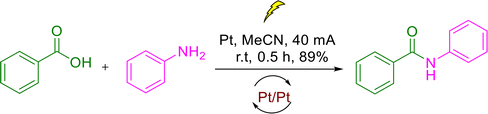Development of a novel GO/Fe@TANG composite electrode for green and sustainable electrosynthesis of N-phenylbenzamides via electrocatalytic carbonylation and hydrogenation
Rustamkhon
Kuryazov
a,
Karkaz
Thalij
 *b,
Ahmed
Aldulaimi
c,
Mohanad Yakdhan
Saleh
d,
Abdulrahman A.
Almehizia
*b,
Ahmed
Aldulaimi
c,
Mohanad Yakdhan
Saleh
d,
Abdulrahman A.
Almehizia
 *e,
Tulkin
Buzrukov
*e,
Tulkin
Buzrukov
 f,
Gularam
Masharipova
f,
Gularam
Masharipova
 g,
Bekzod.
Madaminov
h,
Shakir Mahmood
Saeed
i and
Elyor
Berdimurodov
g,
Bekzod.
Madaminov
h,
Shakir Mahmood
Saeed
i and
Elyor
Berdimurodov
 jklm
jklm
aUrgench State University, Kh. Olimjon st. 14, Urgench, 220100, Uzbekistan. E-mail: rustamxonkuryazov@gmail.com
bFood Science Department, Tikrit University, Iraq. E-mail: kthalij@tu.edu.iq
cAl-Zahrawi University, Karbala, Iraq. E-mail: Ahmedaldulaimi1@gmai.com
dDepartment of Chemistry, College of Education for Pure Science, University of Mosul, Mosul, Iraq. E-mail: mohanadalallaf@uomosul.edu.iq
eDrug Exploration and Development chair (DEDC), Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, College of pharmacy, King Saud University, Riyadh 11451, Saudi Arabia. E-mail: aalmehiziaabdulrahman@gmail.com; mehizia@ksu.edu.sa
fTermez University of Economics and Service, Uzbekistan. E-mail: tulqin_buzrukov@tues.uz
gAlfraganus University, Ministry of Higher Education, Science and Innovation of the Republic of Uzbekista, Yunusabad district, 4m12/17, Tashkent, 100093, Uzbekistan. E-mail: Masharipovagularam2006@gmail.com
hDepartment of General Professional Sciences, Mamun University, Urgench, Uzbekistan. E-mail: madaminov_bekzod@mamunedu.uz
iDepartment of Pharmacy, Al-Noor University College, Nineveh, Iraq. E-mail: shakir.mahmood@alnoor.edu.iq
jFaculty of Chemistry, National University of Uzbekistan, Tashkent, 100034, Uzbekistan
kUniversity of Tashkent for Applied Sciences, Str. Gavhar 1, Tashkent, 100149, Uzbekistan
lSchool of Medicine, Central Asian University, Tashkent, 111221, Uzbekistan
mFaculty of Chemistry and Biology, Karshi State University, Karshi City, Uzbekistan. E-mail: elyor170690@gmail.com
First published on 11th December 2025
Abstract
In this study, a novel GO/Fe@TANG composite catalyst was designed by functionalizing graphene oxide (GO) with iron (Fe) and incorporating a hydrogen (H2) trapping TANG COF. This catalyst was evaluated under mild conditions using a multifunctional MEA/EDA DES that serves as a solvent, an electrolyte and a CO trapping agent. The system efficiently catalyzed the electrochemical carbonylation and hydrogenation of various substrates, including nitrobenzene derivatives 1(a–j), chlorobenzene derivatives 2(a–d), monoxide carbon (CO) 3(a), and H2 gas 4(a), to afford N-phenylbenzamide derivatives 5(a–m) in high yields ranging from 91% to 96% under mild conditions (room temperature, 1.5 h, 15 mA). The MOF displayed a high specific surface area of 1105 m2 g−1 and maintained its catalytic performance over 9 consecutive reuse cycles. Extensive characterization techniques such as FT-IR, SEM, TEM, EDX mapping, TGA, BET, 1H NMR, CHN, CV, and XPS confirmed the structural, morphological, thermal, and chemical properties of both the catalyst and synthesized products 5(a–m). This work demonstrates an effective, environmentally friendly electrocatalytic system that integrates iron-based porous materials and multifunctional electrolytes, achieving sustainable synthesis of valuable amide derivatives in a streamlined, high-yielding manner aligned with green chemistry principles.
Introduction
Amidation in organic chemistry is a fundamental reaction involving the formation of an amide bond through the nucleophilic attack of an amine or ammonia (NH3) on carbon monoxide (CO), typically from a carboxylic acid or its derivatives. Amidation is crucial in drug synthesis as it enables the construction of amide and peptide bonds, which are key functional groups in many pharmaceuticals.1,2 This reaction provides a versatile and efficient route for assembling complex molecules with high selectivity and is central to both small-molecule drug development and biopolymer synthesis. Several commercially important drugs can be synthesized via electro-organic methodologies that employ the reduction processes of nitrobenzene, aryl halides, and carbon monoxide as key steps.3,4 This electrochemical strategy facilitates the efficient formation of crucial amide and aniline functional groups embedded within diverse drug scaffolds, including those of atorvastatin (cardiovascular),5,6 ropivacaine (anesthetic),7 amisulpride (schizophrenia, acute psychotic),8 ataciguat (aortic valve stenosis),9 amisulpride (chronic schizophrenia),10 and avoralstat (hereditary angioedema)11,12 (Fig. 1). Such transformations provide a streamlined, green, and sustainable synthetic route for accessing pharmaceutically relevant molecules,13,14 minimizing the use of hazardous reagents and costly metals and enhancing overall synthetic efficiency. These advantages highlight the potential of electro-organic synthesis as an enabling platform for the development and manufacturing of complex drug structures in an environmentally responsible manner. | ||
| Fig. 1 Commercial drugs that can be synthesized by the reduction of nitrobenzene, aryl halides, and carbon monoxide. | ||
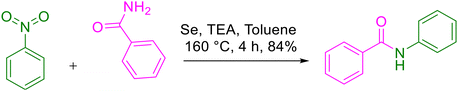
Table 1 summarizes various traditional methodologies reported for the carbonylation reaction leading to the synthesis of N-phenylbenzamides, highlighting diverse catalytic systems, reaction conditions, and efficiencies. In entry 1, ferric chloride (FeCl3) is employed as the catalyst in acetonitrile (MeCN) at 30 °C for 36 hours, affording the product with an 81% yield. In entry 2, selenium (Se) in triethylamine (TEA) and toluene at an elevated temperature of 160 °C for 4 hours achieves an 84% yield, indicating the efficiency of this metal catalyst under harsher conditions. In entry 3, MgO is utilized as a base in methyl acetate (MeOAc) solvent and treated at 80 °C for 12 hours, resulting in an 85% yield. Entry 4 presents a series of methods employing magnesium (Mg) in tetrahydrofuran (THF) at 90 °C for 12 hours (89% yield), TiO2 in ethanol (EtOH) under microwave irradiation for 2.5 hours (92% yield), and iron-dimethylformamide (Fe-DMF) at 200 °C for 8 hours (94% yield), collectively showcasing the flexibility of metal catalysts and activation methods. Entry 5 introduces a multi-component system involving HCl and amino groups with a formyl moiety under palladium (Pd) catalysis and triethylamine (TEA) at room temperature for 10 hours, achieving 54% yield under Pd/Co mediation. Finally, entry 6 reports iron-catalyzed conditions at 110 °C for 5 hours achieving a 93% yield. The reaction conditions outlined in the table have several limitations. For instance, entry 1 requires an extended reaction time of 36 hours while providing a moderate yield of 81%. Entry 2 involves a relatively high temperature of 160 °C, which could be energy-intensive. Similarly, entries 3 and 4 employ long reaction times ranging from 2.5 to 12 hours, with temperatures spanning from 80 °C to 200 °C, potentially limiting efficiency. Entry 5 shows a comparatively lower yield of 54% under mild conditions but necessitates the use of a Pd catalyst, which is costly. Overall, many of these traditional methods rely on prolonged reaction durations, elevated temperatures, or expensive and potentially toxic catalysts, underscoring the need for more sustainable, efficient, and greener alternatives.
Recent studies have reported various electrocatalytic reactions for amide synthesis23–25 and CO2 conversion, underscoring the growing scientific interest in this area.26,27 These processes utilize electric current as a green and renewable oxidant, playing a crucial role in the sustainable and environmentally friendly synthesis of amide compounds and the conversion of CO2. Table 2 compiles previous reports on the electro-catalytic synthesis of N-phenylbenzamide derivatives, detailing the key reaction parameters for each case. In entry 1, the electrochemical coupling between nitrobenzene and aniline derivatives was conducted at room temperature in MeCN solvent, applying a current of 40 mA for 0.5 hours using a Pd electrode, which resulted in a high yield of 89%. Entry 2 describes the use of 8 mA current with carbon/carbon (C/C) electrodes in MeCN at ambient temperature for 3 hours, providing a 73% yield for the N-phenylation reaction involving nitrobenzene and hydrazine substrates. In entry 3, the electro-reduction and carbonylation of nitrobenzene took place over 2 hours at 35 mA current using platinum (Pt) electrodes in MeCN, affording a 70% yield. Entry 4 employed nickel (Ni) electrodes at a lower current of 6 mA for 6 hours in methanol (MeOH) solvent and achieved an 87% yield, demonstrating an alternative catalytic metal and a longer reaction time for the amide synthesis. Entry 5 reports a 72% yield obtained via a Pt electrode system at 35 mA current over 3 hours, maintaining moderate electrolysis conditions. Finally, entry 6 highlights the use of Au and Pt electrodes at a low cell potential of 0.23 V in MeCN at ambient temperature for 2 hours with a 71% yield, showcasing the effectiveness of noble metals under mild electrochemical potential. Collectively, these studies showcase progressing electro-catalytic methodologies for N-phenylbenzamide synthesis, with various electrode materials (Pt, Ni, and Au) and electrolysis conditions such as current intensity, solvent systems, and reaction times. The electro-catalytic reaction conditions outlined in the table have several limitations. For example, entry 1 employs an expensive Pt electrode with a relatively high current of 40 mA, which may lead to increased operational costs and energy consumption. Entry 2 uses a lower current (8 mA) but requires a longer reaction time of 3 hours with carbon-based electrodes, resulting in moderate yield (73%). Entries 3 and 5 also rely on Pt electrodes with currents of 35 mA applied over 2–3 hours, indicating the continued dependence on costly metals and relatively high current densities. Entry 4 utilizes nickel electrodes at 6 mA over an extended 6-hour period, increasing the overall reaction time. Finally, entry 6 involves noble metal electrodes (Au/Pt) at low potential but still requires 2 hours of reaction time. Overall, these methods often depend on expensive electrode materials, relatively high currents or prolonged electrolysis times, which can limit their scalability and economic feasibility, emphasizing the need for more cost-effective and energy-efficient electro-catalytic systems.
Graphene oxide (GO) has emerged as a versatile material in organic synthesis and electrosynthesis due to its rich surface chemistry and excellent conductivity. Its abundant oxygen-containing functional groups enable GO to act as an effective carbo-catalyst for various organic transformations, including oxidation, reduction, and coupling reactions, often serving as a metal-free alternative.34,35 In electrosynthesis, the GO conductive network facilitates efficient electron transfer, enhancing catalytic activity and selectivity. Moreover, GO possesses tunable electrical conductivity, which can be further optimized by reduction or functionalization, making it a promising component in designing advanced catalytic systems for sustainable synthetic applications. Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) are an emerging class of crystalline porous polymers composed of organic building blocks linked by strong covalent bonds to form two- or three-dimensional structures.35,36 They exhibit high thermal and chemical stability, permanent porosity, and large surface areas, making them highly tunable for diverse applications such as gas storage (H2 and CO), catalysis (H2 trapping), sensing, and energy storage.37,38
To overcome these limitations, a novel electrocatalyst composite, GO/Fe@TANG, was engineered by functionalizing GO with Fe and integrating a TANG COF as a carbonyl-trapping moiety. This catalyst was evaluated under mild electro-synthetic conditions employing a multifunctional MEA/EDA DES that simultaneously served as a solvent, a co-catalyst and an electrolyte. The system effectively catalyzed the carbonylation and hydrogenation of substrates including nitrobenzenes 1(a–j), chlorobenzenes 2(a–d), CO 3(a), and H24(a) gas, yielding N-phenylbenzamide derivatives 5(a–m) with high efficiency (91–96% yields). The TANG COF plays a critical role in the electrocatalytic system due to its high surface area, which facilitates effective hydrogen gas adsorption and increases active reaction sites. However, its inherent lack of electrical conductivity limits its use in electro-organic reactions. This limitation is overcome by integrating graphene oxide and Fe, which enhance the composite's electrical conductivity and catalytic efficiency. This synergistic effect improves charge transport, thereby boosting the overall electrocatalytic performance. Comprehensive catalyst and product characterization was conducted through advanced techniques such as FT-IR, SEM, TEM, EDX, TGA, BET 1H NMR, CHN, CV, and XPS. The integration of iron-based porous materials with multifunctional electrolytes within this electrocatalytic system demonstrates a sustainable, environmentally benign approach for the high-yielding synthesis of valuable amide derivatives, aligning with green chemistry principles through a streamlined and efficient process (Fig. 2).
