2-Oxoindolin-thiazoline hybrids as scaffold-based therapeutics for T2DM-associated cognitive impairment: design, synthesis, in vitro and in silico studies
Wesam S.
Qayed
 *a,
Mostafa A.
Hassan
*a,
Mostafa A.
Hassan
 a,
Halil
Şenol
b,
Parham
Taslimi
a,
Halil
Şenol
b,
Parham
Taslimi
 c and
Tarek
Aboul-Fadl
c and
Tarek
Aboul-Fadl
 a
a
aDepartment of Medicinal Chemistry, Faculty of Pharmacy, Assiut University, 71526 Assiut, Egypt. E-mail: Wesam.qayed@aun.edu.eg
bDepartment of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Faculty of Pharmacy, Bezmialem Vakif University, 34093 Fatih, İstanbul, Türkiye
cDepartment of Biotechnology, Faculty of Science, Bartin University, 74110 Bartin, Türkiye
First published on 14th November 2025
Abstract
Alzheimer's disease (AD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are closely linked neurodegenerative and metabolic disorders, sharing overlapping pathological mechanisms. In this study, structure-based drug design combined with molecular hybridization strategies was employed to develop dual-acting compounds targeting both conditions. A series of twenty hybrid molecules, comprising 2-oxoindolin-3-thiosemicarbazones (3a–i) and thiazolines (4a–k) were successfully synthesized and characterized using spectroscopic techniques and elemental analysis. Biological evaluations demonstrated that compounds 3d and 3h exhibit potent inhibitory activity against α-glucosidase (α-Glu) and α-amylase (α-Amy), surpassing the efficacy of acarbose. These findings highlight their promising antidiabetic potential and support further investigation into their therapeutic relevance for AD and T2DM comorbidity (3d (α-glucosidase Ki = 41.41 ± 2.53 nM; α-amylase IC50 = 1.25 ± 0.02 nM), 3h (α-glucosidase Ki = 44.19 ± 2.41 nM; α-amylase IC50 = 2.87 ± 0.16 nM and acrabose (α-glucosidase Ki = 101.20 ± 7.53, α-amylase IC50 9.73 ± 0.20). Furthermore, compounds 3i and 4i exhibited significantly higher inhibitory activity against acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) compared to the reference drug tacrine. Notably, compound 4i demonstrated exceptional multi-enzyme inhibition, with kinetic parameters indicating strong binding affinity: 3i (AChE Ki = 59.71 ± 2.24 nM; BChE Ki = 8.43 ± 0.97 nM), 4i (AChE Ki = 53.31 ± 1.74 nM; BChE Ki = 10.72 ± 2.19 nM), and tacrine (AChE Ki = 132.35 ± 5.90 nM; BChE Ki = 137.42 ± 4.01 nM). Molecular docking and dynamics simulations corroborated these findings by revealing stable and favorable interactions within the active sites of both enzymes. Additionally, in silico ADME profiling indicated desirable pharmacokinetic properties, further supporting the therapeutic potential of these compounds as dual-action agents for the management of Alzheimer's disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
1. Introduction
The global prevalence of both Alzheimer's disease (AD) and diabetes mellitus (DM) is increasing at an alarming rate. A 2024 meta-analysis reported that individuals with diabetes have a 59% higher risk of developing AD compared to non-diabetic individuals. By 2030, it is estimated that the number of people living with diabetes will reach 643 million, while those affected by Alzheimer's disease will number approximately 74.7 million.1 Emerging evidence suggests that insulin-based therapeutic strategies may hold promise in slowing the progression of AD or potentially preventing its associated complications. Considering AD as a neurodegenerative manifestation of diabetes opens new avenues for innovative treatment approaches, particularly those integrating antidiabetic agents to mitigate or delay the onset and advancement of Alzheimer's disease.The precise relationship between Alzheimer's disease (AD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) remains a subject of ongoing investigations. However, evidence suggests that poorly regulated blood glucose levels may increase the risk of developing AD. Due to the significant overlap in pathological mechanisms, AD has been referred to by some researchers as “type 3 diabetes” or “diabetes of the brain”.2,3 This terminology stems from the observing impaired insulin signaling contributes to both the accumulation and toxicity of amyloid-beta (Aβ) precursor protein, as well as to decreased Aβ clearance. Additionally, insulin resistance is linked to cellular energy imbalance, promoting the progression of AD. Several shared pathological pathways, such as disrupted insulin and insulin-like growth factor (IGF) signaling, activation of glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK-3β), oxidative stress, inflammation, and neurofibrillary tangle formation, further underscore the connection between these two disorders.4
1H-Indole-2,3-dione (isatin) has garnered increasing attention as a multifunctional scaffold with significant therapeutic potential. As an endogenous molecule, isatin interacts with specific binding proteins, mediating a variety of biological functions.5 Advanced techniques such as surface plasmon resonance have revealed that isatin modulates the behavior of intracellular amyloid-binding proteins and affects the stability of protein4 complexes, offering insight into its protective role against β-amyloid toxicity and its regulatory influence on protein interactions.6 Pharmacological studies have demonstrated that isatin and its derivatives inhibit AChE and BuChE, suggesting their utility in restoring acetylcholine levels in the brain and treating neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer's disease. Furthermore, isatin-based compounds have shown promise in diabetes management by inhibiting α-glucosidase and α-amylase, two key enzymes involved in carbohydrate digestion.7 Thiosemicarbazones, on the other hand, represent another critical class of bioactive compounds, known for their therapeutic effects across multiple disease domains, including bacterial, fungal, parasitic, viral, and neurodegenerative conditions.8,9 Their structural resemblance to thioureas makes them valuable intermediates in synthesizing pharmacologically active frameworks.
The thiazoline moiety is also a well-known scaffold in medicinal chemistry and has been used to develop new potential bioactive molecules including the well known anti-diabetic drugs pioglitazone and troglitazone.10 The proven benefits of thiazolines in AD treatment were also reported.11
Pharmacophoric integration is a rational drug design approach that combines multiple pharmacophoric elements from different bioactive compounds into a unified scaffold. This strategy aims to enhance biological activity, improve target selectivity, enable multifunctional mechanisms of action, and minimize adverse effects.
Motivated by our previous results on the differing pharmacological profiles of these compound families, a hybridization strategy to combine their key structural features into a single scaffold was pursued.12,13 In the current work, design, synthesis, and evaluation of a novel set of 1H-indole-2,3-dione-based thiosemicarbazones and their cyclized thiazolidine derivatives were undertaken. The synthesized compounds were tested for inhibitory activity against α-amylase, α-glucosidase, AChE, and BChE, aiming to identify candidates with dual antidiabetic and anti-Alzheimer's activity. Additionally, molecular docking and in silico modeling were employed to predict and rationalize their biological activity at the molecular level.
1.1. Rationale of design
Encouraged by the established therapeutic potential of isatin-based molecular hybrids,14 particularly those incorporating thiosemicarbazones15 and thiazolines,12,13 and recognizing the urgent need for dual-acting agents capable of addressing both diabetes and Alzheimer's disease, we designed a novel series of hybrid compounds (Fig. 1). These new entities combine all two pharmacophores within one distinct scaffold, intending to achieve both antidiabetic and anti-Alzheimer activities. These novel entities integrate two pharmacophores, thiazolidinone (as in the antidiabetic agent pioglitazone) and indole (as in the anti-Alzheimer drug donepezil), within a single scaffold, with the goal of achieving dual antidiabetic and anti-Alzheimer activities.Drug discovery is inherently complex, costly, and time-consuming. To accelerate the development of novel therapeutics, virtual screening (VS) has emerged as a vital computational tool for identifying lead compounds from chemical libraries.16 VS strategies are broadly categorized into ligand-based methods, such as pharmacophore modeling, QSAR, and similarity searches, and structure-based approaches, including molecular docking, homology modeling, and molecular dynamics (MD), which exploit 3D protein structures to assess protein–ligand interactions. In the current study, the molecular docking was implemented to virtually screen the designed isatin–thiosemicarbazone intermediates (3a–i) and cyclized isatin–thiazolidine derivatives (4a–k) against four target enzymes: α-amylase (α-Amy), α-glucosidase (α-Glu), acetylcholinesterase (AChE), and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE). Docking results were benchmarked against acarbose for α-Amy and α-Glu, and tacrine for AChE and BChE, to evaluate the inhibitory potential of the proposed compounds.
Based on the docking outcomes, compounds (3a–i) and (4a–k) fit the active pocket of the targeted proteins with variable docking scores and binding affinities comparable to those of reference drugs (acarbose and tacrine). For acetylcholinesterase (AChE), compound 4i showed strong binding with three hydrogen bonds (two with Tyr-124 and one with Phe-295) and three π–π stacking interactions involving Trp-286, Phe-338, and Tyr-341(docking score −12.391 kcal mol−1). In contrast, compound 3h, with the lowest docking score (−6.543 kcal mol−1), formed only a single π–π stacking interaction with Tyr-337, indicating weak binding.
Similarly, for butyrylcholinesterase (BChE), compound 3i hydrogen-bonded with Trp-82 and Thr-120 with a docking score −10.165 kcal mol−1, whereas 3g, the least active (docking score −5.925 kcal mol−1), binds through only one hydrogen bond with Glu-197 and one π–π stacking with Tyr-332. In the case of α-amylase, compound 3d formed four hydrogen bonds with Asp-300 (twice), Asp-197, and Glu-233 (docking score −5.797 kcal mol−1), supporting its strong interaction profile, while compound 3i exhibited only a single π–π stacking interaction with Trp-59 (docking score −4.768 kcal mol−1). For α-glucosidase, compound 3d again stood out with two hydrogen bonds involving Asn-202 and Glu-271, compared to 4e, which formed hydrogen bonds with Asn-333 and Arg-400, likely involving less catalytically relevant residues with docking scores −8.356 and −5.244 kcal mol−1, respectively. Docking patterns and binding interactions are illustrated in the figures provided in the SI (Fig. S1). The promising in silico binding affinity of these compounds toward the target proteins suggests their potential as dual-acting modulators, justifying subsequent synthetic efforts and in vitro profiling to confirm their mechanism. Additionally, the correlation between docking scores and expected activity underscores the reliability of our computational framework.
