Defect-engineered Pd/WO3−x nanostructures with tunable morphology for enhanced visible-NIR light-driven catalysis
Priyanka
a,
Rashmi
a,
Hideyuki
Kawasoko
 b,
Soichi
Kikkawa
b,
Soichi
Kikkawa
 b,
Seiji
Yamazoe
b,
Seiji
Yamazoe
 b,
Ryo
Watanabe
b,
Ryo
Watanabe
 c,
Choji
Fukuhara
c and
Priyanka
Verma
c,
Choji
Fukuhara
c and
Priyanka
Verma
 *a
*a
aDepartment of Chemistry, Indian Institute of Technology Delhi, Hauz Khas, New Delhi 110016, India. E-mail: pverma@chemistry.iitd.ac.in
bDepartment of Chemistry, Graduate School of Science, Tokyo Metropolitan University, 1-1 Minami-Osawa, Hachioji, Tokyo 192-0397, Japan
cDepartment of Applied Chemistry and Biochemical Engineering, Graduate School of Engineering, Shizuoka University, 3-5-1 Johoku, Chuo-ku, Hamamatsu, Shizuoka 432-8561, Japan
First published on 7th January 2026
Abstract
Semiconductor-based heterogeneous photocatalysis has garnered significant attention, showing considerable promise as a strategy for addressing problems associated with renewable energy and environmental remediation. Plasmonic semiconductors enhance photocatalysis by enabling localized surface plasmon resonance that enhances the light absorption and generates hot carriers. These carriers drive redox reactions efficiently, improving the photocatalytic performance. Herein, Pd nanoparticles (NPs) (2.5 wt%) were successfully deposited onto a non-stoichiometric form of tungsten trioxide (WO3−x) with oxygen defects using a controlled morphology technique. Generating oxygen-deficient states in the WO3 structure significantly enhanced its electronic properties, facilitating improved charge carrier separation and superior catalytic performance. The prepared catalysts were characterized using various techniques, including UV-vis spectroscopy, EPR, FT-EXAFS, HR-TEM, Mott–Schottky, XPS, and N2 physisorption analysis. The light-driven catalytic performance of the prepared nanocatalyst was evaluated through the conversion of 4-nitrophenol (4-NP) to 4-aminophenol (4-AP), utilizing hydrogen generated in situ from ammonia borane (AB). A superior reaction rate of 0.75 min−1 was obtained for Pd colloids/WO3−x catalyst, a 2.5 times enhancement in comparison to the reaction performed in dark conditions. The study demonstrates a crucial role of Pd NPs supported on WO3−x and morphology-controlled photocatalytic activity. Based on scavenger experiments, a plausible reaction mechanism is suggested to explain the enhanced charge separation and photocatalytic performance. Our findings underscore the potential of WO3−x-based materials with plasmonic properties in photocatalytic application reactions.
Introduction
The accelerated exhaustion of fossil energy resources is intensifying the global energy crisis while simultaneously contributing to an increase in environmental pollution.1 Consequently, environmentally sustainable energy alternatives that do not produce greenhouse gas emissions have become increasingly important.2 In recent years, solar energy harvesting and conversion have garnered significant scientific interest.3 Among diverse renewable energy strategies, the direct transformation of solar energy into chemical fuels through photocatalysis has gained considerable attention as an efficient and sustainable route.4,5 The distinctive ability of plasmon-active nanomaterials to capture light via localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) has attracted significant research interest.6–11 Photocatalysis has emerged as a key technology in sustainability, addressing critical problems related to energy and the environment, including wastewater treatment, organic synthesis, and the generation of solar fuels.12,13WO3 is an efficient visible-light semiconductor (band gap 2.6–2.8 eV) and often outperforms TiO2 under visible irradiation.14 The previously reported studies have shown that WO3 morphology strongly influences 4-NP degradation, and its photocatalytic activity can be significantly enhanced through ozonation or noble-metal deposition.15–17 Oxygen vacancies in metal oxides are widely recognized for boosting photocatalytic performance. Introducing such vacancies into WO3 and integrating Pd as a cocatalyst creates a synergistic enhancement, enabling plasmon-assisted charge transfer.18–20 This work demonstrates a morphology-dependent, vacancy-engineered Pd/WO3−x system, providing new insights for designing visible-NIR responsive photocatalysts for environmental applications.21,22