Experimental
Materials and methods
This study employed a diverse array of chemical reagents and materials critical for the synthesis, characterization, and catalytic evaluation. The DES components included monoethanolamine hydrochloride (MEA) and ethylenediamine (EDA); urea, choline chloride (ChCl), acetic acid (Ac), tetrapropylammonium bromide (TPAB), and formic acid (FA) were also employed during solvent screening experiments to investigate their effects on catalytic performance. Key reagents for catalyst preparation and synthetic transformations comprised nitric acid (HNO3, 65%), triangulene (a covalent organic framework precursor), acetic anhydride ((CH3CO)2O), glacial acetic acid (CH3CO2H), 1,4-dioxane, tetrahydrofuran (THF), silver nitrate (AgNO3), potassium chromate (K2CrO4), and palladium on carbon (Pd/C). Organic building blocks included 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalaldehyde, serving as a linker in COF formation. Solvents and ancillary chemicals such as methanol (MeOH), sulfuric acid (H2SO4, 98%), phosphoric acid (H3PO4, 98%), toluene, ethyl acetate, hexane, isopropanol (iPrOH), acetonitrile (MeCN), N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF), and sodium chloride (NaCl), carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen (H2) gas capsules, nitrobenzenes 1(a–j), and chlorobenzenes 2(a–d) served as reaction media, extraction solvents, or electrolytes. Graphitic materials including graphite powder and graphite rods were utilized as electrode substrates. Oxidizing agents, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) potassium permanganate (KMnO4), and hydrochloric acid (HCl, 35%) were employed in the synthesis and functionalization of GO. Iron chloride (FeCl3) was used both as a catalyst precursor and as an effective mediator in electrochemical reactions. Aluminium thin-layer chromatography (TLC) plates facilitated monitoring of reaction progress and product purification. A range of advanced instruments were employed to ensure thorough characterization and quality control throughout the study. Mechanical stirring and heating (IKA RW20 and Heidolph units) provided uniform reaction conditions, while phase separation and solvent removal were achieved using a ZentriMix 380 R centrifuge and an RV 8 V-C rotary evaporator, respectively. Electrochemical properties were investigated with a custom PS3010H DC power supply and by cyclic voltammetry. Structural and compositional analyses involved FT-IR (JASCO, FT/IR-8X) spectroscopy for functional groups, SEM and TEM for morphology and nanostructure, and EDX mapping for elemental distribution (FlexSEM 1000 II). Thermal stability was assessed by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA, ToronTGA), and surface area measurements were done via BET (Belsorp-miniX) analysis. Metal content was precisely quantified using ICP-OES (ICP2060t), while the molecular structure of organic products was confirmed by 1H NMR (Bruker). Elemental analysis (CHN, EMA 502) and surface chemistry (XPS, Kratos AXIS Supra) offered further insights into composition and chemical states. Altogether, this suite of characterization techniques enabled a detailed understanding and optimization of the GO/Fe@TANG composite electrocatalyst, supporting its development as an efficient and sustainable material for green synthesis.Procedure for synthesis of monoethanolamine hydrochloride–ethylenediamine DES (MEA/EDA)
Inside a 100 mL round-bottom flask, a 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 molar mixture of monoethanolamine hydrochloride (MEA) and ethylenediamine (EDA) was prepared by combining the components and stirring the mixture at 60 °C for 30 minutes until a clear solution was obtained. To prevent precipitate formation due to excess H2O, the resulting reaction mixture was subsequently dried under vacuum at 70 °C. This process yielded a clear DES composed of MEA/EDA. Other DESs, including tetrapropylammonium bromide–formic acid (1
1 molar mixture of monoethanolamine hydrochloride (MEA) and ethylenediamine (EDA) was prepared by combining the components and stirring the mixture at 60 °C for 30 minutes until a clear solution was obtained. To prevent precipitate formation due to excess H2O, the resulting reaction mixture was subsequently dried under vacuum at 70 °C. This process yielded a clear DES composed of MEA/EDA. Other DESs, including tetrapropylammonium bromide–formic acid (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2, TPAB
2, TPAB![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) FA), choline chloride–acetic acid (1
FA), choline chloride–acetic acid (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2, ChCl
2, ChCl![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Ac), and urea–choline chloride (2
Ac), and urea–choline chloride (2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, urea
1, urea![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ChCl), were synthesized following the same procedure (Fig. 3).39
ChCl), were synthesized following the same procedure (Fig. 3).39
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 mixture of MeOH and THF. Finally, the product was dried overnight under high vacuum, resulting in the TANG-COF being isolated as a black powder in 65% yield (0.97 g). The careful control of reaction conditions, solvents, and purification processes ensured the formation of a pure, well-defined covalent organic framework suitable for further characterization (Fig. 4).40
1 mixture of MeOH and THF. Finally, the product was dried overnight under high vacuum, resulting in the TANG-COF being isolated as a black powder in 65% yield (0.97 g). The careful control of reaction conditions, solvents, and purification processes ensured the formation of a pure, well-defined covalent organic framework suitable for further characterization (Fig. 4).40
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 8 volume ratio and stirred gently at ambient temperature for 15 minutes to create a strongly acidic environment promoting graphite intercalation. The mixture was then cooled to approximately 3–7 °C in a water and ice bath to slow down oxidation kinetics and control the reaction rate. Subsequently, 0.6 g of graphite powder was slowly introduced under continuous stirring to facilitate even dispersion and initial intercalation of sulfuric acid molecules between graphite layers.
8 volume ratio and stirred gently at ambient temperature for 15 minutes to create a strongly acidic environment promoting graphite intercalation. The mixture was then cooled to approximately 3–7 °C in a water and ice bath to slow down oxidation kinetics and control the reaction rate. Subsequently, 0.6 g of graphite powder was slowly introduced under continuous stirring to facilitate even dispersion and initial intercalation of sulfuric acid molecules between graphite layers.
After stabilization of the graphite dispersion, 1.57 g of KMnO4 was gradually added in small portions to oxidize the graphite progressively while maintaining the temperature at 5 °C. The reaction mixture was vigorously agitated at this low temperature for 1 hour to encourage controlled oxidation and prevent overheating. Then, the temperature was raised to 85 °C and maintained for 6 hours to promote deep oxidation and conversion of graphite intercalation compounds to graphite oxide, confirmed by the development of a characteristic dark green coloration. After the heating period, the mixture was cooled back to ambient temperature. To quench the residual oxidizing agents and terminate the reaction, 0.8 mL of 25% H2O2 was added dropwise over 15 minutes, generating an exothermic reaction that further reduces manganese species and stabilizes the GO product. Following stabilization, 13 mL of 35% HCl and 35 mL of deionized H2O were added to wash away manganese by-products and acid impurities.
The suspension was then subjected to centrifugation at 4000 rpm for 10 minutes, separating the solid GO from the supernatant, which was decanted. The residual solid was washed repeatedly four times with 12% HCl and deionized H2O to remove acidic contaminants. Finally, the purified GO solution was dried in a convection oven set at 85 °C for 22 hours until a dry, pure GO powder suitable for subsequent applications was obtained. This modified protocol enhances reaction control by using a mixed acid system (H2SO4/H3PO4) and staged temperature steps, enabling a safer, more efficient oxidation process with improved material quality and reduced toxic gas evolution compared to the conventional Hummers’ method (Fig. 5).41,42
Procedure for synthesis of GO/Fe
A suspension comprising 600 mg of GO/Fe dispersed in 50 mL of MeOH was subjected to ultrasonic treatment using an ultrasonic cleaning bath for 20 minutes at ambient temperature to ensure homogeneous dispersion. Subsequently, 10 mL of an FeCl3 solution prepared by completely dissolving 300 mg of FeCl3 in 20 mL of MeOH was gradually added to the suspension. This combined mixture underwent further sonication for 40 minutes employing an ultrasonic homogenizer to promote effective interaction and incorporation of Fe species onto the GO/Fe substrate.Following ultrasonic treatment, the resulting GO/Fe composite was isolated via centrifugation at an appropriate speed and duration to achieve efficient sedimentation. The precipitate was then repeatedly washed with deionized H2O to remove residual solvents and unreacted reagents. Subsequent filtration was performed to separate the solid material from the liquid phase. Finally, the obtained GO/Fe material was thoroughly dried in an oven operated at 70 °C for 3 hours to eliminate residual moisture and complete dehydration, yielding the final product ready for further characterization and application (Fig. 6).43
Procedure for synthesis of GO/Fe modified with the TANG COF (GO/Fe@TANG)
In a 250 mL two-necked round-bottom flask, 350 mg of GO/Fe, 400 mg of the TANG COF, and 50 mL of toluene were combined. The reactor was equipped with a condenser and a mechanical stirrer, after which the mixture was refluxed with vigorous stirring for 9 hours to ensure thorough interaction and formation of the composite. Upon completion of the reaction, the mixture was allowed to cool naturally to room temperature, and the resultant suspension was subjected to vacuum filtration. The collected solid was sequentially washed with toluene and acetone to remove residual impurities. The purified precipitate, designated as the GO/Fe@TANG composite, was then dried under vacuum at 70 °C for 6 hours to obtain the final composite material. The detailed synthesis procedure is illustrated in Fig. 7.Preparation of the GO/Fe@TANG composite modified SPE electrode
The preparation of the GO/Fe@TANG composite-modified screen-printed electrode (SPE) involved a multi-step procedure designed to ensure uniform deposition and optimal performance. Initially, the bare SPE electrode surface was meticulously cleaned by washing with MeOH to remove any contaminants and subsequently dried at 60 °C for 1 hour to ensure complete solvent evaporation and a pristine substrate. Following surface preparation, 200 mg of the as-synthesized GO/Fe@TANG composite was precisely weighed and dispersed in 10 mL of MeOH. This suspension was subjected to ultrasonic treatment for 25 minutes to achieve a homogeneous dispersion and prevent agglomeration of the composite particles. Subsequently, a mixture was then filtered.Next, a single drop of conductive adhesive was placed on the surface of SPE and allowed to spread. Subsequently, 100 mg of GO/Fe@TANG was weighed and evenly distributed onto the adhesive-coated surface. The electrode was then dried in an oven at 60 °C for 1.5 hours, a process critical for solvent evaporation and the firm immobilization of the GO/Fe@TANG composite layer onto the electrode surface. The resulting GO/Fe@TANG-modified SPE electrode was then subjected to CV analysis to characterize its electrochemical properties and confirm the successful integration of the composite material. Ultimately, this prepared electrode served as the working electrode for the investigation of electrocatalytic carbonylation and hydrogenation reactions, with its performance illustrated in Fig. 8.44
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 volumetric ratio as the eluent. The dried reaction mixture was then introduced onto the column, and purification was carried out by gradient elution chromatography, effectively isolating the desired N-phenylbenzamide products in analytically pure form. The chromatographic process is depicted schematically in Fig. 9.
1 volumetric ratio as the eluent. The dried reaction mixture was then introduced onto the column, and purification was carried out by gradient elution chromatography, effectively isolating the desired N-phenylbenzamide products in analytically pure form. The chromatographic process is depicted schematically in Fig. 9.
A constant current of 15 mA was applied throughout the process, while CO gas 3(a) and H2 gas 4(a) were concurrently and continuously bubbled into the reaction mixture for the entire duration of 1.5 hours. The reaction progress was monitored periodically by thin-layer chromatography (TLC) to assess substrate conversion and product formation. Upon completion of the electrolysis, both the electric current and gas flows were terminated. The reaction mixture was quenched by adding 100 mL of distilled water and 200 mL of ethyl acetate (EtOAc), followed by thorough mixing to achieve phase equilibration. The organic and aqueous layers were separated using a separatory funnel. The aqueous phase, containing residual MEA/EDA DES, was recovered and concentrated under reduced pressure via rotary evaporation for potential reuse, demonstrating a sustainable solvent management approach. The organic layer was similarly concentrated under vacuum to remove residual solvents. Approximately 6 g of silica gel (particle size 90–120 mesh) was added to the concentrated organic residue and dried under full vacuum to form a dry adsorbent slurry. This slurry was loaded onto a silica gel column (50 cm length, 3 cm inner diameter) pre-equilibrated with a hexane:ethyl acetate (7![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 v/v) eluent. Purification was carried out by gradient elution chromatography, effectively isolating the target N-phenylbenzamide 5(a) products in analytically pure form (yield 94%).
1 v/v) eluent. Purification was carried out by gradient elution chromatography, effectively isolating the target N-phenylbenzamide 5(a) products in analytically pure form (yield 94%).
Examination to substantiate the radical pathway of the reaction
In a 100 mL undivided electrolysis cell equipped with a graphite rod cathode, a GO–Fe@TANG SPE anode, and a magnetic stirrer, a mixture of nitrobenzene 1(a) (0.004 mol) and chlorobenzene 2(a) (0.004 mol) was dissolved in 10 mL of the MEA/EDA DES at room temperature. A 1 cm magnetic bar was placed inside the cell to ensure efficient agitation, while gentle heating was provided by the integrated heating stirring system of the electrolyzer. Electrolysis was conducted under a constant current of 15 mA, during which a continuous and simultaneous flow of CO gas 3(a), H2 gas 4(a) and 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidin-1-ol (TEMPO, 0.002 mol) was introduced directly into the reaction medium, thereby maintaining reductive and carbonylative conditions throughout the process. The electrolysis proceeded for 60 minutes, the current was switched off and the reaction mixture was subjected to mass spectrometric (MS) analysis. The trapped product, 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidin-1-yl benzoate, was unambiguously detected. MS (ESI): m/z = 262 [M + H]+; calculated for C16H24NO2: 262 [M + H]+.Protocol for the determination of chlorine (Cl2) in reaction mixtures by titration using K2CrO4 as an indicator (Mohr's method)
A general procedure for the titration of chloride ions involves using a standardized AgNO3 solution as the titrant and K2CrO4 as the indicator. During the electrosynthesis reaction, after one hour of reaction time, approximately 15 mL of the reaction mixture is transferred into a clean conical flask. To this, about 1 mL of K2CrO4 indicator is added, imparting a pale-yellow color to the solution. The titration is then performed by gradually adding the AgNO3 solution from a burette while continuously stirring the mixture. The endpoint is identified by a sudden color change from yellow to brick red, indicating the formation of silver chromate precipitate. This color change occurs only after all chloride ions have precipitated as silver chloride (AgCl). This titrimetric method is widely employed due to its simplicity, reliability, and accuracy in determining chloride content in aqueous samples. Furthermore, this titration confirms the formation of chlorine species in the reaction mixture.45![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 hexane
1 hexane![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) CHCl3), yield = 94%; m.p. = 162–164 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δH = 7.17 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar–H, 1H), 7.38 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.47 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.56 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar–H, 1H), 7.64 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.82–7.90 (m, Ar–H + NH, 3H) ppm. Anal calcd for C13H11NO: C, 79.17; H, 5.62; N, 7.10; O, 8.11%. Found: C, 79.12; H, 5.66; N, 7.13%.