Table 1 summarizes docking scores and MM-GBSA ΔG binding free energies for the designed compounds 3(a–i) and 4(a–k), including their E/Z diastereoisomers, and the target proteins, α-Amy, α-Glu, AChE, and BChE, offering insight into their prospective biological activity. Although the diastereomers revealed similar binding affinities, the result was consistent with earlier reports, where the binding energies of different proteins differed significantly, suggesting subtle structural influences on ligand–protein interaction dynamics.12,13
| Docking Scores (kcal mol−1) | MM-GBSA ΔG bind. (kcal mol−1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Codes | AChE | BChE | α-Amy | α-Glu | AChE | BChE | α-Amy | α-Glu |
| 4EY7 | 6EP4 | 5E0F | 3WY1 | 4EY7 | 6EP4 | 5E0F | 3WY1 | |
| 3a | −7.274 | −6.661 | −5.815 | −5.988 | −31.87 | −25.15 | −28.55 | −25.88 |
| 3b | −6.621 | −7.002 | −5.797 | −6.049 | −42.90 | −33.94 | −36.63 | −33.31 |
| 3c | −8.629 | −9.469 | −4.905 | −7.230 | −13.25 | −35.35 | −41.31 | −45.42 |
| 3d | −6.766 | −8.250 | −8.112 | −8.356 | −27.97 | −29.28 | −41.28 | −45.09 |
| 3e | −6.717 | −7.612 | −5.823 | −5.452 | −20.47 | −21.07 | −37.99 | −32.28 |
| 3f | −7.597 | −9.334 | −5.735 | −6.908 | −47.82 | −33.15 | −41.30 | −44.08 |
| 3g | −7.042 | −5.925 | −5.623 | −5.558 | −30.64 | −22.32 | −33.79 | −27.51 |
| 3h | −6.543 | −6.900 | −6.072 | −8.008 | −22.04 | −33.20 | −31.70 | −57.39 |
| 3i | −10.767 | −10.165 | −4.768 | −6.919 | −69.39 | −51.84 | −35.19 | −47.89 |
| 4a | −7.960 | −7.432 | −6.047 | −5.501 | −54.16 | −38.93 | −37.08 | −28.91 |
| (E) 4b | −8.766 | −7.504 | −5.033 | −6.518 | −45.96 | −48.34 | −31.86 | −30.17 |
| (Z) 4b | −6.678 | −6.692 | −5.009 | −6.917 | −47.99 | −44.75 | −41.52 | −35.03 |
| (E) 4c | −7.780 | −8.251 | −5.783 | −6.916 | −50.29 | −53.04 | −43.51 | −40.62 |
| (Z) 4c | −7.443 | −7.728 | −5.44 | −7.841 | −44.96 | −38.18 | −42.92 | −51.49 |
| 4d a | −8.677 | −8.321 | −5.671 | −6.774 | −30.23 | −36.92 | −45.76 | −32.21 |
| 4e | −8.208 | −6.285 | −6.552 | −5.244 | −52.74 | −34.23 | −35.70 | −27.64 |
| 4f | −7.853 | −8.002 | −5.159 | −6.189 | −39.17 | −33.97 | −42.17 | −29.07 |
| 4g | −9.268 | −8.260 | −5.331 | −5.417 | −40.88 | −51.57 | −42.04 | −25.67 |
| (E) 4h | −8.347 | −7.490 | −5.657 | −5.768 | −52.69 | −44.79 | −41.91 | −36.82 |
| (Z) 4h | −7.838 | −7.111 | −5.015 | −7.656 | −41.87 | −34.30 | −44.68 | −43.88 |
| 4i | −12.391 | −9.313 | −5.331 | −5.417 | −91.53 | −71.58 | −42.04 | −25.67 |
| 4j | −6.861 | −7.774 | −5.710 | −5.528 | −40.95 | −50.82 | −42.60 | −19.08 |
| 4k | −8.497 | −8.438 | −4.990 | −5.997 | −61.84 | −46.36 | −48.78 | −33.29 |
| Acarbose | — | — | −13.205 | −7.151 | — | — | −67.05 | 3.96 |
| Tacrine | −7.241 | −7.132 | — | — | −39.15 | −28.97 | — | — |
2. Results and discussions
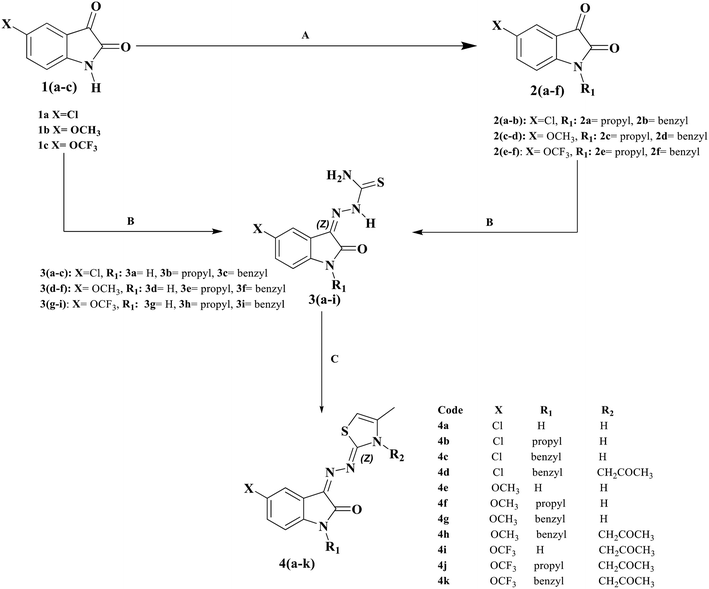
2.1. Chemistry
Scheme 1 illustrates the synthesis of the novel compounds 4(a–k) from the reported intermediates 3(a–i).12,13 Unsubstituted thiazolidine products were obtained from 3a, 3b, 3d, and 3e, whereas N-substituted derivatives resulted from 3g, 3h, and 3i. Interestingly, 3c and 3f yielded mixtures of both forms, which were subjected to chromatographic purification to isolate the pure compounds.The synthesis of compounds 4(a–k) extends our previous work in this domain. Earlier analogues featuring N-methyl or N-ethyl substitutions on the thiazolidine ring limited further modification with chloroacetone. This study focused on the use of unsubstituted thiosemicarbazones, enabling N-alkylation with chloroacetone through nucleophilic substitution.
The designed compounds 4(a–k) were synthesized following the pathway outlined in Scheme 1. Alkylation of 5-substituted indole-2,3-diones (step A) and the subsequent condensation with thiosemicarbazide (step B) produced the corresponding thiosemicarbazones proceeded efficiently, affording intermediates in high yields of more than 80%. The final cyclisation with chloroacetone (step C) was more sensitive to substituent effects at the 5-position and the N1 substituent, providing the target compounds in slightly lower yields after chromatographic purification and separation. Compounds bearing chloro or trifluoromethyl generally formed single diastereomers, except for the chloro derivative with a benzyl substituent at N1, which produced an E/Z mixture (4c). Similarly, the methoxy substituent provided single diastereomers when N1 was H or n-Pr, whereas benzyl substitution again led to E/Z mixtures (4g).
All products were obtained as colored solids and fully characterized by 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy and elemental analysis, confirming the proposed structures. Mixtures of E/Z isomers were distinguished by characteristic NMR signals such reactions, common in heterocyclic chemistry involving α-haloketones,17,18 yielded either pure thiazolidines, acetone-substituted derivatives, or mixtures, depending on the substituents and conditions applied. In particular, compounds 4i, 4j, and 4k formed exclusively as acetone-substituted products, suggesting that the presence of a trifluoromethoxy (OCF3) group may favor this transformation by enhancing nucleophilicity at the thiazolidine nitrogen. A comprehensive investigation of this proposal is planned for a future study.
In certain cases, the reaction favors the formation of stable, unsubstituted thiazolidine rings, as observed in compounds 4a, 4b, 4e, and 4f. This selectivity is likely driven by stabilizing effects from substituents such as 5-Cl or 5-OCH3 and small aliphatic groups at R1, which may reduce N–H reactivity and inhibit alkylation by chloroacetone. Conversely, compounds 3c and 3f yielded both acetone-substituted and unsubstituted products (e.g., 4c, 4d, 4f, 4g), indicating the substituents do not favor a single dominant pathway. In these cases, groups like benzyl at R1 combined with 5-substituents allow dual product formation, highlighting the nuanced role of electronic and steric effects. The stereoselectivity of the reaction, yielding exclusively Z-isomers for compounds 3(a–i), is consistent with prior findings. NMR data confirm this configuration, in line with earlier structural reports by our group,12,13 including those supported by X-ray crystallography.
2.2. Enzyme inhibition studies
The in vitro inhibitory properties of the synthesized compounds were investigated against enzymes implicated in diabetes (α-Amy and α-Glu) and neurodegenerative diseases (AChE and BChE). Acarbose (ACR) and tacrine (TAC) were utilized as benchmark inhibitors. The results, including IC50 values from inhibition assays and Ki values from enzyme kinetics, are summarized in Table 2.| IC50 [nM] | K i [nM] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Codes | α-Gly | α-Amy | AChE | BChE | α-Gly | AChE | BChE |
| 3a | 102.54 ± 0.85 | 6.39 ± 0.18 | 100.21 ± 4.13 | 26.32 ± 0.12 | 118.35 ± 3.09 | 91.03 ± 2.07 | 21.08 ± 1.36 |
| 3b | 74.11 ± 2.03 | 7.36 ± 0.49 | 125.51 ± 0.68 | 29.52 ± 2.31 | 60.37 ± 4.48 | 119.47 ± 1.24 | 23.71 ± 1.41 |
| 3c | 82.71 ± 0.42 | 8.21 ± 0.13 | 131.08 ± 4.71 | 41.24 ± 0.34 | 89.14 ± 4.25 | 122.61 ± 2.38 | 32.53 ± 3.28 |
| 3d | 45.19 ± 0.62 | 1.25 ± 0.02 | 135.52 ± 0.19 | 33.04 ± 0.44 | 41.41 ± 2.53 | 131.74 ± 1.29 | 27.51 ± 2.80 |
| 3e | 90.27 ± 2.66 | 8.55 ± 0.21 | 136.93 ± 3.28 | 44.29 ± 2.19 | 85.09 ± 2.24 | 132.59 ± 3.32 | 41.17 ± 3.38 |
| 3f | 79.17 ± 2.53 | 9.18 ± 0.20 | 137.38 ± 4.91 | 46.54 ± 0.33 | 75.52 ± 2.48 | 130.79 ± 2.46 | 35.75 ± 2.49 |
| 3g | 54.32 ± 1.73 | 3.43 ± 0.67 | 77.41 ± 1.28 | 19.25 ± 1.32 | 60.48 ± 2.70 | 68.54 ± 5.63 | 15.38 ± 1.04 |
| 3h | 46.70 ± 1.51 | 2.87 ± 0.16 | 82.32 ± 1.35 | 16.09 ± 1.80 | 44.19 ± 2.41 | 71.65 ± 4.39 | 12.94 ± 1.05 |
| 3i | 63.28 ± 1.70 | 3.19 ± 0.36 | 70.81 ± 1.19 | 10.87 ± 1.17 | 59.71 ± 2.24 | 62.51 ± 5.02 | 8.43 ± 0.97 |
| 4a | 79.32 ± 1.29 | 6.84 ± 0.24 | 116.07 ± 2.32 | 35.16 ± 1.41 | 94.42 ± 5.65 | 102.23 ± 2.19 | 30.12 ± 2.54 |
| 4b | 76.91 ± 1.33 | 7.97 ± 0.56 | 128.32 ± 3.05 | 38.04 ± 1.74 | 92.28 ± 3.07 | 120.52 ± 4.41 | 36.24 ± 3.64 |
| 4c | 72.63 ± 3.55 | 9.28 ± 0.27 | 130.40 ± 1.23 | 45.41 ± 2.11 | 79.52 ± 5.46 | 115.18 ± 4.84 | 39.62 ± 4.21 |
| 4d | 88.06 ± 2.22 | 8.39 ± 0.98 | 133.64 ± 0.54 | 43.19 ± 1.25 | 102.73 ± 2.39 | 129.34 ± 1.06 | 37.47 ± 3.73 |
| 4e | 70.46 ± 2.19 | 6.92 ± 0.06 | 138.15 ± 2.39 | 39.12 ± 1.70 | 68.35 ± 3.19 | 134.21 ± 4.07 | 32.39 ± 1.52 |
| 4f | 89.30 ± 1.08 | 7.32 ± 0.35 | 139.04 ± 1.52 | 35.41 ± 3.24 | 86.27 ± 5.36 | 135.48 ± 3.87 | 30.29 ± 1.64 |
| 4g | 91.47 ± 4.14 | 6.74 ± 1.06 | 134.21 ± 0.66 | 43.71 ± 2.98 | 87.64 ± 1.37 | 121.03 ± 1.51 | 40.60 ± 1.56 |
| 4h | 96.05 ± 0.62 | 9.36 ± 0.29 | 139.74 ± 3.12 | 48.63 ± 2.01 | 92.20 ± 3.56 | 136.16 ± 1.29 | 42.51 ± 3.23 |
| 4i | 59.03 ± 2.48 | 4.22 ± 0.32 | 65.29 ± 2.70 | 13.48 ± 3.54 | 52.35 ± 3.66 | 53.31 ± 1.74 | 10.72 ± 2.19 |
| 4j | 51.09 ± 0.34 | 5.04 ± 0.37 | 78.15 ± 0.61 | 15.34 ± 0.22 | 48.08 ± 2.38 | 70.22 ± 2.48 | 10.81 ± 0.38 |
| 4k | 69.31 ± 2.19 | 5.75 ± 0.62 | 89.45 ± 0.22 | 13.05 ± 0.38 | 74.82 ± 2.59 | 81.42 ± 3.33 | 11.51 ± 1.09 |
| ACR | 101.20 ± 7.53 | 9.73 ± 0.20 | — | — | 90.42 ± 6.03 | — | — |
| TAC | — | — | 137.95 ± 9.04 | 44.27 ± 3.60 | — | 132.35 ± 5.91 | 37.42 ± 4.01 |
The IC50 values revealed that several compounds exhibited significant inhibitory activity against the target enzymes. Remarkably, compounds 3d, 3g, 3h, 3i, 4i, and 4j displayed the most potent effects. Compound 3d, in particular, showed outstanding inhibition of α-Glu (IC50 = 45.19 ± 0.62 nM, Ki = 41.41 ± 2.53 nM) and α-Amy (IC50 = 1.25 ± 0.02 nM), along with appreciable activity against AChE and BChE.