However, metal oxides exhibiting oxygen vacancies, including oxygen-deficient tungsten oxide (WO3−x), molybdenum oxide (MoO3−x), and copper sulfide (Cu2−xS) nanomaterials, have attracted considerable attention because of their distinct photoabsorption capabilities over a wide range, particularly in the near-infrared region.23–27 These materials are highly promising for diverse applications due to their capability to harness vis-NIR light efficiently.28 In semiconductor-based systems, incident light induces the generation of excited electron and hole pairs, facilitating various photochemical processes.29 Specifically, non-stoichiometric tungsten oxide (WO2.72) has emerged as a diverse material with applications in smart window technologies, electrochromic devices, photothermal therapy, and NIR radiation shielding, highlighting its multifunctional utility in both energy and biomedical fields.30 The various crystalline forms of tungsten oxide, including the monoclinic W18O49 phase, have garnered significant attention owing to their characteristic defect-abundant crystal lattice.7,31,32 WO3−x serves as a promising host for LSPR, attributed to its unique electronic structure, particularly the presence of outer d-valence electrons. The non-stoichiometric nature of WO3−x, attributed to a high density of oxygen vacancies, plays a crucial role in modulating its electronic properties. These vacancies effectively reduce the band gap, thereby enhancing the optical response.32 Among the various mechanisms of plasmonic photocatalysis, including both direct and indirect, our research primarily centres on the direct photocatalytic pathway where the semiconductor acts as an efficient light absorber, and the co-catalyst (Pd) acts as a catalytically active site.33
Herein, we have reported the synthesis of Pd/WO3−x nanocatalyst with varied morphologies, including nanorods, sheets, and blocks, exhibiting light-induced plasmonic excitation across the visible and near-infrared (NIR) wavelength range. Tailoring the morphological features of photocatalytic materials plays a critical role in optimizing their surface area, active site availability, light-harvesting efficiency, and charge carrier dynamics. This work highlights the effect of specific morphologies of WO3−x on enhancing the plasmonic interactions, improving photogenerated charge separation, and ultimately leading to superior photocatalytic activity. The Pd deposited WO3−x hybrids were synthesized via two distinct approaches: impregnation of a colloidal solution of Pd NPs onto WO3−x support, and one-pot solvothermal synthesis. The WO3−x support was synthesized via the solvothermal method using tungsten hexachloride (WCl6) as the precursor. The resulting Pd/WO3−x hybrid nanocatalysts demonstrated outstanding performance in the catalytic hydrogenation of 4-NP to 4-AP, under both light irradiation and dark conditions. Additionally, the influence of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) as a surfactant during synthesis was examined, revealing its impact on the morphology, structural characteristics, and catalytic efficiency of the hybrids. This work introduces a novel strategy for designing plasmonic photocatalysts by integrating Pd NPs with oxygen-deficient sites in WO3−x to enhance the catalytic performance under visible-NIR illumination. The insights gained from this study contribute to a broader understanding of defect engineering in plasmon-enhanced photocatalysis and offer a potential route towards advancing nano-catalysts for environmentally friendly and sustainable applications.
Experimental section
Materials
Tungsten chloride (WCl6) was purchased from Tokyo Chemical Industry. Commercial tungsten oxide (WO3), polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), and palladium acetate [Pd(OAc)2] were supplied by Sigma-Aldrich Co. 4-nitrophenol (NO2C6H4OH) and ammonia borane (NH3BH3) were supplied by Merck Chemicals. Ethanol (C2H5OH) received from Changshu Hongsheng Fine Chemical Co. Ltd. DMSO (Dimethyl sulfoxide) purchased from Actylis Pharma India Pvt. Ltd. IPA (isopropyl alcohol) was supplied by Avantor Performance Materials India Pvt. Ltd. The reagents were used directly without pre-treatment or purification.Synthesis procedure of WO3−x
Sub-stoichiometric WO3−x nanostructure was synthesized using a solvothermal approach, as reported in the literature.31 500 mg tungsten hexachloride (WCl6) was dissolved in 100 mL of ethanol under constant stirring until the solution turned blue, indicative of the formation of reduced tungsten species. The resulting solution was poured into a Teflon-lined stainless-steel autoclave and heated at 180 °C for 24 hours. Afterwards, the autoclave was allowed to cool down to room temperature. The resulting blue precipitate was collected via centrifugation and repeatedly washed with deionized water to remove any remaining impurities. The purified product was then dried at 60 °C overnight, yielding a blue WO3−x powder.Synthesis procedure of Pd/WO3−xvia the impregnation method
