Abstract
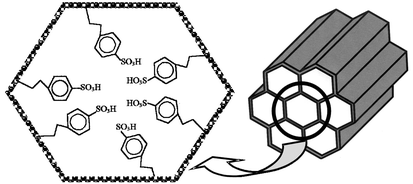
SBA-15 mesoporous silica has been functionalized with arenesulfonic acid groups by means of a one-step simple synthesis approach involving co-condensation of tetraethoxysilane (TEOS) and 2-(4-chlorosulfonylphenyl)ethyltrimethoxysilane (CSPTMS) in the presence of a poly(alkylene oxide) block copolymer (Pluronic 123) under acid silica-based catalysis. The resultant materials show hexagonal mesoscopic order and pores sizes up to 60 Å, with acid exchange capacities of ca. 1.3 mequiv. H+ per g SiO2 and surface areas up to 600 m2 g−1. The sulfonic groups anchored to the silica surface of the pore walls are thermally stable to temperatures up to 380 °C and resistant to leaching in organic and aqueous solutions under mild conditions. 31P MAS NMR measurements of chemically adsorbed triethylphosphine oxide and the catalytic properties confirm the presence of Brönsted acid centers in these mesoporous materials containing arenesulfonic acid groups that are stronger than those found in propanesulfonic-modified SBA-15 and Al-MCM-41.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...