CHCl3), yield = 94%; m.p. = 162–164 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δH = 7.17 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar–H, 1H), 7.38 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.47 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.56 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar–H, 1H), 7.64 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.82–7.90 (m, Ar–H + NH, 3H) ppm. Anal calcd for C13H11NO: C, 79.17; H, 5.62; N, 7.10; O, 8.11%. Found: C, 79.12; H, 5.66; N, 7.13%.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 hexane
1 hexane![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) CHCl3), yield = 96%; m.p. = 156–158 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δH = 2.35 (s, Me, 3H), 7.18 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.47 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.54–7.56 (m, Ar–H, 3H), 7.81 (s, NH, 1H), 7.88 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar–H, 2H) ppm. Anal calcd for C14H13NO: C, 79.59; H, 6.20; N, 6.63; O, 7.57%. Found: C, 79.53; H, 6.24; N, 6.68%.
CHCl3), yield = 96%; m.p. = 156–158 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δH = 2.35 (s, Me, 3H), 7.18 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.47 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.54–7.56 (m, Ar–H, 3H), 7.81 (s, NH, 1H), 7.88 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar–H, 2H) ppm. Anal calcd for C14H13NO: C, 79.59; H, 6.20; N, 6.63; O, 7.57%. Found: C, 79.53; H, 6.24; N, 6.68%.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 hexane
1 hexane![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) CHCl3), yield = 96%; m.p. = 157–160 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δH = 3.83 (s, Me, 3H), 6.87 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.47 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.51–7.56 (m, Ar–H + NH, 3H), 7.79–7.86 (m, Ar–H, 3H) ppm. Anal calcd for C14H13NO2: C, 73.99; H, 5.77; N, 6.16; O, 14.08%. Found: C, 79.92; H, 5.79; N, 6.19%.
CHCl3), yield = 96%; m.p. = 157–160 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δH = 3.83 (s, Me, 3H), 6.87 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.47 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.51–7.56 (m, Ar–H + NH, 3H), 7.79–7.86 (m, Ar–H, 3H) ppm. Anal calcd for C14H13NO2: C, 73.99; H, 5.77; N, 6.16; O, 14.08%. Found: C, 79.92; H, 5.79; N, 6.19%.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 hexane
1 hexane![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) CHCl3), yield = 95%; m.p. = 111–114 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δH = 1.34 (s, Me, 9H), 7.38 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.46 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.51–7.57 (m, Ar–H, 3H), 7.79 (s, NH, 1H), 7.88 (d, J = 7.4 Hz, Ar–H, 2H) ppm. Anal calcd for C17H19NO: C, 80.60; H, 7.56; N, 5.53; O, 6.32%. Found: C, 80.62; H, 5.53; N, 5.58%.
CHCl3), yield = 95%; m.p. = 111–114 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δH = 1.34 (s, Me, 9H), 7.38 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.46 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.51–7.57 (m, Ar–H, 3H), 7.79 (s, NH, 1H), 7.88 (d, J = 7.4 Hz, Ar–H, 2H) ppm. Anal calcd for C17H19NO: C, 80.60; H, 7.56; N, 5.53; O, 6.32%. Found: C, 80.62; H, 5.53; N, 5.58%.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 hexane
1 hexane![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) CHCl3), yield = 92%; m.p. = 176–178 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δH = 7.04–7.10 (m, Ar–H, 2H), 7.45–7.51 (m, Ar–H, 2H), 7.55 (d, J = 6.4, Ar–H, 1H), 7.57–7.64 (m, Ar–H, 2H), 7.79 (s, NH, 1H), 7.87 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, Ar–H, 2H) ppm. Anal calcd for C13H10FNO: C, 72.55; H, 4.68; F, 8.83; N, 6.51; O, 7.43%. Found: C, 72.59; H, 4.65; N, 6.56%.
CHCl3), yield = 92%; m.p. = 176–178 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δH = 7.04–7.10 (m, Ar–H, 2H), 7.45–7.51 (m, Ar–H, 2H), 7.55 (d, J = 6.4, Ar–H, 1H), 7.57–7.64 (m, Ar–H, 2H), 7.79 (s, NH, 1H), 7.87 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, Ar–H, 2H) ppm. Anal calcd for C13H10FNO: C, 72.55; H, 4.68; F, 8.83; N, 6.51; O, 7.43%. Found: C, 72.59; H, 4.65; N, 6.56%.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 hexane
1 hexane![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) CHCl3), yield = 94%; m.p. = 190–193 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δH = 7.36 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.51 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.57 (d, J = 6.2 Hz, Ar–H, 1H), 7.62 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.82 (s, NH, 1H), 7.88 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, Ar–H, 2H) ppm. Anal calcd for C13H10ClNO: C, 67.40; H, 4.35; Cl, 15.30; N, 6.05; O, 6.91%. Found: C, 67.45; H, 4.39; N, 5.99%.
CHCl3), yield = 94%; m.p. = 190–193 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δH = 7.36 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.51 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.57 (d, J = 6.2 Hz, Ar–H, 1H), 7.62 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.82 (s, NH, 1H), 7.88 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, Ar–H, 2H) ppm. Anal calcd for C13H10ClNO: C, 67.40; H, 4.35; Cl, 15.30; N, 6.05; O, 6.91%. Found: C, 67.45; H, 4.39; N, 5.99%.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 hexane
1 hexane![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) CHCl3), yield = 95%; m.p. = 199–201 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δH = 7.47–7.53 (m, Ar–H, 4H), 7.54–7.61 (m, Ar–H, 3H), 7.78 (s, NH, 1H), 7.88 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, Ar–H, 2H) ppm. Anal calcd for C13H10BrNO: C, 56.55; H, 3.65; Br, 28.94; N, 5.07; O, 5.79%. Found: C, 56.58; H, 3.62; N, 5.01%.
CHCl3), yield = 95%; m.p. = 199–201 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δH = 7.47–7.53 (m, Ar–H, 4H), 7.54–7.61 (m, Ar–H, 3H), 7.78 (s, NH, 1H), 7.88 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, Ar–H, 2H) ppm. Anal calcd for C13H10BrNO: C, 56.55; H, 3.65; Br, 28.94; N, 5.07; O, 5.79%. Found: C, 56.58; H, 3.62; N, 5.01%.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 hexane
1 hexane![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) CHCl3), yield = 93%; m.p. = 122–124 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δH = 2.38 (s, Me, 3H), 6.95 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, ArH, 1H), 7.23–7.26 (m, ArH, 1H), 7.43 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, Ar–H, 1H), 7.44–7.51 (m, Ar–H, 3H), 7.53 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, Ar–H, 1H), 7.78 (s, NH, 1H), 7.85 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, Ar–H, 2H) ppm. Anal calcd for C14H13NO: C, 79.59; H, 6.20; N, 6.63; O, 7.57%. Found: C, 79.53; H, 6.25; N, 6.59%.
CHCl3), yield = 93%; m.p. = 122–124 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δH = 2.38 (s, Me, 3H), 6.95 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, ArH, 1H), 7.23–7.26 (m, ArH, 1H), 7.43 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, Ar–H, 1H), 7.44–7.51 (m, Ar–H, 3H), 7.53 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, Ar–H, 1H), 7.78 (s, NH, 1H), 7.85 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, Ar–H, 2H) ppm. Anal calcd for C14H13NO: C, 79.59; H, 6.20; N, 6.63; O, 7.57%. Found: C, 79.53; H, 6.25; N, 6.59%.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 hexane
1 hexane![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) CHCl3), yield = 91%; m.p. = 145–147 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δH = 2.35 (s, Me, 3H), 7.15 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, Ar–H, 1H), 722–7.30 (m, Ar–H, 2H), 7.51 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.56 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, Ar–H, 1H), 7.67 (s, NH, 1H), 7.88 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.94 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, Ar–H, 1H) ppm. Anal calcd C14H13NO: C, 79.59; H, 6.20; N, 6.63; O, 7.57%. Found: C, 79.54; H, 6.24; N, 6.67%.
CHCl3), yield = 91%; m.p. = 145–147 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δH = 2.35 (s, Me, 3H), 7.15 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, Ar–H, 1H), 722–7.30 (m, Ar–H, 2H), 7.51 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.56 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, Ar–H, 1H), 7.67 (s, NH, 1H), 7.88 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.94 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, Ar–H, 1H) ppm. Anal calcd C14H13NO: C, 79.59; H, 6.20; N, 6.63; O, 7.57%. Found: C, 79.54; H, 6.24; N, 6.67%.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 hexane
1 hexane![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) CHCl3), yield = 96%; m.p. = 158–161 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δH = 2.35 (s, Me, 3H), 2.43 (s, Me, 3H), 7.16 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.25 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.53 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.75 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.86 (s, NH, 1H) ppm. Anal calcd C15H15NO: C, 79.97; H, 6.71; N, 6.22; O, 7.10%. Found: C, 79.92; H, 6.75; N, 6.18%.
CHCl3), yield = 96%; m.p. = 158–161 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δH = 2.35 (s, Me, 3H), 2.43 (s, Me, 3H), 7.16 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.25 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.53 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.75 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.86 (s, NH, 1H) ppm. Anal calcd C15H15NO: C, 79.97; H, 6.71; N, 6.22; O, 7.10%. Found: C, 79.92; H, 6.75; N, 6.18%.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 hexane
1 hexane![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) CHCl3), yield = 92%; m.p. = 141–144 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δH = 2.33 (s, Me, 3H), 2.56 (s, Me, 3H), 7.15 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, Ar–H, 1H), 7.25 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, NH, 1H), 7.31 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, Ar–H, 4H), 7.37 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, Ar–H, 1H), 7.55 (d, J = 7.4 Hz, Ar–H, 1H), 8.03 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, NH, 1H) ppm. Anal calcd C15H15NO: C, 79.97; H, 6.71; N, 6.22; O, 7.10%. Found: C, 79.93; H, 6.74; N, 6.19%.
CHCl3), yield = 92%; m.p. = 141–144 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δH = 2.33 (s, Me, 3H), 2.56 (s, Me, 3H), 7.15 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, Ar–H, 1H), 7.25 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, NH, 1H), 7.31 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, Ar–H, 4H), 7.37 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, Ar–H, 1H), 7.55 (d, J = 7.4 Hz, Ar–H, 1H), 8.03 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, NH, 1H) ppm. Anal calcd C15H15NO: C, 79.97; H, 6.71; N, 6.22; O, 7.10%. Found: C, 79.93; H, 6.74; N, 6.19%.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 hexane
1 hexane![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) CHCl3), yield = 96%; m.p. = 128–131 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δH = 1.23–1.31 (m, Me, 6H), 2.64 (q, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 2.73 (q, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.21 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.32 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.56 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.81 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, Ar–H + NH, 3H) ppm. Anal calcd C17H19NO: C, 80.60; H, 7.56; N, 5.53; O, 6.32%. Found: C, 80.63; H, 7.59; N, 5.57%.
CHCl3), yield = 96%; m.p. = 128–131 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δH = 1.23–1.31 (m, Me, 6H), 2.64 (q, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 2.73 (q, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.21 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.32 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.56 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.81 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, Ar–H + NH, 3H) ppm. Anal calcd C17H19NO: C, 80.60; H, 7.56; N, 5.53; O, 6.32%. Found: C, 80.63; H, 7.59; N, 5.57%.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 hexane
1 hexane![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) CHCl3), yield = 95%; m.p. = 204–207 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δH = 7.41 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.61 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.81 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.97 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 10.42 (s, NH, 1H) ppm. Anal calcd C13H9Cl2NO: C, 58.67; H, 3.41; Cl, 26.64; N, 5.26; O, 6.01%. Found: C, 58.61; H, 3.46; N, 5.22%.
CHCl3), yield = 95%; m.p. = 204–207 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δH = 7.41 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.61 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.81 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 7.97 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, Ar–H, 2H), 10.42 (s, NH, 1H) ppm. Anal calcd C13H9Cl2NO: C, 58.67; H, 3.41; Cl, 26.64; N, 5.26; O, 6.01%. Found: C, 58.61; H, 3.46; N, 5.22%.