These findings position compound 3d as a promising multi-target inhibitor. Compounds 3g, 3h, 3i, 4i, and 4j revealed comparable potency across several enzymatic targets. Among them, compound 3i exhibited remarkable selectivity for AChE (70.81 ± 1.19 nM) and BChE (10.87 ± 1.17 nM). Compound 3g effectively inhibited BChE (19.25 ± 1.32 nM) and α-amylase (3.43 ± 0.67 nM), while 3 h showed balanced inhibition against BChE and α-glucosidase. Compounds 4i and 4j delivered the most potent effects, especially against BChE and α-amylase, evidenced by their extremely low IC50 values. In addition to the most potent candidates, other synthesized compounds, including 3a–f and 4a, 4c–4h, and 4k, also showed noteworthy inhibitory effects. Their IC50 values ranged from 6–10 nM for α-amylase and 70–100 nM for α-glucosidase. For BChE, inhibition fell between 30–50 nM, while AChE inhibition was observed in the 120–140 nM range. These results highlight the broader potential of the compound series as multi-target enzyme inhibitors. Enzyme kinetic analyses further confirmed that all compounds act through a competitive inhibition mechanism.
Based on the evaluation results, compounds 3d (α-glucosidase Ki = 41.41 ± 2.53 nM; α-amylase IC50 = 1.25 ± 0.02 nM) and 3h (α-glucosidase Ki = 44.19 ± 2.41 nM; α-amylase IC50 = 2.87 ± 0.16 nM) emerged as promising dual-action hit candidates targeting both α-glucosidase and α-amylase. In contrast, compound 3i (AChE Ki = 59.71 ± 2.24 nM; BChE Ki = 8.43 ± 0.97 nM) and compound 4i (AChE Ki = 53.31 ± 1.74 nM; BChE Ki = 10.72 ± 2.19 nM) were identified as potent hits for cholinesterase inhibition, showing strong activity against both AChE and BChE.
2.3. Molecular docking studies
Molecular docking studies were carried out to gain insight into the binding behavior and interaction profiles of key compounds with their respective target enzymes. Based on their exceptional inhibitory performance and the lowest IC50 and Ki values, compounds 3d, 3h, 3i, and 4i were selected for computational analysis. The induced fit docking (IFD) method was applied to allow for receptor flexibility and optimize docking accuracy. To quantitatively evaluate binding affinity, MM-GBSA (molecular mechanics/generalized born surface area) calculations were used to estimate the free energy of binding for each ligand–target complex.Docking simulations identified compounds 3d and 3h as top candidates for α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibition. Compound 3d exhibited docking scores of −8.112 kcal mol−1 (α-Amy) and −8.356 kcal mol−1 (α-Glu), while 3h yielded −6.072 kcal mol−1 and −8.008 kcal mol−1, respectively. MM-GBSA analysis revealed favorable binding free energies, particularly for 3h with −57.39 kcal mol−1 against α-Glu. These results are consistent with experimental IC50 values, confirming the strong dual-target potential of these compounds for diabetes management.
Targeting cholinesterases, compound 3i showed superior binding affinity, with docking scores of −10.767 kcal mol−1 (AChE) and −10.165 kcal mol−1 (BChE), along with MM-GBSA ΔG values of −69.39 and −51.84 kcal mol−1. Similarly, compound 4i demonstrated exceptional interactions, especially with AChE (−12.391 kcal mol−1; ΔG = −91.53 kcal mol−1). The strong in vitro inhibitory activity of both compounds against AChE and BChE underscores their potential as dual-action neuroprotective agents, reinforcing their development as therapeutic candidates for Alzheimer's disease.
Several other synthesized compounds showed moderate yet meaningful binding affinities. Compound 3c, for example, achieved docking scores of −4.905 kcal mol−1 (α-Amy) and −7.230 kcal mol−1 (α-Glu), guaranteed by MM-GBSA values of −41.31 and −45.42 kcal mol−1, respectively. Compound (E)-4c also performed well against α-glucosidase, with a docking score of −6.916 kcal mol−1 and a binding free energy of −40.62 kcal mol−1. For cholinesterase inhibition, tacrine exhibited moderate binding with AChE and BChE (docking scores: −7.241 and −7.132 kcal mol−1; MM-GBSA: −39.15 and −28.97 kcal mol−1). However, compounds 3i and 4i demonstrated significantly better docking and free energy profiles, suggesting superior efficacy. Although acarbose showed a strong docking score for α-amylase (−13.205 kcal mol−1), its MM-GBSA value for α-glucosidase (+3.96 kcal mol−1) was weak, indicating poor binding stability. In contrast, compound 3h exhibited better docking and MM-GBSA results for both enzymes, underscoring its broader and more effective inhibitory profile.
| Complex | PDB ID | ΔG bind | ΔG bind Coulomb | ΔG bind covalent | ΔG bind Hbond | ΔG bind lipo | ΔG bind solv GB | ΔG bind vdW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3d –α-Amy | 5E0F | −41.28 | −36.35 | −0.03 | −3.27 | −9.04 | 34.94 | −27.00 |
| 3h –α-Amy | 5E0F | −31.15 | −7.49 | 9.08 | −1.75 | −15.01 | 26.20 | −40.80 |
| 3d –α-Glu | 3WY1 | −45.09 | −36.89 | 4.84 | −2.74 | −12.14 | 39.65 | −37.32 |
| 3h –α-Glu | 3WY1 | −57.39 | −30.74 | 1.41 | −0.96 | −16.46 | 40.43 | −50.57 |
| 3i –AChE | 4EY7 | −69.39 | −13.11 | 3.91 | −1.40 | −30.51 | 25.76 | −45.82 |
| 4i –AChE | 4EY7 | −91.53 | −24.52 | 5.32 | −1.26 | −39.55 | 43.96 | −65.45 |
| 3i –BChE | 6EP4 | −51.84 | −11.11 | 0.91 | −1.53 | −23.88 | 33.26 | −45.09 |
| 4i –BChE | 6EP4 | −71.58 | −21.25 | 9.07 | −0.53 | −35.64 | 50.90 | −65.11 |
The binding analysis for α-amylase revealed that compound 3d has a high affinity (ΔG_bind = −41.28 kcal mol−1), predominantly through strong coulombic interactions (−36.35 kcal mol−1), with additional support from van der Waals (−27.00 kcal mol−1) and lipophilic (−9.04 kcal mol−1) forces. In contrast, compound 3h showed less favorable binding (−31.15 kcal mol−1), where the weaker coulombic component (−7.49 kcal mol−1) was offset by substantial van der Waals (−40.80 kcal mol−1) and lipophilic (−15.01 kcal mol−1) contributions. For α-glucosidase, both compounds showed strong binding, with 3d yielding a ΔG_bind of −45.09 kcal mol−1, dominated by coulombic (−36.89 kcal mol−1) and van der Waals (−37.32 kcal mol−1) interactions. Compound 3h surpassed this, exhibiting the highest affinity (−57.39 kcal mol−1), due to exceptional van der Waals (−50.57 kcal mol−1) and solid coulombic (−30.74 kcal mol−1) contributions, pointing to a well-balanced electrostatic and hydrophobic interaction profile.
The binding of compound 3i to AChE yields a ΔG_bind of −69.39 kcal mol−1, mainly due to van der Waals forces (−45.82 kcal mol−1) and coulombic interactions (−13.11 kcal mol−1), though solvation energy contributes positively (+25.76 kcal mol−1). Comparatively, compound 3b shows superior affinity to AChE (−91.53 kcal mol−1), with stronger coulombic (−24.52 kcal mol−1) and van der Waals (−65.45 kcal mol−1) contributions, suggesting a more robust interaction profile.
In BChE binding, 3i exhibits a ΔG_bind of −51.84 kcal mol−1, similarly dominated by van der Waals (−45.09 kcal mol−1) and coulombic (−11.11 kcal mol−1) forces. Compound 3b again stands out (−71.58 kcal mol−1), with high van der Waals (−65.11 kcal mol−1) and coulombic (−21.25 kcal mol−1) energies, reaffirming the importance of both electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions in its binding efficiency.
Overall, the robust binding of 4i to AChE and BChE, along with the high affinity of 3h for α-glucosidase, reflects the dominant influence of coulombic and van der Waals interactions. This suggests that these compounds are well-optimized for selective and potent inhibition of their target enzymes.
 | ||
| Fig. 2 Molecular docking 2D ligand protein interaction analysis on α-Glu and α-Amy. (a) 3d–α-Glu complex, (b) 3h–α-Glu complex, (c) 3d–α-Amy complex and (d) 3h–α-Amy complex. | ||
 | ||
| Fig. 3 Molecular docking 3D ligand protein interaction analysis on α-Glu and α-Amy. (a) 3d–α-Glu complex, (b) 3h–α-Glu complex, (c) 3d–α-Amy complex and (d) 3h–α-Amy complex. | ||
Fig. 2a illustrates the 2D ligand–protein interaction of compound 3d with α-glucosidase (α-Glu), whereas Fig. 2b shows the interaction of compound 3h with the same enzyme. Compound 3d establishes hydrogen bonds with the active site residues Asp-202 and Glu-271. In contrast, compound 3h forms a total of four hydrogen bonds: two with Asp-202, and one each with His-332 and Asp-333. Notably, in both complexes, the ketone oxygen participates in hydrogen bonding with Asp-202; however, compound 3h demonstrates additional interactions through its urea moiety, enhancing its binding affinity.
Fig. 2c and d illustrate how compounds 3d and 3h interact with α-amylasein 2D binding diagrams. Compound 3d forms four hydrogen bonds: one each with Asn-197 and Glu-233, and two with Asp-300. Compound 3h also forms four hydrogen bonds, including one with Asp-300, which is a shared interaction in both ligands. The thiourea group plays a key role in binding to Asp-300 in both cases. Additionally, 3h forms bonds with Gln-63 and His-305. The IC50 values obtained from α-Amy inhibition tests were 1.25 nM for 3d and 2.87 nM for 3h, emphasizing the importance of hydrogen bonding in enzyme inhibition.
The 3D binding conformations of compounds 3d and 3h with α-glucosidase and α-amylase are presented in Fig. 3a–d. Specifically, Fig. 3a and b display their interactions with α-Glu, while Fig. 3c and d illustrate the α-Amy complexes. Yellow dashed lines identify hydrogen bond formations. The grayish surface corresponds to the protein binding site, and the bluish surface delineates the ligand's spatial fit. Enhanced overlap between these surfaces suggests a more favorable ligand orientation and stronger binding affinity.
