic acid. The compounds were synthesized with the aim to develop a new class of more efficient extraction agents for liquid–liquid extraction of polyvalent cations, i.e. lanthanides and actinides, from high-level activity nuclear waste. All compounds were characterized by a combination of 11B NMR, 1H high field NMR, Mass Spectrometry with Electrospray and MALDI TOF ionisation, HPLC and other techniques. The molecular structure of the supramolecular Ln3+ complex of the anion 5b was determined by single crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. Crystallographic results proved that the Ln(III) atom is bonded to three functionalised cobalt bis(dicarbollide) anions in a charge compensated complex. The cation is tightly coordinated by six oxygen atoms of the CMPO terminal groups (two of each ligand) and by three water molecules completing the metal coordination number to 9. Atoms occupying the primary coordination sphere form a tri-capped trigonal prismatic arrangement. Very high liquid–liquid extraction efficiency of all anionic species was observed. Moreover, less polar toluene can be applied as an auxiliary solvent replacing the less environmentally friendly nitro- and chlorinated solvents used in the current dicarbollide liquid–liquid extraction process. The extraction coefficients are sufficiently high for possible technological applications.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...