Palladium NPs (2.5 wt%) were loaded onto the as-synthesized WO3−x support through an impregnation technique followed by hydrogen reduction. In a typical procedure, WO3−x was uniformly suspended in 50 mL of ethanol to which a 5 mM palladium(II) acetate [Pd(OAc)2] solution was added under continuous magnetic stirring. The mixture was continuously stirred for 4 hours to ensure uniform distribution of the Pd precursor. Subsequently, the solvent was removed using a rotary evaporator. The obtained solid was then subjected to thermal reduction in a tubular furnace under a 5% H2 and 95% N2 gas flow at 200 °C for 3 hours. The final product was designated as Pd/WO3−x. The preparation of Pd colloids was performed following an established procedure detailed in Fig. S1 of the SI.34–36 The Pd colloids were then impregnated on the WO3−x support and labelled as Pd colloids/WO3−x.Synthesis of Pd–WO3−xvia the solvothermal method
Palladium NPs (2.5 wt%) were supported on WO3−xvia a solvothermal synthesis followed by hydrogen reduction. WCl6 was suspended in 100 mL of ethanol, followed by adding a 5 mM solution of palladium(II) acetate [Pd(OAc)2] under continuous magnetic stirring. The prepared mixture was transferred to a stainless-steel vessel lined with Teflon and treated solvothermally at 180 °C for 24 hours. After cooling to room temperature, the solid was separated using centrifugation and thoroughly rinsed with distilled water and ethanol to eliminate any impurities. The dark brown product was dried overnight at a temperature of 60 °C. At last, the dried powder was reduced under a H2/N2 (5/95%) atmosphere at 200 °C for 3 hours to prepare the Pd-supported WO3−x catalyst. The prepared sample was labelled as Pd-WO3−x-S. The Pd-WO3−x-S (PVP) was also prepared following the same procedure using a mass ratio of 0.6![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 for polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) to tungsten hexachloride (WCl6).
1 for polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) to tungsten hexachloride (WCl6).
Characterization
Diffuse reflectance UV-vis measurements were carried out using a JASCO V-770 UV-vis-NIR spectrophotometer to analyze the optical properties of the samples. Structural characterization was performed by recording powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns on a Bruker D8 Advance diffractometer utilizing Cu Kα radiation (λ = 1.54178 Å) in continuous scanning mode. Morphological features were investigated through SEM analysis with a Hitachi tabletop instrument, while transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis was conducted using a JEOL JEM-1400 microscope to capture high-resolution images. The high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM) was performed on a JEM-ARM200F NEOARM electron microscope operating at an electron voltage of 200 keV. The reduction reaction of 4-NP to 4-AP was monitored via an Agilent Cary 60 spectrophotometer. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was conducted using a Kratos Axis Supra system equipped with Al Kα radiation, with reference to the C 1s peak at 285 eV. Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectra were obtained at room temperature using a Bruker A300 spectrometer. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was carried out on a Perkin Elmer SII instrument, applying a heating rate of 10 °C per minute. The Mott Schottky analysis was performed in a three-electrode system with FTO-supported working electrode, Pt counter, Ag/AgCl reference, in 0.5 M Na2SO4 electrolyte, with an AC potential frequency of 1 kHz under dark conditions using a Zahner workstation with model PP211. Specific surface area and porosity were evaluated using the BELSORP-MaxII analyzer (Microtrac BEL Corp) at liquid nitrogen temperature (−196 °C). X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) measurements at the W L3- and Pd K-edges were performed in transmission mode at SPring-8 of Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute in Japan, utilizing ionization chambers as detectors. Data processing was completed using xTunes software.37Photocatalytic reaction
A 7 mM aqueous solution of 4-nitrophenol was used as a stock solution in the reaction. An aliquot of 10 mL from this solution was added to a glass reactor equipped with a magnetic stir bar. Subsequently, 5 mg of powdered catalyst was added to the reactor. The nitrogen gas was bubbled into the reactor system for 15 min to establish an inert environment. A freshly made aqueous solution of AB (0.025 M) was obtained via dissolving 7.7 mg AB in 10 mL of distilled water. The reduction reaction was initiated by introducing the AB solution into the reactor through the rubber septum. After the addition of AB, the color of the 4-NP solution immediately changed, indicating the formation of the 4-nitrophenolate ion. The reaction was monitored by withdrawing 1 mL aliquots of the reaction mixture at specific time intervals. The absorbance was measured at 400 nm and 296 nm, corresponding to nitrophenolate ion and 4-AP, respectively. The influence of light irradiation on catalytic performance was examined by evaluating the reaction under both illuminated and dark conditions. The source of light irradiation was a 300 W Xenon arc lamp (Newport).Results and discussion