As shown in Fig. 3a, compound 3d forms two strong hydrogen bonds with α-Glu, both measuring 1.97 Å. In contrast, compound 3h exhibits slightly longer hydrogen bonds ranging from 2.10 Å to 2.57 Å (Fig. 3b). For both compounds, the near-complete overlap between ligand and protein binding surfaces indicates excellent fit within α-Glu. In Fig. 3c, the 3d–α-Amy complex forms hydrogen bonds of 1.90 Å, 1.94 Å, and 2.32 Å. However, the thiourea moiety protrudes outside the binding surface. Similarly, in Fig. 3d, the 3h–α-Amy complex features hydrogen bonds ranging from 1.61 Å to 2.65 Å, with part of the thiourea group and a segment of a five-membered ring on the protein lying beyond the binding site. Despite this, both ligands retain inhibitory efficacy, mainly due to hydrogen bonding with the key Asp-300 residue.
 | ||
| Fig. 4 Molecular docking 2D ligand protein interaction analysis on AChE and BChE. (a) 3i-AChE complex, (b) 4i-AChE complex, (c) 3i-BChE complex, and (d) 4i-BChE complex. | ||
 | ||
| Fig. 5 Molecular docking 3D ligand protein interaction analysis on AChE and BChE. (a) 3i-AChE complex, (b) 4i–AChE complex, (c) 3i–BChE complex, and (d) 4i-BChE complex. | ||
As shown in Fig. 4a, compound 3i forms four hydrogen bonds with Arg-296 and Ser-293, and three π–π stacking interactions with Tyr-341 and Tyr-72 in its complex with AChE. In Fig. 4b, compound 4i interacts via three hydrogen bonds (with Tyr-124 and Phe-295) and three π–π interactions (with Tyr-341, Phe-338, and Trp-286). The strong interaction of 3i is reflected in a calculated ΔG of −91.53 kcal mol−1 and a docking score of −12.391 kcal mol−1, while 4i also shows considerable binding affinity through its multi-point interactions with the AChE active site.
In Fig. 4c, compound 3i forms three hydrogen bonds with Thr-120 and Trp-82via its thio-urea group in the BChE binding pocket. On the other hand, compound 4i (Fig. 4d) forms a hydrogen bond with Glu-197 and a π–π stacking interaction with Tyr-440. The binding energy (ΔG) for 4i is −71.58 kcal mol−1, reflecting strong and stable interaction at the BChE active site. While both compounds show similar docking scores, the energy profile indicates that compound 4i achieves a more favorable binding interaction than compound 3i.
The 3D binding orientations of 3i and 4i within AChE are illustrated in Fig. 5a and b, respectively. In all representations, hydrogen bonds are shown as yellow dashed lines, while π–π stacking interactions are denoted by turquoise lines. The gray cloud represents the protein surface, and the blue cloud denotes the ligand surface. For the 3i–AChE complex (Fig. 5a), hydrogen bonds range from 1.85 to 2.77 Å, and π–π stacking occurs at distances between 3.73 and 5.34 Å. The close alignment of the ligand within the protein's surface suggests strong binding. Similarly, in 4i–AChE (Fig. 5b), hydrogen bond lengths are 2.01, 2.17, and 2.71 Å, and π–π stacking occurs at 3.96 to 5.21 Å, indicating another well-fitting interaction. The 3D binding pose of compound 3i with BChE (Fig. 5c) shows hydrogen bond interactions with distances between 1.77 and 2.22 Å. In Fig. 5d, the 4i–BChE complex reveals a hydrogen bond of 2.12 Å and a π–π stacking interaction at 4.73 Å. A portion of the trifluoromethyl group in 3i and the thiazolidine ring in 4i extend beyond the protein's surface area, suggesting partial solvent exposure and peripheral positioning within the binding site.
In summary, compound 4i is the most promising cholinesterase inhibitor identified in this study, supported by its outstanding docking score (−12.391 kcal mol−1) and ΔG bind. (−91.53 kcal mol−1) for AChE, and robust binding to BChE (docking score: −9.313 kcal mol−1; ΔG: – 71.58 kcal mol−1). This strong affinity is facilitated by interactions with essential residues including Glu-199, Ser-203, His-447 (AChE) and Ser-198, Trp-82, Phe-329 (BChE). Compound 3i also showed high affinity, particularly with AChE (glide score: −10.767; ΔG: −69.39 kcal mol−1) and BChE (−10.165; ΔG: −51.84 kcal mol−1), involving the same set of key residues. Additionally, compound 3h presents a compelling case as a dual-target agent, exhibiting moderate inhibition of α-amylase (glide score: −6.072 kcal mol−1; ΔG: −31.15 kcal mol−1) through interactions with Glu-233, Gln-63, and Asp-197, thus potentially offering antidiabetic as well as cholinesterase inhibitory effects.
2.4. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations
Stability and dynamic behavior of the ligand–protein complexes were analyzed via 500 ns MD simulations performed on eightsystems: 3d/3h–α-Amy, 3d/3h–α-Glu, 3i/4i–AChE, and 3i/4i–BChE. RMSD values tracked overall structural stability, while RMSF values assessed residue-level flexibility throughout the simulation period. Results are presented in Fig. 6–13.Fig. 6b presents the RMSD plots of protein Cα atoms and ligand atoms. The average RMSD of protein Cα atoms was 1.2 Å (blue), indicating high structural stability, whereas the ligand atoms exhibited an average RMSD of 2.8 Å (red). The ligand's deviation relative to its starting position was only 0.5 Å (pink), suggesting that the binding orientation of 3d remained well conserved within the active site. Fig. 6c and d show the RMSF values of protein residues and ligand atoms, respectively. The average RMSF of protein Cα atoms was 0.75 Å, while that of the ligand was 0.6 Å. Both values are notably low, reflecting a stable and rigid complex during the 500 ns simulation. Fig. 6e displays the fraction of the interaction histogram, where green bars represent hydrogen bonds, blue bars indicate water-mediated hydrogen bonds, and purple bars correspond to hydrophobic interactions. The analysis highlights Arg-200, Glu-271, Arg-400, Asp-62, Ile-146 as the key residues contributing to stable binding interactions with compound 3d.
Fig. 7a shows the 2D ligand–protein interaction map of the 3h–αGlu complex throughout the 500 ns trajectory. The sulfur atom of 3h formed a strong hydrogen bond with Arg-400 (83% of the simulation time). The thiosemicarbazone nitrogens interacted separately with Asp-202 (69% and 48% of the sim.), and the isatin carbonyl oxygen formed a hydrogen bond with Thr-203 (39% of the sim.). An intramolecular hydrogen bond between the carbonyl oxygen and the thiosemicarbazone nitrogen created a five-membered ring, contributing to the conformational stability of the ligand. Fig. 7b presents the RMSD plots of protein Cα atoms and ligand atoms. The average RMSD of protein Cα was 1.2 Å, the ligand RMSD was 1.5 Å, and the ligand's deviation relative to its initial position was 0.5 Å, indicating a stable binding orientation. Fig. 7c and d show RMSF values of protein residues and ligand atoms, respectively. The protein Cα RMSF was 0.9 Å, and the ligand RMSF was 1.0 Å, suggesting moderate flexibility but overall stable interactions. Fig. 7e displays the fraction of the interaction histogram, highlighting hydrogen bonds (green), water-mediated hydrogen bonds (blue), and hydrophobic contacts (purple). Key residues involved in ligand binding are Asp-202, Arg-400, Thr-203, Phe-297, and Tyr-389.
The 500 ns MD simulations indicate that both 3d- and 3h-αGlu complexes are stable, with shared key residues Arg-400 contributing to ligand binding. Compound 3d forms additional interactions with Arg-200, Glu-271, Asp-62, and His-332, while 3h interacts uniquely with Asp-202, Thr-203, Phe-297, and Tyr-389. RMSD and RMSF analyses show that 3d exhibits slightly lower fluctuations and greater rigidity than 3h, suggesting that 3d–αGlu is the more stable complex overall. Hydrogen bonds, water-mediated H-bonds, and hydrophobic contacts dominate in both complexes, supporting strong binding affinity.
Fig. 9 depicts the 500 ns MD simulation analysis of 3h-αAmy complex. Fig. 9a shows that compound 3h maintained multiple interactions throughout the simulation, supporting complex stability.
In Fig. 9a, the thiosemicarbazone–NH2 group formed two hydrogen bonds with Asp-300 (100% and 78% of the simulation time), while an additional H-bond was observed between thiosemicarbazone –HN and Asp-300 (33% of the sim.) and a water-bridged H-bond between the isatin carbonyl oxygen and Asp-300 (74% of the sim.). Thus, Asp-300 emerged as the key anchoring residue. Moreover, the –NH2 group interacted with His-405 (44% of the sim.), and the sulfur atom formed water-mediated H-bonds with Trp-59 (56% of the sim.) and Asp-357 (85% of the sim.). A strong π–π stacking interaction was also observed between the benzene ring and Trp-59 (89% of the sim.). Fig. 9b displays RMSD profiles, with average values of 1.1 Å for protein Cα (blue), 3.75 Å for the ligand (red), and 0.7 Å ligand deviation from its starting pose (pink), indicating that the protein backbone remained highly stable throughout the simulation, while the ligand exhibited moderate flexibility within the binding pocket. Fig. 9c and d show average RMSF values of 0.8 Å for protein residues and 1.5 Å for the ligand, indicating low protein fluctuations and moderate ligand flexibility. Fig. 9e highlights three key residues stabilizing the complex: Asp-300, Trp-59, and Asp-357, with Asp-300 being the most dominant.
The α-Amy MD simulations demonstrated that both 3d and 3h formed stable complexes with the enzyme. In the 3d–αAmy complex, stability was supported by persistent H-bonds with Asp-197 and Asp-300, together with π–π stacking involving His-101. In contrast, 3h–αAmy was dominated by multiple strong and long-lasting interactions with Asp-300, supplemented by π–π stacking and water-mediated H-bonds with Trp-59 and Asp-357. The RMSD and RMSF profiles confirmed high protein backbone stability for both complexes, with 3d showing tighter ligand stability, while 3h exhibited greater flexibility but stronger anchoring via Asp-300.
For the diabetic target enzymes, MD simulations indicate enzyme-specific inhibitor preferences. Compound 3d formed strong and stable interactions with key residues Arg-200, Glu-271, and Asp-62 in α-glucosidase, reflected by low RMSD and RMSF values, making it the more stable and effective inhibitor for this enzyme. Conversely, compound 3h established multiple high-occupancy hydrogen bonds with Asp-300 and π–π stacking with Trp-59 in α-amylase, demonstrating superior anchoring and inhibitory potential compared to 3d.
An intramolecular hydrogen bond between the thiosemicarbazone –NH and the isatin carbonyl (86% of the sim.) creates a five-membered ring, stabilizing the ligand conformation and reducing fluctuations. The isatin carbonyl also interacts with Arg-296 (31% of the sim.). π–π stacking interactions occur between the benzene ring and Trp-286 (78% of the sim.) and between the benzyl ring and Tyr-341 (37% of the sim.). Fig. 10b presents RMSD plots: protein Cα averages 1.5 Å, ligand RMSD 1.5 Å, and ligand deviation relative to its starting pose is 0.7 Å, indicating overall stable binding. Fig. 10c and d show RMSF values, with protein RMSF 0.9 Å and ligand RMSF 1.5 Å, reflecting moderate ligand flexibility and stable protein backbone. Fig. 10e displays the fraction of interactions, highlighting Trp-286, Ser-293, and Tyr-341 as key residues, with additional contributions from Gln-291, Arg-296, and Phe-338.
Fig. 11a shows the 2D ligand–protein interactions of 4i–AChE complex. Multiple π–π stacking and hydrogen bond interactions stabilize the complex. Trp-286 interacts with the benzyl ring (84% of the sim.) and isatin ring (69% of the sim.) via π–π stacking, while Tyr-341 forms π–π interactions with the isatin ring (34% of the sim.) and thiazole ring (32% of the sim.). The thiazole ring also stacks with Phe-338 (43% of the sim.). The isatin carbonyl oxygen forms a strong hydrogen bond with Phe-295 (99% of the sim.), and the thiosemicarbazone imine nitrogen interacts with Tyr-124 (38%). Fig. 11b presents RMSD plots: protein Cα averages 1.5 Å, ligand RMSD 1.5 Å, and ligand deviation from its initial position is 0.6 Å, indicating stable binding. Fig. 11c and d show RMSF values, with protein Cα RMSF 0.9 Å and ligand RMSF 1.0 Å, confirming moderate ligand flexibility and stable protein structure. Fig. 11e displays the fraction of interactions, highlighting Trp-286 as the dominant residue, with notable contributions from Tyr-124, Tyr-337, and Tyr-439.