Results and discussion
Following the synthesis of the GO/Fe@TANG composite, comprehensive characterization was conducted to elucidate its structural properties, functional groups, surface morphology, porosity, specific surface area, thermal stability, electrochemical behavior, and elemental composition. The characterization techniques employed encompassed Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) mapping, inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area analysis, cyclic voltammetry (CV), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The findings from these analytical methods are presented and discussed in the following sections.The FT-IR spectra of the TANG COF, GO, and the GO/Fe@TANG composite are presented in Fig. 10. This figure shows the FT-IR spectra of three samples of GO, TANG COF, and GO/Fe@TANG. Each spectrum highlights the specific vibrational features and functional groups of the corresponding material, indicating their structural differences and successful hybridization. The FT-IR spectrum of GO (black curve) displays characteristic peaks at 1053 cm−1 (C–O stretching), 1411 cm−1 (O–H bending or potentially C–O), 1616 cm−1 (aromatic C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C stretching), 1727 cm−1 (C
C stretching), 1727 cm−1 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretching of carboxyl or carbonyl groups), and a broad absorption at 3410 cm−1 (O–H stretching vibration). These peaks confirm the rich oxygen functionalities (hydroxyl, epoxy, and carboxyl) present on the GO surface, essential for subsequent functionalization. The TANG COF (red spectrum) exhibits distinctive features: peaks at 874 cm−1 (aromatic C–H out-of-plane bending), 1065 cm−1 (aromatic C–N/C–O stretching), 1343 and 1514 cm−1 (C–N and C
O stretching of carboxyl or carbonyl groups), and a broad absorption at 3410 cm−1 (O–H stretching vibration). These peaks confirm the rich oxygen functionalities (hydroxyl, epoxy, and carboxyl) present on the GO surface, essential for subsequent functionalization. The TANG COF (red spectrum) exhibits distinctive features: peaks at 874 cm−1 (aromatic C–H out-of-plane bending), 1065 cm−1 (aromatic C–N/C–O stretching), 1343 and 1514 cm−1 (C–N and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C stretching related to the conjugated COF backbone), and a prominent band at 1622 cm−1 (C
C stretching related to the conjugated COF backbone), and a prominent band at 1622 cm−1 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N stretching, characteristic of imine or Schiff base linkages). These signals verify successful formation of the COF structure via condensation, primarily displaying C
N stretching, characteristic of imine or Schiff base linkages). These signals verify successful formation of the COF structure via condensation, primarily displaying C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N bonds typical for imine-based COFs and aromatic conjugation.
N bonds typical for imine-based COFs and aromatic conjugation.
The GO/Fe@TANG composite (blue spectrum) reveals several key shifts and new bands: the disappearance or shift of the GO strong carbonyl band indicates interaction between GO and the COF. Notable peaks include 962 cm−1 (Fe–O), 1114 cm−1 (C–N/C–O stretching), 1353 and 1475 cm−1 (aromatic and C–N/C–C stretching within the COF structure), 1644 cm−1 (shifted/broadened C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N or C
N or C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O, denoting coordination or conjugation effect), and a broad band at 3402 cm−1 (O–H/N–H stretching, possibly more hydrogen bonding). These changes confirm the presence of both GO and TANG COF functionalities as well as new interactions due to Fe incorporation and hybrid structure formation. These IR bands systematically confirm the integrity of each component and the interaction between GO, TANG COF, and Fe sites within the GO/Fe@TANG composite.46
O, denoting coordination or conjugation effect), and a broad band at 3402 cm−1 (O–H/N–H stretching, possibly more hydrogen bonding). These changes confirm the presence of both GO and TANG COF functionalities as well as new interactions due to Fe incorporation and hybrid structure formation. These IR bands systematically confirm the integrity of each component and the interaction between GO, TANG COF, and Fe sites within the GO/Fe@TANG composite.46
The SEM images of GO shown in Fig. 11(a) and (b) reveal a characteristic layered and wrinkled morphology. The surface appears to consist of thin, sheet-like structures with considerable folding and crumpling, which is typical of exfoliated GO sheets. These wrinkles and folds increase the surface roughness and indicate a high surface area, which is advantageous for various applications such as catalysis or composite formation. The sheets exhibit irregular edges and overlapping layers, suggesting they are few-layered graphene oxide rather than bulk graphite. The porous and flaky nature observed in the images suggests good dispersibility and potential active sites for further functionalization or interaction with other materials. Overall, the SEM micrographs confirm the successful exfoliation and typical morphology of graphene oxide with high surface area and structural defects.
The SEM images of the TANG COF and Fe metal shown in Fig. 11(c) and (d) reveal a highly textured and porous surface morphology. At lower magnification (image c), the material exhibits a rough, granular appearance with densely packed particles, suggesting a heterogeneous surface with significant surface area. At higher magnification (image d), the intricate network of interconnected sheets and wrinkles becomes evident. The surface is characterized by layered, crumpled structures with noticeable porosity, which are typical features of COFs. These morphological traits indicate the presence of abundant micro- and mesopores, which are beneficial for applications involving adsorption, catalysis, or ion transport. The rough and porous architecture observed in the images confirms the successful synthesis of the TANG COF with desirable structural features for enhancing surface interactions.
The SEM analysis of the GO/Fe@TANG COF composite, as shown in Fig. 11, reveals a distinct hierarchical surface morphology at different magnifications. At lower magnification (Fig. 11(e)), the surface appears highly porous and rough, characterized by a network of aggregated particles. This morphology is indicative of a loosely packed, sponge-like structure, likely resulting from the integration of GO/Fe sheets with the TANG COF. Such a porous structure is beneficial for enhancing the surface area and facilitating mass transport, which is advantageous for applications like adsorption or catalysis. At higher magnification (Fig. 11(f)), the image reveals a more compact and uniform distribution of nanostructures. The surface consists of densely packed, rod- or needle-like features, suggesting a well-organized self-assembly or crystallization of the COF and Fe components on the GO surface. This uniform nano-structuring indicates strong interaction and good compatibility between GO/Fe and TANG COF, resulting in a composite material with a high degree of structural order. Overall, the SEM images confirm the successful formation of the GO/Fe@TANG COF hybrid material with a rough, porous texture at the microscale and well-defined nanostructures at the nanoscale, offering potential for applications that require high surface area and structural uniformity.47
The TEM analysis shown in Fig. 12 provides valuable insights into the morphological differences between pristine GO and the GO/Fe@TANG composite. In image A, which corresponds to pure GO, thin, transparent, and wrinkled sheet-like structures are observed. These sheets exhibit a characteristic layered morphology of GO, indicating their high flexibility and large surface area. The transparency of the sheets in the TEM image also suggests their few-layered nature, which is beneficial for surface functionalization. In contrast, image B presents the TEM image of the GO/Fe@TANG composite. Here, the morphology changes significantly, showing the formation of a dense, darker, and less transparent structure. This suggests that the TANG COF and Fe has been successfully grown or deposited onto the GO sheets. The darker contrast and increased thickness imply the formation of a composite layer on the GO surface, indicating strong interaction between GO with Fe and COF material. The previously smooth and thin GO sheets are now coated or embedded within a more textured, amorphous matrix, confirming the effective incorporation of TANG COF and Fe metal into the GO structure.48
EDX mapping (Fig. 13) of the GO/Fe@TANG composite shows a uniform distribution of carbon, oxygen, iron and nitrogen. C, O and Fe are evenly spread due to the GO/Fe substrate and its functional groups, while the consistent presence of N confirms successful incorporation of the nitrogen-rich TANG COF. This elemental uniformity indicates strong interaction and effective coating of the COF on GO/Fe, confirming successful synthesis and suggesting improved surface activity, charge transport, and structural stability for potential catalytic and adsorption uses.
The EDS spectra presented in Fig. 14 illustrate the elemental composition of the GO and GO/Fe@TANG catalysts. In the spectrum corresponding to GO (Fig. 14(a)), prominent peaks for carbon (C) and oxygen (O) are observed, consistent with the characteristic structure of GO. The detected oxygen is attributed to oxygen-containing functional groups such as hydroxyl, epoxide, and carboxyl groups present on the GO surface. In contrast, the EDS spectrum of the TANG COF (Fig. 14(b)) reveals, in addition to carbon and oxygen peaks, the presence of nitrogen (N), which originates from the TANG component. Fig. 14(c) presents the EDS analysis of the GO/Fe@TANG composite catalyst, revealing the elemental composition through distinct spectral peaks. The dominant peaks at low energy levels correspond to carbon and oxygen, reflecting the expected high content of these elements originating from the GO component of the composite. The presence of the Fe peak confirms incorporation of iron, attributed to the GO/Fe moiety within the catalyst. Additionally, the appearance of the N peak indicates nitrogen, likely derived from the TANG COF or additional nitrogen doping. The relative intensities of these peaks demonstrate that carbon and oxygen are the principal constituents, while Fe and nitrogen are present in comparatively smaller amounts. This elemental distribution is consistent with the anticipated composition of the GO/Fe@TANG composite, thereby confirming its successful synthesis and the incorporation of key catalytic elements essential for its function.
Differential thermogravimetric (DTG) and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) curves provide insight into the decomposition behavior and thermal stability of GO, TANG COF, and the GO/Fe@TANG composite (Fig. 15).
For GO, the TGA curve reveals a two-step mass loss pattern. The initial significant mass reduction of approximately 66% occurs by 290 °C, followed by an additional 17% loss up to 415 °C. These weight losses are predominantly attributed to the thermal decomposition of oxygen-containing functional groups such as hydroxyl (OH), carbonyl (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), and carboxyl (CO2H) groups. The DTG curve exhibits corresponding peaks at these temperatures, indicating the rates of mass loss associated with these decompositions. In the case of the TANG COF, the TGA profile shows a more pronounced mass loss, totaling about 97.8% by 412 °C. This substantial degradation is linked to the breakdown of the organic framework's chemical bonds, including C–O, C–N, C
O), and carboxyl (CO2H) groups. The DTG curve exhibits corresponding peaks at these temperatures, indicating the rates of mass loss associated with these decompositions. In the case of the TANG COF, the TGA profile shows a more pronounced mass loss, totaling about 97.8% by 412 °C. This substantial degradation is linked to the breakdown of the organic framework's chemical bonds, including C–O, C–N, C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C, and C–C linkages. The DTG peak at this temperature represents the maximum rate of decomposition, signifying the thermal instability of the pure COF structure beyond this point. The GO/Fe@TANG composite displays a hybrid thermogravimetric behavior characterized by three distinct stages of mass loss: approximately 16% at 203 °C, 21.7% at 444 °C, and a major loss of 48.6% at 532 °C. The initial mass loss is primarily due to the evaporation of adsorbed moisture and the decomposition of labile oxygen-containing groups originating from GO. Subsequent mass losses at elevated temperatures correspond to the decomposition of the organic framework and further breakdown of thermally sensitive functional groups within the TANG COF and GO. Notably, this decomposition step occurs at higher temperatures compared to the individual components, indicating an enhancement in thermal stability. The DTG curve confirms these stages with distinct peaks, reflecting the rates of mass loss during each degradation step. The TGA/DTG analyses demonstrate that combining TANG COF with GO/Fe alters the thermal degradation profile, yielding improved thermal stability in the GO/Fe@TANG composite. This enhanced stability is likely due to strong interfacial interactions and chemical bonding between GO/Fe and TANG, which synergistically reinforce the structural integrity and robustness of the composite material.
C, and C–C linkages. The DTG peak at this temperature represents the maximum rate of decomposition, signifying the thermal instability of the pure COF structure beyond this point. The GO/Fe@TANG composite displays a hybrid thermogravimetric behavior characterized by three distinct stages of mass loss: approximately 16% at 203 °C, 21.7% at 444 °C, and a major loss of 48.6% at 532 °C. The initial mass loss is primarily due to the evaporation of adsorbed moisture and the decomposition of labile oxygen-containing groups originating from GO. Subsequent mass losses at elevated temperatures correspond to the decomposition of the organic framework and further breakdown of thermally sensitive functional groups within the TANG COF and GO. Notably, this decomposition step occurs at higher temperatures compared to the individual components, indicating an enhancement in thermal stability. The DTG curve confirms these stages with distinct peaks, reflecting the rates of mass loss during each degradation step. The TGA/DTG analyses demonstrate that combining TANG COF with GO/Fe alters the thermal degradation profile, yielding improved thermal stability in the GO/Fe@TANG composite. This enhanced stability is likely due to strong interfacial interactions and chemical bonding between GO/Fe and TANG, which synergistically reinforce the structural integrity and robustness of the composite material.
The provided BET adsorption–desorption isotherm graph depicts the nitrogen adsorption and desorption behavior of three samples GO, TANG COF, and the GO/Fe@TANG composite (Fig. 16). The isotherm for the GO sample, represented by the black curve, demonstrates moderate adsorption capacity characterized by a gradual increase in nitrogen uptake, indicative of a mesoporous structure with relatively uniform pore size distribution. In contrast, the TANG COF, illustrated by the orange curve, exhibits a more pronounced increase in adsorption at higher relative pressures, reflecting a greater adsorption capacity and the presence of a more extensively developed porous network. The GO/Fe@TANG composite, depicted by the blue curve, displays a hybrid adsorption behavior combining features of GO, Fe and TANG COF. It shows an initial gradual increase in nitrogen uptake, followed by a marked rise at elevated relative pressures, suggesting enhanced porosity and increased surface area resulting from the synergistic integration of GO and TANG COF. The presence of hysteresis loops, particularly pronounced in the composite isotherm, is indicative of capillary condensation phenomena typical of mesoporous materials. The GO/Fe@TANG composite demonstrates the highest nitrogen adsorption capacity among the samples, highlighting its superior porous characteristics. This enhanced porosity and surface area in the presence of Fe imply that the composite is a promising candidate for applications requiring materials with high surface area, such as catalysis and adsorption processes.
