Electroorganic reactions. Part 55.†Quinodimethane chemistry. Part 3. Transition metal complexes as inter- and intra-molecular redox catalysts for the electrosynthesis of poly(p-xylylene) (PPX) polymers and oligomers‡
Abstract
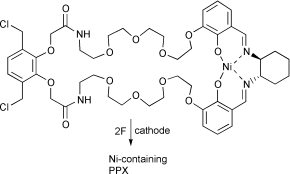
The role of metal complexes as redox mediators in the electrosynthesis of poly(p-xylylenes) (PPXs) has been explored, with a view to designing metal-containing precursors that can act both as mediators and starting materials for metal-containing

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...