The 500 ns MD simulations of 3i–AChE and 4i–AChE complexes demonstrate stable ligand binding within the enzyme active site. In the 3i–AChE complex, persistent hydrogen bonds with Gln-291, Ser-293, and Arg-296, along with an intramolecular hydrogen bond forming a five-membered ring, stabilized the ligand conformation. π–π stacking interactions with Trp-286 and Tyr-341 further reinforced binding, with moderate ligand flexibility (RMSD 1.5 Å, RMSF 1.5 Å). In contrast, 4i–AChE showed stronger π–π stacking interactions with Trp-286, Tyr-341, and Phe-338, and a highly stable hydrogen bond with Phe-295 (99%), while maintaining moderate ligand flexibility (RMSD 1.5 Å, RMSF 1.0 Å). Overall, 4i exhibits slightly stronger anchoring and more extensive π–π interactions, suggesting superior inhibitory potential against AChE compared to 3i.
Fig. 12b presents RMSD profiles: average protein Cα RMSD is 1.2 Å (pale blue), ligand RMSD is 2.0 Å, and ligand deviation from its initial pose is 0.8 Å, indicating stable protein backbone and moderate ligand flexibility. Fig. 12c and d show RMSF values, with protein Cα RMSF 0.9 Å and ligand RMSF 1.5 Å, reflecting low protein fluctuations and moderate ligand mobility. Fig. 12e displays the fraction of interactions, highlighting Trp-82, Ser-79, Tyr-332, and Asp-70 as key residues stabilizing the complex.
Fig. 13a shows the 2D ligand–protein interactions of 4i-BChE complex. The benzyl ring forms a π–π stacking interaction with Trp-82 (81%), while the thiazole ring stacks with Phe-329 (78%). The isatin carbonyl oxygen forms a strong and persistent hydrogen bond with Glu-197 (99%). Additionally, the ketone oxygen in the side chain engages in two water-bridged hydrogen bonds with Ser-287 (30%) and Pro-285 (32%). Fig. 13b presents RMSD plots: average protein Cα RMSD is 1.4 Å, ligand RMSD is 1.1 Å, and ligand deviation from its initial position is 0.6 Å, indicating stable binding. Fig. 13c and d show RMSF values, with protein Cα RMSF 0.8 Å and ligand RMSF 0.9 Å, reflecting low protein fluctuations and moderate ligand stability. Fig. 13e displays the fraction of interactions, highlighting Trp-82 as the dominant residue, with notable contributions from Glu-197 and Phe-329.
MD simulations of 3i–BChE and 4i–BChE complexes indicate stable ligand binding within the enzyme active site. In the 3i–BChE complex, persistent hydrogen bonds with Asp-70, Ser-79, and Trp-82, along with an intramolecular hydrogen bond and π–π stacking with Phe-329 and Tyr-332, stabilized the ligand, although moderate ligand flexibility was observed (RMSD 2.0 Å, RMSF 1.5 Å). In contrast, the 4i–BChE complex exhibited stronger and more permanent interactions, including a hydrogen bond with Glu-197 (99%) and π–π stacking with Trp-82 and Phe-329, supplemented by water-bridged hydrogen bonds with Ser-287 and Pro-285. Ligand flexibility was lower in 4i (RMSD 1.1 Å, RMSF 0.9 Å), indicating tighter anchoring. Overall, 4i demonstrates superior binding stability and interaction profile compared to 3i, suggesting enhanced inhibitory potential against BChE.
2.5. ADME prediction
Understanding a drug's ADME properties—absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion, is fundamental to predicting its performance in vivo. Using computational tools to estimate these parameters helps identify promising drug candidates early, saving time and resources. Key features like oral bioavailability, solubility, and the ability to cross the blood–brain barrier are evaluated in silico. The results of these predictions are provided in Table 4.| Title | CNS | Ro5 | Ro3 | % HOA | QPPCaco | QPPMDCK | QPlogBB | QPlogPo/w | QPlogS | aHB | dHB | MW | RB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tac: tacrine, Acr: acarbose, CNS: predicted CNS activity (−2 to +2). Ro5: Lipinski′s rule violations. Ro3: Jorgensen′s rule violations. % HOA: predicted human oral absorption. QPPCaco: Caco-2 cell permeability. QPPMDCK: MDCK cell permeability. QPlogBB: brain/blood partition coefficient. QPlogPo/w: octanol/water partition coefficient. QPlogS: aqueous solubility. aHB: H-bond acceptors. dHB: H-bond donors. MW: molecular weight 130–725. | |||||||||||||
| 3a | −1 | 0 | 0 | 76 | 238 | 660 | −0.736 | 1.116 | −3.25 | 5 | 3 | 254.69 | 2 |
| 3b | 0 | 0 | 0 | 91 | 624 | 1868 | −0.532 | 2.392 | −4.245 | 6 | 2 | 296.77 | 4 |
| 3c | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 711 | 2152 | −0.496 | 3.293 | −4.903 | 6 | 2 | 344.82 | 4 |
| 3d | −1 | 0 | 0 | 74 | 238 | 268 | −0.969 | 0.824 | −2.841 | 6 | 3 | 250.28 | 3 |
| 3e | −1 | 0 | 0 | 89 | 622 | 756 | −0.772 | 2.022 | −3.786 | 6 | 2 | 292.36 | 5 |
| 3f | −1 | 0 | 0 | 95 | 711 | 873 | −0.736 | 2.923 | −4.618 | 6 | 2 | 340.40 | 5 |
| 3g | −1 | 0 | 0 | 80 | 238 | 1243 | −0.72 | 1.716 | −3.881 | 5 | 3 | 304.25 | 4 |
| 3h | 0 | 0 | 0 | 95 | 620 | 3500 | −0.507 | 3.035 | −4.92 | 5 | 2 | 346.33 | 1 |
| 3i | 0 | 0 | 1 | 100 | 710 | 4049 | −0.47 | 3.877 | −5.716 | 5 | 2 | 394.37 | 6 |
| 4a | 0 | 0 | 0 | 93 | 720 | 1476 | −0.425 | 2.495 | −4.387 | 5 | 2 | 292.74 | 6 |
| (Z) 4b | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 720 | 4155 | −0.17 | 3.802 | −5.456 | 6 | 1 | 334.82 | 3 |
| (E) 4b | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 1800 | 4097 | −0.181 | 3.764 | −5.419 | 6 | 1 | 334.82 | 3 |
| (E) 4c | 0 | 0 | 1 | 100 | 2073 | 4771 | −0.128 | 4.671 | −6.241 | 5 | 1 | 382.87 | 3 |
| (Z) 4c | 0 | 0 | 1 | 100 | 1763 | 3723 | −0.222 | 4.642 | −6.283 | 5 | 1 | 382.87 | 3 |
| 4d | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 1516 | 2320 | −0.422 | 4.263 | −4.927 | 7 | 0 | 438.93 | 5 |
| 4e | 0 | 0 | 0 | 91 | 720 | 599 | −0.665 | 2.135 | −3.951 | 5 | 2 | 288.32 | 2 |
| 4f | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 1881 | 1688 | −0.407 | 3.262 | −4.779 | 6 | 1 | 330.40 | 4 |
| 4g | −1 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 1931 | 1720 | −0.467 | 3.918 | −4.139 | 8 | 0 | 434.51 | 6 |
| (E) 4h | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 2152 | 2015 | −0.344 | 4.285 | −5.681 | 6 | 1 | 378.45 | 4 |
| (Z) 4h | 0 | 0 | 1 | 100 | 1798 | 1537 | −0.446 | 4.232 | −5.701 | 6 | 1 | 378.45 | 4 |
| 4i | −1 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 1931 | 1720 | −0.467 | 3.918 | −4.139 | 8 | 0 | 434.51 | 6 |
| 4j | 0 | 0 | 1 | 100 | 1335 | 4490 | −0.458 | 4.509 | −5.795 | 7 | 0 | 440.44 | 7 |
| 4k | 0 | 1 | 1 | 100 | 1013 | 4030 | −0.515 | 5.08 | −6.109 | 7 | 0 | 488.48 | 7 |
| TAC* | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 2926 | 1579 | 0.039 | 2.572 | −3.095 | 2 | 1 | 198.26 | 0 |
| ACR* | −2 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0.019 | 0.004 | −6.691 | −8.624 | 1.501 | 38 | 16 | 791.75 | 9 |
Tacrine is predicted to have moderate CNS activity (CNS = +1), aligning with its known effects in treating Alzheimer's disease. In contrast, the majority of the synthesized compounds show no CNS activity (CNS = 0), making them more appropriate for peripheral nervous system targets. Most synthesized molecules meet all of Lipinski's rule of five criteria (Ro5 = 0), implying strong potential for oral administration, while tacrine fails one criterion. Jorgensen's rule of three highlights tacrine's poor solubility (Ro3 = 2), whereas most test compounds demonstrate better solubility (Ro3 = 0).
The predicted human oral absorption rates (%HOA) formany synthesized compounds are high (up to 100%), unlike acarbose, which is poorly absorbed (0%) and acts locally. Tacrine shows high permeability (QPPCaco = 2926), and many new compounds also show promising values in this regard. CNS permeability, reflected by QPlogBB, is evident for tacrine, while compounds like 3a, 4a, and 3d show negative values, indicating little to no brain penetration. Tacrine's favorable QPlogPo/w and QPlogS values suggest good lipophilicity and solubility for BBB crossing, while synthesized compounds tend to be more hydrophilic—beneficial for solubility but possibly limiting their membrane permeability. Notably, compounds such as 4a and 3b have higher hydrogen bonding capacities, which may enhance solubility while possibly compromising permeability compared to tacrine.
Detailed ADME profiling of the lead compounds—3d, 3h, 3i, and 4i—highlights favorable pharmacokinetics with peripheral targeting potential. Compound 3d displays moderate oral absorption (74%) and permeability (QPPCaco = 238), but limited CNS penetration (QPlogBB = −0.736). While compliant with Lipinski's rules, its bioavailability could be hindered by low solubility (QPlogS = −3.25).
Compound 3h offers a better pharmacokinetic profile with high oral absorption (95%) and permeability (QPPCaco = 620), and acceptable lipophilicity. However, the QPlogBB of −0.507 implies poor BBB penetration, and its low solubility (QPlogS = −4.92) may restrict formulation. Compound 3i is particularly notable for its perfect absorption rate and outstanding permeability, both intestinal (QPPCaco = 710) and cellular (QPPMDCK = 4049). Despite this, its low solubility (QPlogS = −5.716) could be problematic. Compound 4i also excels in absorption (100%) and permeability (QPPCaco = 1931), with minimal CNS access (QPlogBB = −0.467), reinforcing its peripheral activity profile, though solubility (QPlogS = −4.139) remains a concern. Collectively, these compounds exhibit excellent absorption and permeability characteristics suitable for peripheral applications, with solubility emerging as the primary optimization parameter.
3. Experimental section
3.1. General
Melting points were measured without correction using a Stuart melting point apparatus (Stuart Scientific, UK). Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra were recorded on a Bruker spectrophotometer operating at 400 MHz for 1H and 100 MHz for 13C. Spectra acquisition was performed at the Faculty of Science, Sohag University, Sohag, Egypt, and the NMR facility at the Faculty of Pharmacy, Mansoura University, Mansoura, Egypt. Chemical shifts (δ) are reported in parts per million (ppm) relative to tetramethylsilane (TMS, 0.05% v/v) as the internal standard. Coupling constants (J) are given in hertz (Hz), and the signal multiplicities are designated as follows: singlet (s), doublet (d), triplet (t), quartet (q), and multiplet (m). Deuterated solvents dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO-d6) and chloroform (CDCl3) were used. All compounds were dissolved in DMSO-d6, except for compound 4i, which was prepared in CDCl3. Elemental analyses were conducted at the Regional Centre for Mycology and Biotechnology, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt. High-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) spectra were obtained using the electrospray ionization (ESI) technique on a Thermo Fisher Scientific Q Exactive™ Hybrid Quadrupole-Orbitrap™ instrument. HPLC chromatograms were recorded using the waters preparative HPLC and PDA detector.3.2. Chemistry
The synthesis and characterization of intermediates 3(a–i) have been previously described.12,13 Mass spectra and HPLC purity of compounds 3d, 3h and 3i were performed.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) MeOH (1
MeOH (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1), Rt: 3.99 min, 95.35%.
