Sonochemical process for the preparation of α-CuSe nanocrystals and flakes†
Abstract
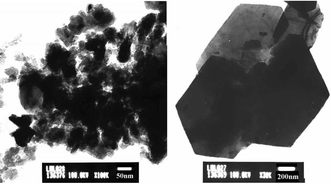
α-CuSe crystals of different sizes and shapes have been synthesized by a sonochemical method using the less hazardous elemental Se and Cu(Ac)2 as precursors under an atmosphere of H2/Ar (5 ∶ 95 v/v).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...