Table 3 presents the results of BET analysis for three samples: GO, TANG COF, and the GO/Fe@TANG composite. The analysis provides key parameters related to the surface properties of these materials. The BET surface area, measured in m2 g−1, is 225.8 for GO, 1189 for the TANG COF, and 1105 for the GO/Fe@TANG composite, indicating that the TANG COF has the highest surface area, suggesting a more porous or highly structured material, while the composite retains a high surface area close to TANG COF, though slightly reduced, possibly due to the integration of GO. The pore volume, measured in cm3 g−1, is 0.22 for GO, 0.52 for the TANG COF, and 0.48 for the composite, showing that the TANG COF and the composite have significantly higher pore volumes than GO, which correlates with their larger surface areas. The average pore diameter, in nm, is 3.98 for GO, 3.1 for TANG COF, and 2.5 for the composite, indicating that the composite has the smallest pore size, which may enhance its adsorption properties due to a more uniform or tighter pore structure. All three samples are classified as mesoporous, with a pore type of 4 and an isotherm type of 4, suggesting similar pore characteristics and adsorption behaviors. The table also lists the treatment conditions, with GO treated at 200 °C for 3 hours, TANG COF at 100 °C for 3 hours, and the composite at 300 °C for 3 hours, indicating varying thermal treatments that might influence the observed properties.
| Sample | GO/Fe | TANG COF | GO/Fe@TANG |
|---|---|---|---|
| BET surface area [m2 g−1] | 225.8 | 1189 | 1105 |
| Pore volume [cm3 g−1] | 0.22 | 0.52 | 0.48 |
| Average pore diameter [nm] | 3.98 | 3.1 | 2.5 |
| Type of pore | Mesoporous | Mesoporous | Mesoporous |
| Isotherm type | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Sample conditions | 200 °C, 3 h | 100 °C, 3 h | 300 °C, 3 h |
Fig. 17 presents the comprehensive XPS analysis of the synthesized GO/Fe@TANG composite catalyst, elucidating its surface chemical composition and electronic states. Fig. 17(a) displays the survey spectrum, highlighting distinct peaks at binding energies of approximately 286 eV (C 1s), 399 eV (N1s), 532 eV (O1s), and 724 eV (Fe 2p). The pronounced peak at 286 eV confirms the predominance of carbon species, which is consistent with the presence of the GO backbone and the TANG component within the composite. The detection of nitrogen at 399 eV (N 1s) signifies successful nitrogen incorporation, likely arising from the triazine-based TANG structure, indicative of nitrogen doping or coordination in the composite matrix. The oxygen peak at 532 eV (O1s) corresponds to oxygen-containing functional groups inherently present in both GO and the TANG COF. Furthermore, the Fe 2p signal at 724 eV verifies the effective loading of iron species into the composite, underscoring their potential catalytic role.
Fig. 17(b) shows the high-resolution O1s spectrum, where the data (black line) are deconvoluted into two primary components: a peak at approximately 532 eV attributed to C–O bonds (blue line), representing hydroxyl or epoxy groups, and a peak near 533.1 eV corresponding to C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O bonds (red line), indicative of carbonyl or carboxyl functionalities. The background contribution is denoted by the green line. These oxygen-containing functional groups are essential for anchoring iron particles and facilitating catalytic activity by providing active surface sites and promoting interactions within the composite material.
O bonds (red line), indicative of carbonyl or carboxyl functionalities. The background contribution is denoted by the green line. These oxygen-containing functional groups are essential for anchoring iron particles and facilitating catalytic activity by providing active surface sites and promoting interactions within the composite material.
In Fig. 17(c), the C1s region is analyzed, showing several distinct peaks reflecting diverse carbon bonding environments. The main peak at 284 eV corresponds to C–N bonds, confirming nitrogen incorporation via TANG modification. A peak at 284.2 eV is assigned to C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O species, while the peak at 285 eV is attributed to C–O groups typical of GO. Peaks at 286 eV and 287.2 eV are ascribed to C–C (sp2-hybridized carbon) and C
O species, while the peak at 285 eV is attributed to C–O groups typical of GO. Peaks at 286 eV and 287.2 eV are ascribed to C–C (sp2-hybridized carbon) and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bonds, respectively. The presence of these various bonding states illustrates the effective functionalization of GO with both oxygen- and nitrogen-containing groups, which are critical for enhancing GO dispersibility and interactions with iron nanoparticles, thereby improving the catalytic performance. Fig. 17(d) presents the Fe 2p1/2 and Fe 2p3/2 high-resolution spectrum, revealing the oxidation states of Fe within the composite. The fitted spectrum (black line) is resolved into four major peaks, one at approximately 714.5 and 722.8 eV (blue line), assigned to Fe3+, and another near 713.2 and 725.5 eV (red line), attributed to Fe2+, with the background indicated in yellow-green. The coexistence of Fe3+ and Fe2+ species confirms the mixed-valence nature of Fe in the composite, an attribute beneficial for redox reactions and catalytic efficacy. This detailed fitting substantiates the incorporation of Fe in its oxidized states within the GO/Fe@TANG matrix and provides insights into the electronic structure of the catalyst.
C bonds, respectively. The presence of these various bonding states illustrates the effective functionalization of GO with both oxygen- and nitrogen-containing groups, which are critical for enhancing GO dispersibility and interactions with iron nanoparticles, thereby improving the catalytic performance. Fig. 17(d) presents the Fe 2p1/2 and Fe 2p3/2 high-resolution spectrum, revealing the oxidation states of Fe within the composite. The fitted spectrum (black line) is resolved into four major peaks, one at approximately 714.5 and 722.8 eV (blue line), assigned to Fe3+, and another near 713.2 and 725.5 eV (red line), attributed to Fe2+, with the background indicated in yellow-green. The coexistence of Fe3+ and Fe2+ species confirms the mixed-valence nature of Fe in the composite, an attribute beneficial for redox reactions and catalytic efficacy. This detailed fitting substantiates the incorporation of Fe in its oxidized states within the GO/Fe@TANG matrix and provides insights into the electronic structure of the catalyst.
Finally, Fig. 17(e) illustrates the N1s binding energy region, spanning 395 to 405 eV. The spectrum includes the fitted data (black line), a C–N component peaking at 399 eV (blue line), and the background (green line). The sharp peak at 399–400 eV confirms the presence of nitrogen chemically bonded to carbon atoms, consistent with nitrogen-containing functional groups derived from TANG in the GO/Fe@TANG composite. The relatively flat background indicates low interference or noise, consolidating the evidence for the successful incorporation of nitrogen, which is critical for enhancing the catalyst's chemical properties and performance.
Fig. 18 presents the XRD patterns of graphene oxide (GO) (black line) and the GO/Fe@TANG composite (blue line). The GO sample exhibits broad diffraction peaks centered around 11.2° and 42.4°, characteristic of its typical layered structure with partial disorder and structural defects. In contrast, the GO/Fe@TANG composite displays multiple sharp and well-defined peaks at 10.3°, 17.3°, 19.4°, 25.1°, 29.9°, 36.7°, and 43.2°, indicative of a highly crystalline material. Notably, the peaks at approximately 10.3° and 43.2° may also be associated with residual GO within the composite. The diffraction peaks observed at 17.3°, 19.4°, 25.1°, and 29.9° correspond to the crystalline planes of the TANG covalent organic framework. Additionally, the peak at 36.7° is ascribed to iron-containing phases present within the composite matrix. The pronounced increase in both the sharpness and number of diffraction peaks in the GO/Fe@TANG composite relative to pristine GO confirms the successful incorporation of iron and COF components, resulting in enhanced crystallinity and improved structural ordering. These findings substantiate the formation of a stable GO/Fe@TANG composite exhibiting distinct crystalline characteristics, which are anticipated to enhance its catalytic and functional performance.
Fig. 19 presents the cyclic voltammetry (CV) analysis results for the catalytic system, examining its electrochemical behavior under varying electrolytes, electrodes, and current conditions, as illustrated across three subfigures. The first subfigure compares the CV curves obtained using different electrolytes, ChCl/AC, urea/ChCl, TPAB/FA, and MEA/EDA. The current response (mA) is plotted against voltage (V), revealing distinct redox peaks for each electrolyte system. Notably, the MEA/EDA electrolyte exhibits the most pronounced redox peaks, indicating superior electrocatalytic activity and efficient C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O trapping capability. In contrast, the TPAB/FA, urea/ChCl, and ChCl/AC electrolytes display broader and less intense peaks, suggesting comparatively lower catalytic performance.
O trapping capability. In contrast, the TPAB/FA, urea/ChCl, and ChCl/AC electrolytes display broader and less intense peaks, suggesting comparatively lower catalytic performance.
The second subfigure compares the electrochemical response of the same system across different electrode materials, Fe–F, GO/Fe, TANG COF, and the GO/Fe@TANG composite. The GO/Fe@TANG composite demonstrates the widest potential window and the highest current density among the electrodes tested, indicative of enhanced electrochemical performance. Conversely, Fe–F and TANG COF electrodes exhibit narrower potential windows and lower current responses. These results suggest that the GO/Fe@TANG composite facilitates improved ion conductivity and stronger electrode–electrolyte interactions, potentially due to abundant hydrogen bonding and structural compatibility within the composite.
The third subfigure investigates the effect of varying current magnitudes 5 mA, 10 mA, 15 mA, and 20 mA on the electrochemical response over a voltage range of −2.0 V to 2.0 V, presumably utilizing the GO/Fe@TANG composite electrode and MEA/EDA electrolyte. The data reveal that a current of 15 mA maximizes the electrochemical performance, further amplifying the superior activity observed in the GO/Fe@TANG and MEA/EDA DES system. In summary, the CV analysis underscores the significant influence of electrolyte composition, electrode material, and applied current on the catalytic system's electrochemical behavior. Among the tested conditions, the combination of MEA/EDA DES electrolyte with the GO/Fe@TANG composite electrode exhibits the highest catalytic activity, with optimal performance achieved at a current of 15 mA.
Catalytic performance evaluation of the GO/Fe@TANG composite
Following the synthesis and thorough characterization of the structural framework, compositional elements, and porosity of the GO/Fe@TANG composite catalyst, its catalytic efficacy was assessed using a model electrochemical carbonylation reaction. The transformation involved nitrobenzene (1a), chlorobenzene (2a), CO gas (3a), and H2 gas (4a) as substrates. Electrolysis was conducted in a custom cell comprising a graphite rod anode and an iron foam cathode (Fe/F) immersed in MeOH solvent containing NaCl as the supporting electrolyte. Under a constant current of 20 mA for 3 hours, the reaction afforded a yield of 42% (Table 2, entry 1). Subsequent solvent screening evaluated iPrOH, MeCN, and DMF, yielding diminished catalytic efficiencies of 31%, 29%, and 26%, respectively (Table 4, entries 2–4). Attempts to enhance catalytic output via temperature elevation to 60 °C proved counterproductive, decreasing the yield to 20% (Table 4, entry 5). These observations suggested that the unique electrochemical environment and gas-phase reactants, specifically CO and H2, necessitate an enlarged effective surface area within both electrolyte and electrode interfaces to facilitate efficient gas adsorption and reaction kinetics. Accordingly, conventional solvents and electrolytes were replaced with DESs possessing biphasic eutectic characteristics, serving dually as solvents and electrolytes. Four DESs, choline chloride/acetic acid (ChCl/Ac), urea/choline chloride (urea/ChCl), tetrapropylammonium bromide/formic acid (TPAB/FA), and monoethanolamine/ethylenediamine (MEA/EDA), were investigated, which produced markedly improved yields of 45%, 48%, 50%, and 65%, respectively (Table 4, entries 6–9). The superior catalytic performance observed with MEA/EDA DES was systematically attributed to its high amine content, enabling the formation of stable carbamate complexes with carbonyl species (CO), thereby facilitating enhanced chemical absorption (up to 33.7 wt%) and effective CO gas trapping. This was corroborated by the presence of multiple amine functionalities offering both strong covalent carbamate formation and favorable physicochemical stability under reaction conditions.39| Entry | ELb | Current (mA) | Time (h) | Heat (°C) | Solvent | Yielda (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Isolated yield. b EL/electrolyte: (NaCl 50%), (NaBr 50%), DES (15 cc). c Graphite anode. d Fe/F. e GO/Fe. f Fe. g GO. h TANG COF. i GO/Fe@TANG. | ||||||
| 1 | NaCl | 20 | 3 | r.t | MeOH | 22cd |
| 2 | NaCl | 20 | 3 | r.t | iPrOH | 31cd |
| 3 | NaCl | 20 | 3 | r.t | MeCN | 29cd |
| 4 | NaCl | 20 | 3 | r.t | DMF | 26cd |
| 5 | NaCl | 20 | 3 | 60 | iPrOH | 20cd |
| 6 | ChCl/Ac | 20 | 3 | r.t | — | 45cd |
| 7 | Urea/ChCl | 20 | 3 | r.t | — | 48cd |
| 8 | TPAB/FA | 20 | 3 | r.t | — | 50cd |
| 9 | MEA/EDA | 20 | 3 | r.t | — | 65cd |
| 10 | MEA/EDA | 20 | 3 | r.t | — | 69ce |
| 11 | MEA/EDA | 20 | 3 | r.t | — | 45cf |
| 12 | MEA/EDA | 20 | 3 | r.t | — | 31cg |
| 13 | MEA/EDA | 20 | 3 | r.t | — | 75ch |
| 14 | MEA/EDA | 20 | 3 | r.t | — | 94ci |
| 15 | MEA/EDA | 15 | 3 | r.t | — | 94ci |
| 16 | MEA/EDA | 10 | 3 | r.t | — | 79ci |
| 17 | MEA/EDA | 5 | 3 | r.t | — | 71ci |
| 18 | MEA/EDA | — | 3 | r.t | — | 32ci |
| 19 | MEA/EDA | 15 | 2 | r.t | — | 94ci |
| 20 | MEA/EDA | 15 | 1.5 | r.t | — | 94ci |
| 21 | MEA/EDA | 15 | 1 | r.t | — | 81ci |
In contrast, TPAB/FA DES, with formic acid as the hydrogen bond donor, engaged primarily via strong acid–base and physical interactions rather than covalent bonding, resulting in moderate CO2 physical adsorption capacity. ChCl/Ac DES, containing the weaker acid acetic acid, exhibited reduced acidity and consequently less effective interaction with CO moieties compared to TPAB/FA and MEA/EDA DESs. The urea/ChCl DES leveraged the hydrogen-bonding ability of urea's amide groups; however, its chemical absorption strength was insufficient for strong CO gas sequestration and primarily enhanced substrate solubilization and functional group activation rather than direct trapping of carbonyl species. Despite improvements, the yields attained with these solvents remained suboptimal for practical applications, prompting investigation into further enhancement strategies via electrode surface area optimization. The catalytic system required the presence of FeCl3 to catalyze crucial reaction steps including the reduction, carbonylation, and coupling stages. Equally important was the effective capture of hydrogen gas during the reduction phase, which motivated the incorporation of TANG COF as a functional scaffold. The resultant GO/Fe@TANG composite catalyst was synthesized, integrating a high specific surface area material capable of trapping H2 gas through interactions with Fe centers within the COF matrix. Comparative studies employing GO/Fe, Fe, GO, TANG COF, and the GO/Fe@TANG composite as cathodes revealed progressive catalytic enhancements with product yields of 69%, 45%, 31%, 75%, and 94%, respectively (Table 4, entries 10–14). These results unequivocally demonstrated the synergistic effect of Fe metal catalysis, H2 trapping by TANG COF, and CO capture within the MEA/EDA DES solvent medium, highlighting the efficacy of this cost-effective and readily accessible catalyst design.