1), Rt: 3.99 min, 95.35%.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) MeOH (1
MeOH (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1), Rt: 3.03 min, 96.98%.
1), Rt: 3.03 min, 96.98%.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) MeOH (1
MeOH (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1), Rt: 3.85 min, 96.14%.
1), Rt: 3.85 min, 96.14%.
3.3. General procedure for the synthesis of compounds 4(a–k)
A solution of 2-oxoindolin-3-(Z)-thiosemicarbazone derivatives 3(a–i) (1 mmol), chloroacetone (1 mmol), and anhydrous sodium acetate (2 mmol) in ethanol (30 mL) was refluxed for 24 hours. After completion of the reaction, the mixture was poured onto crushed ice, resulting in the precipitation of the product. The solid was collected by filtration, washed, and dried to give orange to red compounds. Purification of the crude products was carried out using recrystallization from ethanol and column chromatography, isolating either pure diastereomers or E/Z isomeric mixtures using an n-hexane/ethyl acetate gradient as the eluent system. ). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 178.87 (C
). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 178.87 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 165.63 (thiazole C
O), 165.63 (thiazole C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 141.05 (indole C
N), 141.05 (indole C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 140.29 (C5), 137.39 (C4), 128.89 (C10), 125.40 (C6), 125.21 (C7a), 120.74 (C3a), 110.94 (C7), 101.71 (C11), 13.73 (C10a). Elemental analysis: calculated for C12H9ClN4OS: C, 49.24; H, 3.10; N, 19.14; S, 10.95. Found: C, 49.05; H, 3.07; N, 19.00; S, 10.92.
N), 140.29 (C5), 137.39 (C4), 128.89 (C10), 125.40 (C6), 125.21 (C7a), 120.74 (C3a), 110.94 (C7), 101.71 (C11), 13.73 (C10a). Elemental analysis: calculated for C12H9ClN4OS: C, 49.24; H, 3.10; N, 19.14; S, 10.95. Found: C, 49.05; H, 3.07; N, 19.00; S, 10.92.
 ), 2.25 (s, 3H,
), 2.25 (s, 3H,  ), 1.65 (p, J = 7.3 Hz, 2H,
), 1.65 (p, J = 7.3 Hz, 2H, 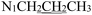 ), 0.90 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H,
), 0.90 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H, 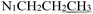 ). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 177.62 (C
). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 177.62 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 164.18 (thiazole C
O), 164.18 (thiazole C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 154.81 (indole C
N), 154.81 (indole C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 137.99 (C5), 136.14 (C13), 135.52 (C4), 114.13 (C6), 113.24 (C7a), 108.60 (C3a), 104.92 (C7), 101.07 (C14), 40.52 (C8), 20.61 (C9), 13.74 (C13a), 11.18 (C10). Elemental analysis: calculated for C15H15ClN4OS: C, 53.81; H, 4.52; N, 16.73; S, 9.58. Found: C, 54.03; H, 4.35; N, 16.52; S, 9.41.
N), 137.99 (C5), 136.14 (C13), 135.52 (C4), 114.13 (C6), 113.24 (C7a), 108.60 (C3a), 104.92 (C7), 101.07 (C14), 40.52 (C8), 20.61 (C9), 13.74 (C13a), 11.18 (C10). Elemental analysis: calculated for C15H15ClN4OS: C, 53.81; H, 4.52; N, 16.73; S, 9.58. Found: C, 54.03; H, 4.35; N, 16.52; S, 9.41.
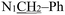 ), 2.19 (d, J = 1.3 Hz, 3H,
), 2.19 (d, J = 1.3 Hz, 3H, 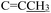 ). (Z, 33%): δ 13.14 (s, 1H, N16H), 7.54 (d, J = 2.1 Hz, 1H, C4H), 7.40–7.22 (m, 6H, Ph protons and C6H), 7.06 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H, C7H), 6.81 (s, 1H, C18H), 5.02 (s, 2H,
). (Z, 33%): δ 13.14 (s, 1H, N16H), 7.54 (d, J = 2.1 Hz, 1H, C4H), 7.40–7.22 (m, 6H, Ph protons and C6H), 7.06 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H, C7H), 6.81 (s, 1H, C18H), 5.02 (s, 2H, 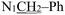 ), 2.26 (d, J = 1.3 Hz, 3H,
), 2.26 (d, J = 1.3 Hz, 3H, 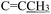 ). 13C NMR (E) (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 178.64 (C
). 13C NMR (E) (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 178.64 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 164.03 (thiazole C
O), 164.03 (thiazole C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 140.20 (indole C
N), 140.20 (indole C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 137.68 (C5), 136.62 (C4), 129.14 (C17), 128.65 (C10), 128.65 (C14), 128.46 (C6), 127.18 (C11), 127.18 (C13), 127.12 (C9), 126.00 (C7a), 125.93 (C12), 125.39 (C3a), 110.09 (C7), 101.63 (C18), 42.45 (C8), 13.37 (C17a). Elemental analysis: calculated for C19H15ClN4OS: C, 59.61; H, 3.95; N, 14.63; S, 8.37. Found: C, 59.11; H, 3.90; N, 14.33; S, 8.07.
N), 137.68 (C5), 136.62 (C4), 129.14 (C17), 128.65 (C10), 128.65 (C14), 128.46 (C6), 127.18 (C11), 127.18 (C13), 127.12 (C9), 126.00 (C7a), 125.93 (C12), 125.39 (C3a), 110.09 (C7), 101.63 (C18), 42.45 (C8), 13.37 (C17a). Elemental analysis: calculated for C19H15ClN4OS: C, 59.61; H, 3.95; N, 14.63; S, 8.37. Found: C, 59.11; H, 3.90; N, 14.33; S, 8.07.
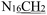 ), 4.96 (s, 2H,
), 4.96 (s, 2H, 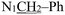 ), 2.34 (s, 3H,
), 2.34 (s, 3H, 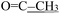 ), 2.21 (d, J = 1.3 Hz, 3H,
), 2.21 (d, J = 1.3 Hz, 3H, 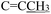 ). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 200.82 (
). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 200.82 (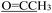 ), 176.24 (C
), 176.24 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 164.15 (thiazole C
O), 164.15 (thiazole C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 140.67 (indole C
N), 140.67 (indole C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 140.20 (C5), 137.48 (C17), 136.62 (C4), 136.44 (C6), 128.65 (C10), 128.65 (C14), 127.36 (C9), 127.18 (C11), 127.18 (C13), 125.13 (C7a), 118.89 (C12), 118.48 (C3a), 110.34 (C7), 102.13 (C18), 54.77 (C19), 42.45 (C8), 27.49 (C20), 13.64 (C17a). Elemental analysis: calculated for C22H19ClN4O2S: C, 60.20; H, 4.36; N, 12.76; S, 7.30. Found: C, 60.27; H, 3.92; N, 12.66; S, 6.98.
N), 140.20 (C5), 137.48 (C17), 136.62 (C4), 136.44 (C6), 128.65 (C10), 128.65 (C14), 127.36 (C9), 127.18 (C11), 127.18 (C13), 125.13 (C7a), 118.89 (C12), 118.48 (C3a), 110.34 (C7), 102.13 (C18), 54.77 (C19), 42.45 (C8), 27.49 (C20), 13.64 (C17a). Elemental analysis: calculated for C22H19ClN4O2S: C, 60.20; H, 4.36; N, 12.76; S, 7.30. Found: C, 60.27; H, 3.92; N, 12.66; S, 6.98.
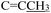 ). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 177.21 (C
). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 177.21 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 165.85 (thiazole C
O), 165.85 (thiazole C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 154.43 (indole C
N), 154.43 (indole C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 138.97 (C5), 135.57 (C4), 134.85 (C10), 118.88 (C6), 114.73 (C7a), 112.97 (C3a), 109.72 (C7), 100.88 (C11), 55.62 (C5a), 13.78 (C10a). Elemental analysis: calculated for C13H12N4O2S: C, 54.16; H, 4.20; N, 19.43; S, 11.12. Found: C, 54.00; H, 4.22; N, 19.02; S, 10.99.
N), 138.97 (C5), 135.57 (C4), 134.85 (C10), 118.88 (C6), 114.73 (C7a), 112.97 (C3a), 109.72 (C7), 100.88 (C11), 55.62 (C5a), 13.78 (C10a). Elemental analysis: calculated for C13H12N4O2S: C, 54.16; H, 4.20; N, 19.43; S, 11.12. Found: C, 54.00; H, 4.22; N, 19.02; S, 10.99.
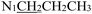 ), 2.25 (s, 3H,
), 2.25 (s, 3H, 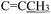 ), 1.65 (p, J = 7.3 Hz, 2H,
), 1.65 (p, J = 7.3 Hz, 2H, 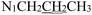 ), 0.90 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H,
), 0.90 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H, 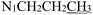 ). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 177.62 (C
). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 177.62 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 164.18 (thiazole C
O), 164.18 (thiazole C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 154.81 (indole C
N), 154.81 (indole C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 137.99 (C5), 136.14 (C13), 135.52 (C4), 114.13 (C6), 113.24 (C7a), 108.60 (C3a), 104.92 (C7), 101.07 (C14), 55.70 (C5a), 40.52 (C8), 20.61 (C9), 13.74 (C13a), 11.18 (C10). Elemental analysis: calculated for C16H18N4O2S: C, 58.16; H, 5.49; N, 16.96; S, 9.70. Found: C, 58.00; H, 5.35; N, 16.90; S, 9.40.
N), 137.99 (C5), 136.14 (C13), 135.52 (C4), 114.13 (C6), 113.24 (C7a), 108.60 (C3a), 104.92 (C7), 101.07 (C14), 55.70 (C5a), 40.52 (C8), 20.61 (C9), 13.74 (C13a), 11.18 (C10). Elemental analysis: calculated for C16H18N4O2S: C, 58.16; H, 5.49; N, 16.96; S, 9.70. Found: C, 58.00; H, 5.35; N, 16.90; S, 9.40.
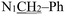 ), 3.77 (s, 3H, OCH3), 2.26 (s, 3H,
), 3.77 (s, 3H, OCH3), 2.26 (s, 3H, 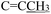 ). (Z, 50%) δ 12.49 (s, 1H, N16H), 7.40–7.25 (m, 6H, Ph protons and C4H), 6.96 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, 1H, C6H), 6.81 (d, J = 2.9 Hz, 1H, C7H), 6.40 (d, J = 1.4 Hz, 1H, C18H), 4.92 (s, 2H,
). (Z, 50%) δ 12.49 (s, 1H, N16H), 7.40–7.25 (m, 6H, Ph protons and C4H), 6.96 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, 1H, C6H), 6.81 (d, J = 2.9 Hz, 1H, C7H), 6.40 (d, J = 1.4 Hz, 1H, C18H), 4.92 (s, 2H, 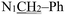 ), 3.74 (s, 3H, OCH3), 2.20 (s, 3H,
), 3.74 (s, 3H, OCH3), 2.20 (s, 3H, 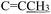 ). 13C NMR (E) (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 178.64 (C
). 13C NMR (E) (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 178.64 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 164.36 (thiazole C
O), 164.36 (thiazole C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 155.02 (indole C
N), 155.02 (indole C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 136.99 (C5), 135.58 (C4), 128.72 (C17), 128.61 (C10), 128.61 (C14), 127.58 (C6), 127.22 (C11), 127.22 (C13), 127.36 (C9), 127.27 (C7a), 113.96 (C12), 113.17 (C3a), 109.03(C7), 101.63 (C18), 55.68 (C5a) 42.43(C8), 13.76 (C17a). Elemental analysis: calculated for C20H18N4O2S: C, 63.47; H, 4.79; N, 14.80; S, 8.47. Found: C, 63.18; H, 4.75; N, 14.78; S, 8.41.