Further parametric evaluation of the applied current density revealed an optimal value of 15 mA, producing the highest yield of 94%. Decreasing the current from 20 to 15, 10, 5, and 0 mA corresponded to yields of 94%, 79%, 71%, and a drastically diminished 32%, respectively (Table 4, entries 15–18), underscoring the necessity of sufficient electric current to maintain catalytic activity. The integral role of applied current in promoting electron transfer and sustaining the electrochemical environment was thus confirmed. Finally, reaction time optimization studies demonstrated that shortening the electrolysis period from 3 hours to 2 and 1.5 hours sustained the maximum yield of 94%, while reducing to 1 hour resulted in a modest decrease to 81% yield (Table 4, entries 19–21). These findings highlight the robustness and efficiency of the optimized catalytic system, promoting shorter reaction times without significant compromise in yield. In summary, the development of the GO/Fe@TANG composite catalyst in conjunction with MEA/EDA DES represents a significant advancement in electrochemical carbonylation catalysis, offering a highly effective strategy for coupling reactions involving gaseous CO and H2. This integrated approach combining molecular-level gas trapping, optimized electrode architecture, and tailored reaction conditions provides a promising avenue for sustainable and scalable catalytic processes.
Table 5 summarizes the synthesis of a series of N-phenylbenzamide derivatives 5(a–m) featuring diverse electron-withdrawing and electron-donating functional groups. These compounds were prepared under mild electrochemical conditions at ambient temperature, for 1.5 hours, applying a constant current of 15 mA in an electrolysis cell fitted with a graphite anode and GO/Fe@TANG composite cathode. The multifunctional MEA/EDA DES served as the solvent, electrolyte, co-catalyst and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O trapping agent enabling efficient catalysis. The data reveal that substituents with varying electronic properties were well tolerated, as high yields were consistently achieved across the series, demonstrating the robustness and broad applicability of this catalytic system. The presence of electron-donating groups (such as methyl and methoxy) as well as electron-withdrawing halogen substituents did not significantly hinder the reaction efficiency, with product yields typically exceeding 90%. Additionally, the melting points of these derivatives, determined experimentally, corroborate the successful synthesis and purity of the compounds, while also reflecting the subtle influence of different substituents on the physicochemical properties. Overall, this study highlights the electrochemical method's versatility and effectiveness in producing a wide array of N-phenylbenzamides under mild, environmentally friendly conditions, with the GO/Fe@TANG composite catalyst playing a key role in enabling the transformation.
O trapping agent enabling efficient catalysis. The data reveal that substituents with varying electronic properties were well tolerated, as high yields were consistently achieved across the series, demonstrating the robustness and broad applicability of this catalytic system. The presence of electron-donating groups (such as methyl and methoxy) as well as electron-withdrawing halogen substituents did not significantly hinder the reaction efficiency, with product yields typically exceeding 90%. Additionally, the melting points of these derivatives, determined experimentally, corroborate the successful synthesis and purity of the compounds, while also reflecting the subtle influence of different substituents on the physicochemical properties. Overall, this study highlights the electrochemical method's versatility and effectiveness in producing a wide array of N-phenylbenzamides under mild, environmentally friendly conditions, with the GO/Fe@TANG composite catalyst playing a key role in enabling the transformation.
| Productb | R1 | R2 | M.p. (°C)lit | M.p. (°C) | Yield%a | E factor | Atom economy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Isolated yield. b Reaction conditions: a mixture of substrates 1(a–j), 2(a–d), along with carbon monoxide 3(a) and hydrogen gas 4(a), was dissolved in 15 mL of MEA/EDA DES. Electrolysis was conducted in an undivided cell featuring a graphite rod anode and a GO/Fe@TANG SPE cathode. The reaction proceeded under a constant applied current of 15 mA for the entire duration of the experiment. | |||||||
| 5a | H | H | 163–16449 | 162–164 | 94 | 0.03 | 81 |
| 5b | 4Me | H | 158–15950 | 156–158 | 96 | 0.04 | 82 |
| 5c | 4OMe | H | 158–15922 | 157–160 | 96 | 0.054 | 82 |
| 5d | 4-tertBu | H | 112–11351 | 111–114 | 95 | 0.053 | 77 |
| 5e | 4F | H | 175–17752 | 176–178 | 92 | 0.087 | 78 |
| 5f | 4Cl | H | 19253 | 190–193 | 94 | 0.052 | 82 |
| 5g | 4Br | H | 200–20154 | 199–201 | 95 | 0.048 | 83 |
| 5h | 3Me | H | 124–12555 | 122–124 | 93 | 0.075 | 79 |
| 5i | 2Me | H | 145–14656 | 145–147 | 91 | 0.098 | 77 |
| 5j | 4Me | 4Me | 158–16057 | 158–161 | 96 | 0.04 | 82 |
| 5k | 2Me | 2Me | 142–14358 | 141–144 | 92 | 0.087 | 79 |
| 5l | 4Et | 4Et | 129–13059 | 128–131 | 96 | 0.04 | 83 |
| 5m | 4Cl | 4Cl | 205–20760 | 204–207 | 95 | 0.052 | 85 |

|
|||||||
To assess the sustainability of the electrocatalytic synthesis of N-phenylbenzamides, the E-factor and atom economy were systematically evaluated, with the E-factor results summarized in Table 5. The calculation of the E-factor deliberately excluded the MEA/EDA DES, owing to its reusability, and instead focused exclusively on the consumed quantities of the starting materials. After completion of the reaction, the mixture was subjected to liquid–liquid extraction using distilled water and ethyl acetate, followed by phase separation via a separatory funnel. The aqueous phase, containing the recyclable MEA/EDA DES, was retained, while the organic phase was concentrated under reduced pressure in a rotary evaporator at 60 °C. The residual mass obtained was weighed and incorporated into the E-factor calculation. This protocol was consistently applied across all derivatives of N-phenylbenzamides 5(a–m), with the corresponding data assembled in Table 5. The resultant E-factor values ranged from 0.02 to 0.098, demonstrating the process's commendable sustainability and alignment with green chemistry principles for the electrocatalytic preparation of N-phenylbenzamides.
The atom economy values ranging from 77 to 85% for our derivatives indicate that a significant proportion of the atoms in the starting materials are incorporated into the desired products (Table 5). This means that only a small portion of the reactants is converted into waste or by-products. From a green chemistry perspective, this high atom economy demonstrates an efficient use of resources and a reduction of chemical waste. It aligns with the principles of green chemistry, which aim to minimize environmental impact by maximizing the incorporation of raw materials into useful products, thus promoting sustainability and reducing the generation of hazardous substances in chemical processes. Therefore, our results suggest that the synthesis routes used are relatively sustainable and environmentally friendly.
The reaction mechanism is shown in Fig. 20. At the anode surface, chloride ions present in the DES undergo electrochemical oxidation, generating chlorine gas (Cl2) in situ.61 This chlorine then diffuses to the cathode, where it reacts with the iron species in the GO/Fe@TANG self-prepared electrode (SPE), forming FeCl3(a). FeCl3 acts as a crucial catalytic mediator for the reduction of the nitro group in nitrobenzene 1(a) in the presence of H24(a) gas. Within the porous catalytic matrix of GO/Fe@TANG SPE, molecular hydrogen (H2) becomes trapped and adsorbed onto the ionic iron centers (Fe3+), facilitating its activation into reactive atomic hydrogen species. Concurrently, the nitro group coordinates to Fe3+, weakening the N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O double bonds and enabling a successive hydrogenation process. The nitro group is stepwise reduced via release of H2O molecules, initially forming nitrosobenzene (b) as an intermediate, which remains coordinated to Fe3+. Continued hydrogenation proceeds through the phenylhydroxylamine intermediate (c), ultimately yielding aniline after elimination of an additional H2O molecule. Throughout this mechanism, the Fe sites serve a dual function by activating both H2 and substrate and by mediating electron transfer, thereby enabling an efficient, surface-catalyzed hydrogenation sequence. Following this reduction, the synthesis of N-phenylbenzamide derivatives proceeds in the presence of ionic iron (Fe3+) through a multi-step catalytic cycle involving aryl halides, CO, and the in situ generated aniline (d). The CO is effectively trapped in the MEA/EDA DES, with this DES serving as a solvent, a co-catalyst and an electrolyte.39 The Fe catalyst undergoes oxidative addition with the aryl halide (Ar–X) to generate an aryl–iron intermediate (f), which activates the aryl moiety for subsequent transformations. Aniline (d) nucleophilically attacks the coordinated CO, forming an isocyanatobenzene intermediate (e). The aryl halide (f) then further reacts with this intermediate, undergoing an intramolecular rearrangement to furnish the targeted N-phenylbenzamide 5(a) product via sequential carbonylation and amidation steps. Utilization of Fe, especially in its ionic form, presents multiple advantages including high natural abundance, low toxicity, and cost-effectiveness relative to precious metal catalysts. Consequently, this iron-catalyzed pathway embodies a sustainable and practical strategy for amide bond formation under mild, green electrochemical conditions. The combination of DES-based solvent systems with porous iron-containing electrocatalysts integrates efficient gas trapping, substrate activation, and redox mediation, collectively enabling a streamlined synthetic route for pharmaceutically relevant amide derivatives in alignment with contemporary green chemistry principles.
O double bonds and enabling a successive hydrogenation process. The nitro group is stepwise reduced via release of H2O molecules, initially forming nitrosobenzene (b) as an intermediate, which remains coordinated to Fe3+. Continued hydrogenation proceeds through the phenylhydroxylamine intermediate (c), ultimately yielding aniline after elimination of an additional H2O molecule. Throughout this mechanism, the Fe sites serve a dual function by activating both H2 and substrate and by mediating electron transfer, thereby enabling an efficient, surface-catalyzed hydrogenation sequence. Following this reduction, the synthesis of N-phenylbenzamide derivatives proceeds in the presence of ionic iron (Fe3+) through a multi-step catalytic cycle involving aryl halides, CO, and the in situ generated aniline (d). The CO is effectively trapped in the MEA/EDA DES, with this DES serving as a solvent, a co-catalyst and an electrolyte.39 The Fe catalyst undergoes oxidative addition with the aryl halide (Ar–X) to generate an aryl–iron intermediate (f), which activates the aryl moiety for subsequent transformations. Aniline (d) nucleophilically attacks the coordinated CO, forming an isocyanatobenzene intermediate (e). The aryl halide (f) then further reacts with this intermediate, undergoing an intramolecular rearrangement to furnish the targeted N-phenylbenzamide 5(a) product via sequential carbonylation and amidation steps. Utilization of Fe, especially in its ionic form, presents multiple advantages including high natural abundance, low toxicity, and cost-effectiveness relative to precious metal catalysts. Consequently, this iron-catalyzed pathway embodies a sustainable and practical strategy for amide bond formation under mild, green electrochemical conditions. The combination of DES-based solvent systems with porous iron-containing electrocatalysts integrates efficient gas trapping, substrate activation, and redox mediation, collectively enabling a streamlined synthetic route for pharmaceutically relevant amide derivatives in alignment with contemporary green chemistry principles.
 | ||
| Fig. 20 Reaction mechanism of electrocatalytic carbonylation and hydrogenation processes for synthesis of N-phenylbenzamides. | ||
Fig. 21 presents two subfigures illustrating the performance and properties of the GO/Fe@TANG composite catalyst after nine catalytic cycles. Fig. 21(a) depicts the reusability performance of the catalyst, showing an initial high catalytic efficiency of 94% during the first cycle, which is consistently maintained through cycles 2 to 5. A gradual decline in activity is observed from cycle 6 onward, with efficiencies of 92%, 91%, 90%, and a more pronounced decrease to 81% at cycle 9. These results indicate that the GO/Fe@TANG catalyst exhibits excellent stability and sustained catalytic performance over the first five cycles, with a progressive loss of activity thereafter, likely attributable to material degradation or loss of active sites. Fig. 21(b) presents the BET adsorption–desorption isotherm of the GO/Fe@TANG composite after nine cycles, where the volume of nitrogen adsorbed (cm3(STP) per g) is plotted against the relative pressure (p/p0) ranging from 0 to 1.0. The isotherm displays characteristics typical of a type IV curve with a distinct hysteresis loop, indicative of mesoporous materials. The adsorption branch reveals a steady increase in nitrogen uptake up to a relative pressure of approximately 0.4, followed by a sharper rise and a hysteresis loop between 0.4 and 0.9, confirming the presence of mesopores within the composite structure. The slight deviation observed in the desorption branch suggests capillary condensation phenomena. Overall, the isotherm profile demonstrates that the porous architecture of the GO/Fe@TANG composite remains largely preserved after nine cycles, although minor alterations in pore volume or surface area are evident. These structural observations correlate with the gradual decrease in catalytic efficiency noted in the reusability study.