N), 136.99 (C5), 135.58 (C4), 128.72 (C17), 128.61 (C10), 128.61 (C14), 127.58 (C6), 127.22 (C11), 127.22 (C13), 127.36 (C9), 127.27 (C7a), 113.96 (C12), 113.17 (C3a), 109.03(C7), 101.63 (C18), 55.68 (C5a) 42.43(C8), 13.76 (C17a). Elemental analysis: calculated for C20H18N4O2S: C, 63.47; H, 4.79; N, 14.80; S, 8.47. Found: C, 63.18; H, 4.75; N, 14.78; S, 8.41.
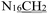 ), 4.92 (s, 2H,
), 4.92 (s, 2H, 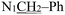 ), 3.75 (s, 3H, OCH3), 2.28 (s, 3H,
), 3.75 (s, 3H, OCH3), 2.28 (s, 3H, 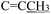 ), 2.16 (s, 3H,
), 2.16 (s, 3H, 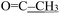 ). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) (E/Z) δ 206.55, 201.32, 176.74, 176.07, 164.24, 154.99, 139.46, 137.17, 136.81, 130.22, 128.62, 128.56, 128.37, 127.73, 127.30, 127.16, 126.65, 117.87, 114.96, 113.54, 112.74, 109.40, 109.35, 101.07, 55.56, 54.65, 48.61, 42.44, 30.70, 27.26, 13.36. Elemental analysis: calculated for C23H22N4O3S: C, 63.58; H, 5.10; N, 12.89; S, 7.38. Found: C, 63.48; H, 4.95; N, 12.74; S, 6.93.
). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) (E/Z) δ 206.55, 201.32, 176.74, 176.07, 164.24, 154.99, 139.46, 137.17, 136.81, 130.22, 128.62, 128.56, 128.37, 127.73, 127.30, 127.16, 126.65, 117.87, 114.96, 113.54, 112.74, 109.40, 109.35, 101.07, 55.56, 54.65, 48.61, 42.44, 30.70, 27.26, 13.36. Elemental analysis: calculated for C23H22N4O3S: C, 63.58; H, 5.10; N, 12.89; S, 7.38. Found: C, 63.48; H, 4.95; N, 12.74; S, 6.93.
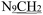 ), 2.27 (s, 3H,
), 2.27 (s, 3H, 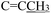 ), 2.18–2.13 (s, 3H,
), 2.18–2.13 (s, 3H, 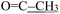 ). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 201.33 (
). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 201.33 (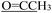 ), 176.75 (C
), 176.75 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 166.06 (thiazole C
O), 166.06 (thiazole C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 143.03 (indole C
N), 143.03 (indole C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 141.43 (C5), 139.44 (C4), 137.79 (C10), 123.50 (C6), 122.09 (C5a), 119.60 (C7a), 118.82 (C3a), 110.88 (C7), 101.84 (C11), 55.10 (C12), 27.41 (C13), 13.80 (C10a). Compound 4i: ESI-HRMS: formula: C23H19F3N4O3S, calculated [M + H]+: 489.12082, found [M + H]+: 489.12052 (deviation: 0.30 ppm); HPLC-PDA: λ 254 nm, MeCN
N), 141.43 (C5), 139.44 (C4), 137.79 (C10), 123.50 (C6), 122.09 (C5a), 119.60 (C7a), 118.82 (C3a), 110.88 (C7), 101.84 (C11), 55.10 (C12), 27.41 (C13), 13.80 (C10a). Compound 4i: ESI-HRMS: formula: C23H19F3N4O3S, calculated [M + H]+: 489.12082, found [M + H]+: 489.12052 (deviation: 0.30 ppm); HPLC-PDA: λ 254 nm, MeCN![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) MeOH (1
MeOH (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1), Rt: 3.03 min, 97.06%. Elemental analysis: calculated for C16H13F3N4O3S: C, 48.24; H, 3.29; N, 14.06; S, 8.05. Found: C, 48.01; H, 3.49; N, 13.97; S, 7.86.
1), Rt: 3.03 min, 97.06%. Elemental analysis: calculated for C16H13F3N4O3S: C, 48.24; H, 3.29; N, 14.06; S, 8.05. Found: C, 48.01; H, 3.49; N, 13.97; S, 7.86.
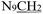 ), 3.71 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H,
), 3.71 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H, 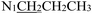 ), 2.28 (s, 3H,
), 2.28 (s, 3H, 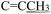 ), 2.16 (s, 3H,
), 2.16 (s, 3H, 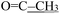 ), 1.61 (h, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H,
), 1.61 (h, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, 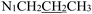 ), 0.87 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H,
), 0.87 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H, 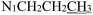 ). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 201.27 (
). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 201.27 (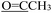 ), 176.98 (C
), 176.98 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 164.58 (thiazole C
O), 164.58 (thiazole C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 143.35 (indole C
N), 143.35 (indole C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 141.85 (C5), 138.37 (C6), 137.91 (C13), 123.31 (C4), 119.50 (C5a), 115.04 (C7a), 118.13 (C3a), 109.85 (C7), 102.10 (C14), 55.16 (C15), 41.18 (C8), 27.42 (C16), 20.97 (C9), 13.80 (C13a), 11.59 (C10). Elemental analysis: calculated for C19H19F3N4O3S: C, 51.81; H, 4.35; N, 12.72; S, 7.28. Found: C, 51.54; H, 4.05; N, 12.24; S, 7.06.
N), 141.85 (C5), 138.37 (C6), 137.91 (C13), 123.31 (C4), 119.50 (C5a), 115.04 (C7a), 118.13 (C3a), 109.85 (C7), 102.10 (C14), 55.16 (C15), 41.18 (C8), 27.42 (C16), 20.97 (C9), 13.80 (C13a), 11.59 (C10). Elemental analysis: calculated for C19H19F3N4O3S: C, 51.81; H, 4.35; N, 12.72; S, 7.28. Found: C, 51.54; H, 4.05; N, 12.24; S, 7.06.
 ), 4.80 (s, 2H,
), 4.80 (s, 2H, 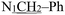 ), 2.24 (s, 3H,
), 2.24 (s, 3H, 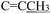 ), 2.09 (s, 3H,
), 2.09 (s, 3H, 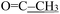 ). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 201.23 (
). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 201.23 (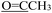 ), 177.15 (C
), 177.15 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 164.72 (thiazole C
O), 164.72 (thiazole C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 143.57 (indole C
N), 143.57 (indole C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N), 141.30 (C5), 138.07 (C17), 138.02 (C4), 136.90 (C6), 129.17 (C10), 129.17 (C14), 127.88 (C9), 127.64 (C11), 127.64 (C13), 123.21 (C7a), 119.46 (C5a), 114.19 (C12), 118.32 (C3a), 110.21 (C7), 102.35 (C18), 55.22 (C19), 43.01 (C8), 27.43 (C20), 13.81 (C17a). Elemental analysis: calculated for C23H19F3N4O3S: C, 56.55; H, 3.92; N, 11.47; S, 6.56. Found: C, 56.09; H, 3.73; N, 11, 26; S, 6.49.
N), 141.30 (C5), 138.07 (C17), 138.02 (C4), 136.90 (C6), 129.17 (C10), 129.17 (C14), 127.88 (C9), 127.64 (C11), 127.64 (C13), 123.21 (C7a), 119.46 (C5a), 114.19 (C12), 118.32 (C3a), 110.21 (C7), 102.35 (C18), 55.22 (C19), 43.01 (C8), 27.43 (C20), 13.81 (C17a). Elemental analysis: calculated for C23H19F3N4O3S: C, 56.55; H, 3.92; N, 11.47; S, 6.56. Found: C, 56.09; H, 3.73; N, 11, 26; S, 6.49.
3.4. Enzyme inhibition
3.5. Computational studies
Molecular docking and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations were performed using Schrödinger Molecular Modeling Suite (version 2025-1), employing the Maestro interface (v14.3) and Desmond software (D. E. Shaw Research, 2024-4). Protein and ligand preparation adhered to previously established protocols.28–30 Ligand structures were processed using the LigPrep module to generate all relevant ionization and tautomeric forms at physiological pH (7.4), followed by geometry optimization using the OPLS4 force field. Protein targets—acetylcholinesterase (AChE, PDB ID: 4EY7), butyrylcholinesterase (BChE, PDB ID: 6EP4), α-glucosidase (α-Glu, PDB ID: 3WY1), and α-amylase (α-Amy, PDB ID: 5E0F)—were retrieved from the Protein Data Bank and prepared using the Protein Preparation Wizard by adding hydrogens, assigning proper protonation states, and performing minimization to resolve steric clashe31 Glide XP and induced fit docking (IFD) protocols were applied to evaluate ligand–receptor interactions. For IFD, a grid box of 20 × 20 × 20 Å was centered on the binding pocket, and 20 docking poses per ligand were generated. The highest-scoring conformations were refined based on IFD docking scores. The protocol incorporated receptor flexibility, enabling iterative adjustments of both ligand and protein conformations to reflect a realistic dynamic binding process.32 Prime MM-GBSA calculations, employing the VSGB solvation model, were performed to estimate the binding free energies of the docked protein–ligand complexes. This method evaluates the energetic favorability of binding by considering electrostatic interactions, van der Waals forces, and solvation effects.33MD simulations were carried out in Desmond using the TIP4P water model for solvation. The system was neutralized with Na+ and Cl− ions, and a 10 × 10 × 10 Å simulation box was employed. After energy minimization to resolve initial steric clashes, the system was equilibrated under NPT conditions at 300 K and 1 atm. A production run was then conducted for 100 ns. RMSD analysis of the protein backbone and ligand atoms was performed to assess conformational stability. Additionally, the persistence of key interactions, including hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic contacts, and salt bridges, was examined to evaluate the strength and stability of ligand binding throughout the simulation.34–36
ADME properties were predicted using QikProp (Schrödinger, 2025-1) to evaluate the pharmacokinetic profiles of the compounds. Parameters such as absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion were computed, providing a data-driven assessment of drug-likeness and bioavailability.31
4. Conclusion
This work demonstrates the successful application of structure-based drug design and molecular hybridization to generate a series of dual-acting hybrid molecules with the potential to address the comorbidity of Alzheimer's disease (AD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). A range of biological activities was observed among the synthesized compounds, with 3d and 3h demonstrating selective and potent inhibition of α-Amy and α-Glu, respectively. Similarly, 3i and 4i exhibited marked inhibitory effects on ACHE and BCHE. These findings suggest the potential of these molecules as promising scaffolds for developing therapeutics targeting diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer's disease. In silico ADME profiling further revealed favorable pharmacokinetic properties consistent with peripheral and central bioavailability, reinforcing their suitability as drug-like candidates. Collectively, these findings position compounds 3d, 3h, 3i, and 4i as promising lead scaffolds for the development of innovative multi-target therapeutics capable of simultaneously addressing the metabolic and neurodegenerative aspects of AD–T2DM comorbidity. Distinctly, MD simulations confirmed that 4i forms stable and sustained interactions with its target, further supporting its advancement in preclinical studies. Building on these findings, future work should focus on in-depth mechanistic studies, in vivo pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic evaluations, and toxicity assessments to validate the safety and efficacy of these hybrid compounds.Author contributions
Wesam S. Qayed, investigation, conceptualization, supervision, visualization, writing – review & editing, Mostafa A. Hassan methodology, conceptualization, data curation, writing – review & editing, Halil Şenol conceptualization, methodology, software, data curation, visualization, writing – review & editing, Parham Taslimi data curation, methodology, writing – original draft, Tarek Aboul-Fadl, investigation, validation, supervision, writing – review & editing, project administration. All authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Data availability
The data supporting this article have been included as part of the supplementary information (SI).Supplementary information is available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d5md00628g.
References
- M. Kciuk, W. Kruczkowska, J. Gałęziewska, K. Wanke, Ż. Kałuzińska-Kołat and M. Aleksandrowicz, et al., Alzheimer's Disease as Type 3 Diabetes: Understanding the Link and Implications, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2024, 25(22), 11955, DOI:10.3390/ijms252211955.