ICP-OES analysis was performed on the reaction mixtures collected after the first and ninth catalytic cycles to evaluate iron leaching from the GO/Fe@TANG composite. The results revealed that approximately 1% of the total Fe content was present in the solution after the initial cycle, whereas this value increased to around 4% following the ninth cycle. These findings indicate a gradual leaching of iron from the composite catalyst into the reaction medium over successive cycles, resulting in a corresponding decrease in the iron content retained on the catalyst surface. This progressive loss of active Fe species is correlated with a decline in the catalytic efficiency of the nanocomposite. This test known as leaching studies is an important indicator of both the chemical and physical stability of the electrode. The GO/Fe@TANG-modified SPE exhibited excellent chemical and physical stability over nine consecutive leaching cycles.
Furthermore, the accumulation of reactant-derived species within the catalyst pores, leading to fouling, in conjunction with the depletion of surface iron, collectively contributes to the observed deterioration of catalytic performance after nine reaction cycles. Table 6 summarizes the BET analysis results for the GO/Fe@TANG composite following 9 consecutive reaction cycles, during which the reaction yield decreased from 94% to 81%. The measured parameters include the BET surface area (427 m2 g−1), pore volume (0.21 cm3 g−1), and average pore diameter (0.85 nm). Notably, the specific surface area of the GO/Fe@TANG composite declined from an initial value of 1105 to 427 m2 g−1, while the pore volume decreased from 0.48 to 0.21 cm3 g−1, and the average pore diameter contracted from 2.5 nm to 0.85 nm. These findings suggest that the composite pore structure undergoes significant alteration after multiple cycles. The reduced pore volume and diminished average pore size imply partial pore blockage or structural modification, likely caused by material degradation or fouling during repeated use. Such changes adversely affect the accessibility of active sites and compromise the porous network, which in turn contributes to the observed decline in catalytic efficiency. Consequently, the deterioration in the material's physicochemical properties provides a plausible explanation for the reduction in reaction yield from 94% to 81% after nine successive runs.
| Sample | BET surface area [m2 g−1] | Pore volume [cm3 g−1] | Average pore diameter [nm] |
|---|---|---|---|
| GO/Fe@TANG COF | 427 | 0.21 | 0.85 |
The surface morphology of the GO–Fe@TANG COF sample was investigated following nine consecutive reaction cycles. To obtain the sample, the material was carefully scraped from the cathode surface after completion of the ninth cycle without any prior cleaning or treatment. The collected sample was subsequently analyzed using SEM, and the resulting micrographs are shown in Fig. 22. This figure presents the SEM analysis of the GO–Fe@TANG sample. Fig. 11(e) shows the morphology of the freshly synthesized sample, characterized by a relatively uniform and well-distributed surface structure, which is favorable for catalytic activity. Fig. 22(a) and (b) depict the sample after 9 reaction cycles, during which the reaction yield decreased significantly from 94% to 81%. This performance decline can be correlated with evident morphological changes observed in the SEM images. Notably, the surface in Fig. 22(a) and (b) appears more agglomerated and rougher compared to the initial state, indicating particle aggregation and possible surface fouling or catalyst deactivation. Such morphological deterioration reduces the active surface area and impedes efficient reactant interaction, ultimately leading to the observed decrease in catalytic efficiency. Therefore, the SEM analysis clearly demonstrates that surface morphology degradation after repeated runs is a key factor contributing to the pronounced decline in reaction yield.
For the evaluation of the stability of the designed electrode, a critical parameter for scaling up the electrosynthesis reaction and process, comprehensive analyses including cycling durability, and leaching studies were conducted. The cycling durability assessment was performed by immersing the GO/Fe@TANG-modified electrode in an electrolyte solution composed of MEA/EDA deep eutectic solvent (DES) within a three-electrode electrochemical cell equipped with a magnetic stirrer to ensure homogeneity. The modified screen-printed electrode (SPE) acted as the working electrode, accompanied by an Ag/AgCl reference electrode and a graphite rod counter electrode. The cell was interfaced with a potentiostat/galvanostat, and a constant current of 15 mA was applied to the working electrode continuously for 24 hours at ambient temperature. Throughout this cycling durability stability test, the potential response versus time was systematically recorded every 2 hours. Both the applied current (maintained at 15 mA) and potential fluctuations were continuously monitored to detect any indications of catalyst degradation, activity loss, or electrode instability. Upon completion of the 24-hour interval, the electrode was extracted, thoroughly rinsed, and dried in an oven at 60 °C. The resulting current versus time plot, depicted in Fig. 23, clearly illustrates that the electrode maintained excellent stability and durability over the extended testing period without any significant change in the electrical current.
Table 7 presents a comparative study of various electro-organic amidation methods, highlighting differences in electrodes, electrolytes, solvents, catalysts, reaction conditions, years of publication, and yields. Most studies employ Pt and Au based electrodes and catalysts, with reaction times ranging from 0.5 to 12 hours and current intensities between 5 and 40 mA. The choice of electrolyte and solvent varies widely, including Bu4NI in methanol, NH4Cl in DMSO, and Et4NBF4 in acetonitrile, among others (Table 7, entries 1–7). Notably, the current work utilizes an Fe/C electrode with MEA/EDA electrolyte under mild conditions (1.5 hours, room temperature, 15 mA) and achieves the highest reported yield of 96% (Table 7, entry 8). This underscores significant progress in catalyst development and reaction efficiency. The table also reflects the evolution of the field from 2017 to 2025, demonstrating optimization of reaction parameters to improve yields and broaden catalyst options. Overall, this comprehensive comparison underscores the superior performance of the newly developed Fe based electrocatalytic (GO/Fe@TANG) system in MEA/EDA DES relative to previous Pt and Au based approaches.
| Entry | Electrode | Electrolyte and reagent | Solvent | Catalyst | Conditions | Year | Yields % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pt/Pt | Bu4NI | MeOH | Pt | 5 h, r.t, 9 mA | 2017 | 7562 |
| 2 | Pt/Pt | NH4Cl | DMSO | Pt | 3 h, 50 °C, 10 mA | 2018 | 8463 |
| 3 | Pt/Pt | NaBr | MeOH | Pt | 6 h, 50 °C, 7 mA | 2019 | 9264 |
| 4 | Pt/Pt | TBAB | H2O | Pt | 0.5 h, r.t, 40 mA | 2019 | 8928 |
| 5 | Pt/Pt | Et4NBF4 | MeCN | Pt | 2 h, r.t, 35 mA | 2023 | 7030 |
| 6 | C/Pt | Et4NBF4 | MeCN | Pt | 4 h, 40 °C, 5 mA | 2025 | 7765 |
| 7 | Au/Pt | KOH | MeCN | Au | 12 h, 80 °C, 5 mA | 2025 | 7133 |
| 8 | Fe/C | MEA/EDA | — | Fe | 1.5 h, r.t, 15 mA | This work | 96 |
Conclusion and outlook
In this work, we successfully designed an innovative and novel GO/Fe@TANG composite electrocatalyst by functionalizing GO with Fe and incorporating a TANG COF designed specifically for carbonyl trapping. When combined with a multifunctional MEA/EDA DES acting simultaneously as a solvent, a co-catalyst, and an electrolyte, this system demonstrated exceptional performance for the electrocatalytic carbonylation and hydrogenation of nitrobenzene 1(a–j), chlorobenzene 2(a–d), CO 3(a), and H24(a) gas. The process yielded a broad range of N-phenylbenzamide derivatives with excellent efficiency (91–96%) under mild ambient conditions, short reaction times (1.5 h), and moderate electric current (15 mA). Comprehensive physicochemical characterization confirmed the catalyst's porous architecture and robust chemical functionality and the synergistic role of its components in facilitating efficient gas trapping and electron transfer. The electrocatalytic system addresses critical challenges in sustainable chemical synthesis by minimizing hazardous waste, reducing reliance on toxic reagents and costly precious metals, and consolidating multistep transformations into a single-step, environmentally benign process aligned with green chemistry principles. Optimization studies underscored the importance of the multifunctional DES medium and the high surface area composite catalyst in enabling enhanced adsorption and activation of gaseous reactants, contributing to the markedly improved catalytic outcomes compared to conventional systems.Looking forward, this work opens promising avenues for further advancement in electro-organic synthesis and catalytic design. The integration of porous, earth-abundant metal-based frameworks with tailored solvent environments exemplifies a versatile platform that can potentially be extended to other challenging carbonylation, hydrogenation, and coupling reactions. Future research may focus on scaling up the system toward continuous flow electrochemical reactors, expanding substrate scope to structurally diverse and industrially relevant compounds, and probing mechanistic insights through in situ spectroscopic methods. Moreover, exploring alternative DES solvents with tunable physicochemical properties could further enhance selectivity and efficiency.
Author contributions
Rustamkhon Kuryazov: investigation, methodology; Karkaz Thali: formal analysis, resources, writing – review and editing; Ahmed Aldulaimi: investigation, validation; Mohanad Yakdhan Saleh: methodology, software, investigation; Abdulrahman A. Almehizia: software, visualization, funding acquisition; Tulkin Buzrukov: investigation, methodology; Gularam Masharipova: investigation, supervision, writing – original draft; Bekzod Madaminov: visualization, project administration; Shakir Mahmood Saeed: data curation, writing – original draft; Elyor Berdimurodov: conceptualization, software.Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.Data availability
Data underpinning the findings of this study can be accessed by contacting the corresponding author upon making a reasonable request.Acknowledgements
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research, King Saud University for funding through Vice Deanship of Scientific Research Chairs; (Drug Exploration and Development Chair), Project no. (MED-P-S-02-2025-29).References
- R. G. Mahardika, A. Danova, E. Hermawati and A. Alni, Electrosynthesis of amide: A green pathway for future pharmaceuticals, Earth Environ. Sci, 2024, 1419, 012021 Search PubMed.
- H. Jing, Y. Yihua, Z. Zhanhui and L. Shouxin, Recent progress on green methods and technologies for efficient formation of amide bonds, Chin. J. Org. Chem., 2024, 44, 409 CrossRef.
- B. Song, L. Nie, K. Bozorov, C. Niu, R. Kuryazov, H. Akber Aisa and J. Zhao, Furo [2,3-d] pyrimidines as Mackinazolinone/Isaindigotone Analogs: Synthesis, Modification, Antitumor Activity, and Molecular Docking Study, Chem. Biodiversity, 2023, 20, e202201059 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Song, L. Nie, K. Bozorov, R. Kuryazov, J. Zhao and H. A. Aisa, Design, combinatorial synthesis and cytotoxic activity of 2-substituted furo [2,3-d] pyrimidinone and pyrrolo [2,3-d] pyrimidinone library, Mol. Diversity, 2023, 27, 1767–1783 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. G. Neilan, T. Quinaglia, T. Onoue, S. S. Mahmood, Z. D. Drobni, H. K. Gilman, A. Smith, J. C. Heemelaar, P. Brahmbhatt and J. S. Ho, Atorvastatin for anthracycline-associated cardiac dysfunction: the STOP-CA randomized clinical trial, JAMA, 2023, 330, 528–536 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Zeng, L. Nie, L. Liu, C. Niu, Y. Li, K. Bozorov, J. Zhao, J. Shen and H. A. Aisa, Design, synthesis, in vitro evaluation of a new pyrrolo [1,2-a] thiazolo [5,4-d] pyrimidinone derivatives as cholinesterase inhibitors against Alzheimer's disease, J. Heterocycl. Chem., 2022, 59, 1086–1101 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Li, L. Guo, Z. Huang, F. Lin and L. Pan, Effects of dexmedetomidine as an adjuvant to ropivacaine or ropivacaine alone on duration of postoperative analgesia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, PLoS One, 2023, 18, e0287296 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. L. Haber, A. Graybill and A. Minasian, Amisulpride: a new drug for management of postoperative nausea and vomiting, Ann. Pharmacother., 2021, 55, 1276–1282 CrossRef CAS.
- E. L. Gaillard, B. J. Arsenault, N. S. Nurmohamed, E. S. G. Stroes and S. M. Boekholdt, The Future of Pharmacological Prevention of Aortic Valve Stenosis, Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation, CRC Press, 2024, pp. 348–354 Search PubMed.
- M.-H. Zhu, Z.-J. Liu, Q.-Y. Hu, J.-Y. Yang, Y. Jin, N. Zhu, Y. Huang, D.-H. Shi, M.-J. Liu and H.-Y. Tan, Amisulpride augmentation therapy improves cognitive performance and psychopathology in clozapine-resistant treatment-refractory schizophrenia: a 12-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, Mil. Med. Res., 2022, 9, 59 CAS.
- Y. J. Sun, G. Velez, D. E. Parsons, K. Li, M. E. Ortiz, S. Sharma, P. B. McCray, A. G. Bassuk and V. B. Mahajan, Structure-based phylogeny identifies avoralstat as a TMPRSS2 inhibitor that prevents SARS-CoV-2 infection in mice, J. Clin. Invest., 2021, 131, e147973 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Song, L. Nie, K. Bozorov, R. Kuryazov, H. A. Aisa and J. Zhao, Parallel synthesis of condensed pyrimidine-thiones and their antitumor activities, Res. Chem. Intermed., 2023, 49, 1327–1348 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Lu, L. Nie, D. Tang, K. Bozorov, J. Zhao and H. A. Aisa, Synthesis of tricyclic pyrazolopyrimidine arylidene ester derivatives and their cytotoxic and molecular docking evaluations, J. Heterocycl. Chem., 2024, 61, 651–668 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Nasrullaev, K. Bozorov, K. Bobakulov, J. Zhao, L. F. Nie, K. K. Turgunov, B. Elmuradov and H. A. Aisa, Synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial activity of novel hydrazone-bearing tricyclic quinazolines, Res. Chem. Intermed., 2019, 45, 2287–2300 CrossRef CAS.
- R. P. S. Rajan, C. E. Hong, K. Park and S. Lee, Photocatalytic Synthesis of Diaryl Amides via Direct Coupling of Methyl Arenes and Nitroarenes, Org. Lett., 2025, 27, 4580–4585 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Chen, G. Ling, Z. Yu, S. Wu, X. Zhao, X. Wu and S. Lu, N-Arylamides from Selenium-Catalyzed Reactions of Nitroaromatics and Amides in the Presence of Carbon Monoxide and Mixed Organic Bases, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2004, 346, 1267–1270 CrossRef CAS.
- S. K. Jain, K. A. A. Kumar, S. B. Bharate and R. A. Vishwakarma, Facile access to amides and hydroxamic acids directly from nitroarenes, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2014, 12, 6465–6469 RSC.
- L. Ling, C. Chen, M. Luo and X. Zeng, Chromium-Catalyzed Activation of Acyl C–O Bonds with Magnesium for Amidation of Esters with Nitroarenes, Org. Lett., 2019, 21, 1912–1916 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Zand, F. Kazemi and A. Partovi, Photocatalytic synthesis of anilides from nitrobenzenes under visible light irradiation: 2 in 1 reaction, J. Photochem. Photobiol., B, 2015, 152, 58–62 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q.-D. Wang, X. Liu, Y.-W. Zheng, Y.-S. Wu, X. Zhou, J.-M. Yang and Z.-L. Shen, Iron-mediated reductive amidation of triazine esters with nitroarenes, Org. Lett., 2023, 26, 416–420 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Li, M. Peng, W. Huang, L. Zhao, S. Wang, C. Kang, G. Jiang and F. Ji, Electrochemical Oxidative Carbonylation of N H-Sulfoximines, Org. Lett., 2023, 25, 7529–7534 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. R. Rajamanickam, M. Park, K. Park and S. Lee, FeCl3-Catalyzed Photochemical Reductive Transamidation of Nitroarenes: A Sustainable Approach Using Sacrificial C–H Bonds, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2025, 367, e202401574 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Li, D. D. Ma, J. Zhao, W. Wei, S. G. Han, X. T. Wu, R. Zou, Q. Xu and Q. L. Zhu, Modular Synchronous Synthesis of Amides and α-Ketoamides Realized by Matching Electrolysis-Paired Tandems, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2025, 64, e202503440 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Wang, Y. Wang, P. Li, X. Zhang, J. Liu, Y. Hou, Y. Zhang, Q. Zhu and B. Han, Synthesis of High Value-Added Chemicals Via Electrocatalytic C–N Coupling Involving CO2 and Nitrogen-Containing Small Molecules, ChemCatChem, 2024, 16, e202401138 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Qi, X. Wang, G. Wang, S. R. Dubbaka, P. O'Neill, H. T. Ang and J. Wu, Sustainable electrocatalytic oxidation of N-alkylamides to acyclic imides using H2O, Green Chem., 2024, 26, 306–311 RSC.
- B. S. Al-Salaheen, B. Al-Saida, R. A. Shawabkeh and M. M. A. Allouzi, Electrocatalytic conversion of carbon dioxide to alcohols using composites of nano-Cu, Ag, and graphite electrodes, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., 2025, 1–18 Search PubMed.
- G. G. Nezhad, H. Esfandian and M. S. Lashkenari, Synthesis and Electrocatalytic Performance of Cu–Pb/RGO Composite for Efficient CO2 Reduction to Methanol, Results Eng., 2025, 105436 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Ke, Y. Xu, S. Zhu, X. Lin, C. Lin, S. Zhou and H. Su, Electrochemical N-acylation synthesis of amides under aqueous conditions, Green Chem., 2019, 21, 4329–4333 RSC.
- D. M. M. M. Dissanayake and A. K. Vannucci, Selective N1-Acylation of Indazoles with Acid Anhydrides Using an Electrochemical Approach, Org. Lett., 2019, 21, 457–460 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Strekalova, A. Kononov, V. Morozov, O. Babaeva, E. Gavrilova and Y. Budnikova, Electrochemical approach to amide bond formation, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2023, 365, 3375–3381 CrossRef CAS.
- I. M. Taily, D. Saha and P. Banerjee, Direct synthesis of paracetamol via site-selective electrochemical Ritter-type C–H amination of phenol, Org. Lett., 2022, 24, 2310–2314 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Rerkrachaneekorn, T. Tankam, M. Sukwattanasinitt and S. Wacharasindhu, NaI-mediated oxidative amidation of benzyl alcohols/aromatic aldehydes to benzamides via electrochemical reaction, Tetrahedron Lett., 2021, 70, 153017 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Sato, M. Fujita, N. Shida and M. Atobe, Electrochemical Amide Bond Formation via Chemoselective Oxidation of Hemiaminals with Gold Electrocatalyst, ACS Electrochem., 2024, 1, 45–51 CrossRef.
- F. Ataie, A. Davoodnia and A. Khojastehnezhad, Graphene oxide functionalized organic-inorganic hybrid (GO–Si–NH2–PMo): An efficient and green catalyst for the synthesis of tetrahydrobenzo[b]pyran derivatives, Polycyclic Aromat. Compd., 2021, 41, 781–794 CrossRef CAS.
- B. B. Mulik, S. T. Dhumal, V. S. Sapner, N. N. M. A. Rehman, P. P. Dixit and B. R. Sathe, Graphene oxide-based electrochemical activation of ethionamide towards enhanced biological activity, RSC Adv., 2019, 9, 35463–35472 RSC.
- A. Khojastehnezhad, F. Moeinpour, M. Jafari, M. K. Shehab, A. Samih ElDouhaibi, H. M. El-Kaderi and M. Siaj, Postsynthetic modification of core–shell magnetic covalent organic frameworks for the selective removal of mercury, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2023, 15, 28476–28490 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Khojastehnezhad, K. Rhili, M. K. Shehab, H. Gamraoui, Z. Peng, A. Samih ElDouhaibi, R. Touzani, B. Hammouti, H. M. El-Kaderi and M. Siaj, Rapid, mild, and catalytic synthesis of 2D and 3D COFs with promising supercapacitor applications, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2023, 6, 12216–12225 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Gamraoui, A. Khojastehnezhad, M. Bélanger-Bouliga, A. Nazemi and M. Siaj, Covalent Organic Framework-Templated N-Heterocyclic Carbene-Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles for the Catalytic Reduction of Nitrophenol, ACS Appl. Nano Mater., 2024, 7, 22570–22580 CrossRef CAS.
- T. J. Trivedi, J. H. Lee, H. J. Lee, Y. K. Jeong and J. W. Choi, Deep eutectic solvents as attractive media for CO2 capture, Green Chem., 2016, 18, 2834–2842 RSC.
- V. Lakshmi, C.-H. Liu, M. Rajeswara Rao, Y. Chen, Y. Fang, A. Dadvand, E. Hamzehpoor, Y. Sakai-Otsuka, R. S. Stein and D. F. Perepichka, A two-dimensional poly (azatriangulene) covalent organic framework with semiconducting and paramagnetic states, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142, 2155–2160 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Méndez-Lozano, F. Pérez-Reynoso and C. González-Gutiérrez, Eco-friendly approach for graphene oxide synthesis by modified Hummers’ method, Materials, 2022, 15, 7228 CrossRef.
- X. Chen, Z. Qu, Z. Liu and G. Ren, Mechanism of oxidization of graphite to graphene oxide by the Hummers’ method, ACS Omega, 2022, 7, 23503–23510 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Mirza-Aghayan, M. Mohammadi and R. Boukherroub, Synthesis and characterization of palladium nanoparticles immobilized on graphene oxide functionalized with triethylenetetramine or 2,6-diaminopyridine and application for the Suzuki cross-coupling reaction, J. Organomet. Chem., 2022, 957, 122160 CrossRef CAS.
- A. A. Zen, Z. A. I. Alaridhee, R. K. Jameel, M. S. Mahdi, A. S. Mansoor, U. K. Radi, A. H. Idan, H. Bahai, E. Berdimurodov and I. Eliboev, Designing a reusable chiral SPE electrode with Mg nanoparticles on graphene oxide for efficient enantioselective Grignard carboxylation of (1-bromoethyl) benzenes in a deep eutectic solvent, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2025, 15, 1185–1202 RSC.
- D. Korkmaz, Determination of Chloride Ion Concentration by Titration (Mohr's Method), University of Cantearbury, 2011, pp. 1–2 Search PubMed.
- U.-a Kanta, V. Thongpool, W. Sangkhun, N. Wongyao and J. Wootthikanokkhan, Preparations, characterizations, and a comparative study on photovoltaic performance of two different types of graphene/TiO2 nanocomposites photoelectrodes, J. Nanomater., 2017, 2017, 2758294 Search PubMed.
- E. Hamzehpoor, P. Ghamari, Y. Tao, M. G. Rafique, Z. Zhang, M. Salehi, R. S. Stein, J. Ramos-Sanchez, A. W. Laramée and G. Cosa, Azatriangulene-Based Conductive C
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C Linked Covalent Organic Frameworks with Near-Infrared Emission, Adv. Mater., 2024, 36, 2413629 CrossRef CAS.
C Linked Covalent Organic Frameworks with Near-Infrared Emission, Adv. Mater., 2024, 36, 2413629 CrossRef CAS. - A. V. Munde, B. B. Mulik, P. P. Chavan and B. R. Sathe, Enhanced electrocatalytic activity towards urea oxidation on Ni nanoparticle decorated graphene oxide nanocomposite, Electrochim. Acta, 2020, 349, 136386 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Li, Y. Wang, H. Xie, S. Ren, J.-B. Liu, N. Luo and G. Qiu, Iron-catalyzed cross-coupling of N-methoxy amides and arylboronic acids for the synthesis of N-aryl amides, Mol. Catal., 2021, 516, 111993 CAS.
- A. T. Nguyen, T. G. Luu and H.-K. Kim, Copper-catalyzed photoredox reaction of aldehydes with O-benzoyl hydroxylamines for the formation of amides, New J. Chem., 2024, 48, 17485–17491 RSC.
- Y. Fan, C. Chen, Z. Zhang, X. Meng, X. Liu, J. Cao, Y.-Y. Jiang and Y. Zhao, CO2 Transient Promotion Function Enabled the Selective Electrochemical Transformation of Imines, Org. Lett., 2023, 25, 9202–9206 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Roy, K. Mondal, P. Halder, A. Sengupta and P. Das, CuF2/DTBP-Catalyzed Chan–Lam Coupling of Oxazolidinones with Arylboronic Acid Pinacol Ester: Scope and Application, J. Org. Chem., 2025, 90, 6219–6232 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Rani, D. K. Aneja, M. Kinger, R. Soni, M. Sihag and S. Malik, Metal-Free Selective para-Tosyloxylation of N-Arylbenzamides using [Hydroxy (tosyloxy) iodo] benzene, Lett. Org. Chem., 2024, 21, 456–465 CrossRef.
- S. Pandey, S. Kumar, V. Singh, V. Srivastava and S. Singh, Photocatalytic Approach Toward the Synthesis of Amides via S–C Cleavage: A Mild Approach, J. Org. Chem., 2025, 90, 6423–6433 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Fan, Y. Yang, J. Lei, Q. Jiang and W. Zhou, Copper-Catalyzed N-Benzoylation of Amines via Aerobic C–C Bond Cleavage, J. Org. Chem., 2015, 80, 8782–8789 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Roy, A. Saha, B. Saha, S. Banerjee, C. D. Mukhopadhyay, S. K. Sahu and L. Adak, Reusable Iron–Copper Catalyzed Cross-Coupling of Primary Amides with Aryl and Alkyl Halides: Access to N-Arylamides as Potential Antibacterial and Anticancer Agents, Chem. – Eur. J., 2025, 31, e202403649 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Tian, Q. Zhang and K. Ablajan, Iodine-Promoted N-Acylation of Amines with Hydrazide: An Efficient Metal-Free Amidation, Synthesis, 2022, 4353–4360 CAS.
- S. Li, Y. Li, R. Zhu, J. Bai, Y. Shen, M. Pan and W. Li, Synthesis of ortho-Methylated Benzamides via Palladium-Catalyzed Denitrogenative Cross-Coupling Reaction of [1,2,3]-Benzotriazin-4 (3H)-ones with DABAL-Me3, Org. Lett., 2023, 25, 5443–5447 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. K. Körner, F. C. Tucci, D. M. Rudkevich, T. Heinz and J. J. Rebek, A self-assembled cylindrical capsule: New supramolecular phenomena through encapsulation, Chem. – Eur. J., 2000, 6, 187–195 CrossRef.
- Z. Akrami and M. Hosseini-Sarvari, Ni/g-C3N4 Photocatalysis: Aerobic Oxidative Coupling Reaction Leading to Amidation of Aldehydes with Amines and C–N, C–O, and C–C Cross-Coupling Reaction, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2022, e202200429 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Ahdenov, A. A. Mohammadi, S. Makarem, S. Taheri and H. Mollabagher, Eelectrosynthesis of benzothiazole derivatives via C–H thiolation, Heterocycl. Commun., 2022, 28, 67–74 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Qian, J.-H. Su, Y. Wang, M. Bi, Z. Zha and Z. Wang, Electrocatalytic C–H/N–H coupling of 2′-aminoacetophenones for the synthesis of isatins, J. Org. Chem., 2017, 82, 6434–6440 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Chang, Q. Zhang and C. Guo, Electrochemical reductive Smiles rearrangement for C–N Bond formation, Org. Lett., 2018, 21, 10–13 CrossRef PubMed.
- L. Li, M. Xue, X. Yan, W. Liu, K. Xu and S. Zhang, Electrochemical Hofmann rearrangement mediated by NaBr: practical access to bioactive carbamates, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2018, 16, 4615–4618 RSC.
- L. Chen, J. D. F. Thompson and C. Jamieson, eAmidation: An Electrochemical Amidation of Aldehydes via the Oxidation of N-Aryl Hydrazones, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2025, 367, e9587 CrossRef CAS.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique 2026 |