- H. M. Al-Kuraishy, G. M. Sulaiman, H. A. Mohammed, S. G. Mohammed, A. I. Al-Gareeb and A. K. Albuhadily, et al., Amyloid-β and heart failure in Alzheimer's disease: the new vistas, Front. Med., 2025, 12, 1–12 CrossRef.
- T. T. Nguyen, Q. T. H. Ta, T. K. O. Nguyen, T. T. D. Nguyen and G. V. Van, Type 3 diabetes and its role implications in alzheimer's disease, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2020, 21(9), 1–16 CrossRef.
- T. Ponce-Lopez, Peripheral Inflammation and Insulin Resistance: Their Impact on Blood–Brain Barrier Integrity and Glia Activation in Alzheimer's Disease, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2025, 26(9), 4209, DOI:10.3390/ijms26094209.
- R. Nath, S. Pathania, G. Grover and M. J. Akhtar, Isatin containing heterocycles for different biological activities: Analysis of structure activity relationship, J. Mol. Struct., 2020, 1222, 128900 CrossRef CAS , available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022286020312254.
- B. Mavroidi, A. Kaminari, D. Matiadis, D. Hadjipavlou-Litina, M. Pelecanou and A. Tzinia, et al., The Prophylactic and Multimodal Activity of Two Isatin Thiosemicarbazones against Alzheimer's Disease In Vitro, Brain Sci., 2022, 12(6), 806, DOI:10.3390/brainsci12060806.
- S. Patil, S. G. Alegaon, S. Gharge, S. D. Ranade and N. A. Khatib, Molecular hybridization, synthesis, in vitro α-glucosidase inhibition, in vivo antidiabetic activity and computational studies of isatin based compounds, Bioorg. Chem., 2024, 153, 107783, DOI:10.1016/j.bioorg.2024.107783.
- Z. Bakherad, H. Bakherad, S. Sepehri, M. A. Faramarzi, K. Mahnam and S. Mojtabavi, et al., In silico and in vitro studies of thiosemicarbazone-indole hybrid compounds as potent α-glycosidase inhibitors, Comput. Biol. Chem., 2022, 97, 107642, DOI:10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2022.107642.
- A. Y. Alzahrani, Y. A. Ammar, M. Abu-Elghait, M. A. Salem, M. A. Assiri and T. E. Ali, et al., Development of novel indolin-2-one derivative incorporating thiazole moiety as DHFR and quorum sensing inhibitors: synthesis, antimicrobial, and antibiofilm activities with molecular modelling study, Bioorg. Chem., 2021, 119, 105571, DOI:10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105571.
- H. E. Lebovitz, Differentiating members of the thiazolidinedione class: a focus on safety, Diabetes/Metab. Res. Rev., 2002, 18(S2), S23–S29, DOI:10.1002/dmrr.252.
- M. Michailidis, D. A. Tata, D. Moraitou, D. Kavvadas, S. Karachrysafi and T. Papamitsou, et al., Antidiabetic Drugs in the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2022, 23(9), 4641, DOI:10.3390/ijms23094641.
- W. S. Qayed, M. A. Hassan, A. M. Abouwarda, Y. M. Ibrahim and T. Aboul-Fadl, Computational Design of Azine-Linked Hybrids of 2-Indolinone-Thiazolodine Scaffold as Novel and Promising Quorum Sensing Inhibitors, Polycyclic Aromat. Compd., 2024, 44(1), 1–24, DOI:10.1080/10406638.2023.2165511.
- W. S. Qayed, M. A. Hassan, W. M. El-Sayed, A. S. Rogério and T. Aboul-Fadl, Novel Azine Linked Hybrids of 2-Indolinoneand ThiazolodinoneScaffolds as CDK2 Inhibitors with Potential Anticancer Activity: In Silico Design, Synthesis, Biological, Molecular Dynamics and Binding Free Energy Studies, Bioorg. Chem., 2022, 126, 104366, DOI:10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.10436.
- B. D. Varpe, A. A. Kulkarni, S. B. Jadhav, A. S. M. Jadhav and S. Y. Jadhav, Isatin Hybrids and Their Pharmacological Investigations, Mini-Rev. Med. Chem., 2021, 21, 1182–1225 CrossRef CAS PubMed , available from: http://www.eurekaselect.com/node/188949/article.
- H. Yakan, M. Azam, S. Kansız, H. Muğlu, M. Ergül, P. Taslimi, Ü. M. Koçyiğit, M. Karaman, A. Siar and K. Min, Evaluation as anti-proliferative agents and metabolic enzyme, Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop., 2023, 37(5), 1221–1236 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Gong, S. Li, J. Huang, S. Tan, Q. Zhang and Y. Tian, et al., Discovery of potent LRRK2 inhibitors by ensemble virtual screening strategy and bioactivity evaluation, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2024, 279, 116812, DOI:10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116812.
- H. El-Kashef, G. Badr, N. Abo El-Maali, D. Sayed, P. Melnyk and N. Lebegue, et al., Synthesis of a novel series of (Z)-3,5-disubstituted thiazolidine-2,4-diones as promising anti-breast cancer agents, Bioorg. Chem., 2020, 96, 103569, DOI:10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.103569.
- A. Stana, B. Tiperciuc, M. Duma, L. Vlase, O. Crişan and A. Pîrnău, et al., Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity of Some New N-substituted-5-arylidene-thiazolidine-2,4-diones, J. Heterocyclic Chem., 2014, 51(2), 411–417, DOI:10.1002/jhet.1726.
- G. L. Ellman, K. D. Courtney, V. Andres and R. M. Featherstone, A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity, Biochem. Pharmacol., 1961, 7(2), 88–95, DOI:10.1016/0006-2952(61)90145-9.
- L. Durmaz, H. Karageçili, A. Erturk, E. M. Ozden, P. Taslimi and S. Alwasel, et al., Hamamelitannin's Antioxidant Effect and Its Inhibition Capability on α-Glycosidase, Carbonic Anhydrase, Acetylcholinesterase, and Butyrylcholinesterase Enzymes, Processes, 2024, 12(11), 2341, DOI:10.3390/pr12112341.
- H. Yalazan, D. Koç, F. Aydın Kose, S. Fandaklı, B. Tüzün and M. İ. Akgül, et al., Design, syntheses, theoretical calculations, MM-GBSA, potential anti-cancer and enzyme activities of novel Schiff base compounds, J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn., 2023, 42(23), 13100–13113, DOI:10.1080/07391102.2023.2274972.
- S. Zareei, M. Mohammadi-Khanaposhtani, M. Shahali, H. Şenol, M. Badbedast and A. Moazzam, et al., Phenyldiazenyl-phenoxy-1,2,3-triazol-acetamide derivatives as new dual cholinesterase Inhibitors: Design, synthesis, in vitro, and in silico enzymatic inhibition evaluations, J. Mol. Struct., 2025, 1321, 139686, DOI:10.1016/j.molstruc.2024.139686.
- Y. Tao, Y. Zhang, Y. Cheng and Y. Wang, Rapid screening and identification of α-glucosidase inhibitors from mulberry leaves using enzyme-immobilized magnetic beads coupled with HPLC/MS and NMR, Biomed. Chromatogr., 2012, 27(2), 148–155, DOI:10.1002/bmc.2761.
- Z. Xiao, R. Storms and A. Tsang, A quantitative starch–iodine method for measuring alpha-amylase and glucoamylase activities, Anal. Biochem., 2006, 351(1), 146–148, DOI:10.1016/j.ab.2006.01.036.
- M. H. Sayahi, S. Zareei, M. Halimi, M. Alikhani, A. Moazzam and M. Mohammadi-Khanaposhtani, et al., Design, synthesis, in vitro, and in silico anti-α-glucosidase assays of N-phenylacetamide-1,2,3-triazole-indole-2-carboxamide derivatives as new anti-diabetic agents, Sci. Rep., 2024, 14(1), 15791 CrossRef CAS , Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38982268.
- R. D. Alharthy, S. Khalid, S. Fatima, S. Ullah, A. Khan and S. N. Mali, et al., Synthesis of the chromone-thiosemicarbazone scaffold as promising α-glucosidase inhibitors: An in vitro and in silico approach toward antidiabetic drug design, Arch. Pharm., 2024, 357(8), 2400140, DOI:10.1002/ardp.202400140.
- M. B. Haider, A. Saeed, A. Ahmed, M. Azeem, H. Ismail and S. Mehmood, et al., Exploring Acyl Thiotriazinoindole Based Pharmacophores: Design, Synthesis, and SAR Studies with Molecular Docking and Biological Activity Profiling against Urease, α-amylase, α-glucosidase, Antimicrobial, and Antioxidant Targets, Protein J., 2024, 43(5), 1009–1024, DOI:10.1007/s10930-024-10229-6.
- F. S. Tokalı, H. Şenol, Ş. Ateşoğlu, P. Tokalı and F. Akbaş, Exploring highly selective polymethoxy fenamate isosteres as novel anti-prostate cancer agents: Synthesis, biological activity, molecular docking, molecular dynamics, and ADME studies, J. Mol. Struct., 2025, 1319, 139519, DOI:10.1016/j.molstruc.2024.139519.
- I. Mamedov, H. Şenol, F. Naghiyev, V. Khrustalev, N. Sadeghian and P. Taslimi, New tetrahydro-isoquinoline derivatives as cholinesterase and α-glycosidase inhibitors: Synthesis, characterization, molecular docking & dynamics, ADME prediction, in vitro cytotoxicity and enzyme inhibition studies, J. Mol. Liq., 2024, 404, 125006, DOI:10.1016/j.molliq.2024.125006.
- H. Şenol, 4-Furfuryloxymethyl-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl-acetohydrazide Hybrids as Cholinesterase and Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors: Synthesis, Characterization and Comprehensive Biological Activity Studies, ChemistrySelect, 2024, 9(6), 202303927, DOI:10.1002/slct.202303927.
- N. Kılınç, Inhibition profiles and molecular docking studies of antiproliferative agents against aldose reductase enzyme, Int. J. Chem. Technol., 2021, 5(1), 77–82, DOI:10.32571/ijct.944049.
- F. S. Tokalı, H. Şenol, Ş. Ateşoğlu and F. Akbaş, A series of quinazolin-4(3H)-one-morpholine hybrids as anti-lung-cancer agents: Synthesis, molecular docking, molecular dynamics, ADME prediction and biological activity studies, Chem. Biol. Drug Des., 2024, 104(1), 14599, DOI:10.1111/cbdd.14599.
- K. B. Zengin, D. Öztürk Civelek, E. B. Çakmak, Y. Kolcuoğlu, H. Şenol and B. N. Sağlık Özkan, et al., Synthesis of Sorafenib-Ruthenium Complexes, Investigation of Biological Activities and Applications in Drug Delivery Systems as an Anticancer Agent, J. Med. Chem., 2024, 67(6), 4463–4482 CrossRef PubMed , Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38471014.
- Z. Arslan, E. Okuroğlu, H. Şenol and Z. Türkmen, 1-Benzhydryl-piperazine: Isolation, structure determination, and in silico studies for a novel potential narcotic agent detected in sports supplements, J. Food Compos. Anal., 2024, 135, 106682, DOI:10.1016/j.jfca.2024.106682.
- E. Hacıosmanoğlu-Aldoğan, D. Lama, H. İ. Yetke, H. Şenol and F. D. Yöntem, Necroptotic Suppression of Lung Cancer Cell Proliferation and Migration: A Comprehensive In Vitro and In Silico Study to Determine New Molecular Targets for Pexidartinib, Cell Biochem. Funct., 2025, 43(3), 70068, DOI:10.1002/cbf.70068.
- F. Çakır, Ş. Ateşoğlu, Z. R. Müderrisoğlu, F. Demirel, F. Akbaş and F. S. Tokalı, et al., Targeting Lung Cancer With Carvacrol-Triazole-Arylidene Hydrazide Hybrids: In Vitro and In Silico Cytotoxicity Assessments, Chem. Biodiversity, 2025, 2963, DOI:10.1002/cbdv.202402963.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2026 |