XRD analysis
Fig. 1(a and b) depicts a schematic representation of the synthesis procedure used to prepare the photocatalysts via the solvothermal and impregnation approach. X-ray diffraction (XRD) measurements were performed for the synthesized materials to determine their crystal structure and assess phase purity. As represented in Fig. 1(c), XRD analysis confirmed that the prepared samples consisted of a monoclinic phase, consistent with standard data for W18O49 (JCPDS No. 71-2450).31 The diffraction peaks associated with the (010) plane, with 2θ values of 23°, were found in all samples, indicating that W18O49 likely grows in the (010) direction.31 The sharpness and intensity of the peaks also suggest good crystallinity of the materials. The Pd/WO3−x retains the characteristic sharp and strong (010) reflection of WO3−x. No distinct peaks for Pd were detected in the Pd-loaded WO3−x samples, which could be attributed to the small amount of Pd used or its even distribution on the surface. There are some impurity peaks in the XRD pattern of Pd colloids/WO3−x, probably due to the surfactants used in the colloidal suspension. The XRD pattern of Pd-WO3−x-S suggests nanostructures grow along more than one direction. For the Pd-WO3−x-S (PVP), the XRD patterns show further suppression of the (010) peak and overall reduced intensity, likely due to the introduction of surfactant (PVP), which affects nucleation and growth kinetics, leading to smaller crystallites or more amorphous structures. The progressive reduction in peak intensity and broadening from commercial WO3 to Pd-deposited WO3−x samples reflects the increasing disorder and nanoscale nature of the materials.38The synthesized WO3−x nanowires appeared blue when dispersed in ethanol, indicating their unique optical properties. Fig. 1(d) shows the optical profile of WO3−x-based catalysts, exhibiting absorption from the visible to the near-infrared range, due to the collective excitation of free electrons attributed to the existence of oxygen vacancies along the interface, leading to LSPR.29 It is well known that oxygen-deficient sites in metal oxides are tuned to affect the LSPR behavior.39 The commercial WO3 also showed negligible absorption. The Pd-decorated WO3−x composites show comparatively weaker absorption than WO3−x. These findings indicate that surface oxygen vacancies potentially facilitate the nucleation of Pd NPs. The Pd deposition on WO3−x interferes with the light absorption by WO3−x, leading to reduced intensity.40 Among the Pd-modified samples, Pd-WO3−x-S (PVP) demonstrates the highest absorption intensity across the visible region (350–700 nm). In contrast, the surfactant-free sample Pd-WO3−x-S exhibits lower absorption intensity, indicating limited surface modification. The Pd colloids/WO3−x and Pd/WO3−x samples also show improved visible light absorption compared to commercial WO3, though to a lesser extent than Pd-WO3−x-S (PVP). Conversely, Pd/commercial WO3 shows only marginal improvement over the unmodified WO3, suggesting that Pd alone, without accompanying oxygen deficiency or structural modification, is insufficient to alter the optical properties significantly. To justify the origin of LSPR in WO3−x, the UV-vis-NIR absorption spectra of WO3−x show a broad visible-NIR absorption peak originating from vacancy-induced free carriers, unlike stoichiometric WO3. Overall, it was revealed that both oxygen deficiency and the method of Pd incorporation play critical roles in tuning the visible and near-infrared absorption properties of WO3-based nanomaterials.
Morphology analysis
The SEM and TEM analyses were conducted to examine the morphological features of the synthesized samples, as displayed in Fig. 2 and 3. The SEM analysis of commercial WO3, as demonstrated in Fig. 2(a), revealed a mixture of different morphologies (cubic, spherical, and cuboidal) without a well-defined structural pattern. In contrast, Fig. 2(b and c) displays the SEM micrographs of WO3−x with nanorod-like structures. Additionally, Pd-WO3−x-S (PVP) in Fig. 2(d) exhibits a smooth block-like morphology. Fig. 2(e and f) depicts the morphology of Pd-WO3−x-S with a sheet-like morphology. The SEM images of Pd colloids/WO3−x in Fig. 2(g and h) show a spherical shape. The SEM images of Pd/WO3−x and Pd/Commercial WO3 are displayed in Fig. S2. The TEM images of WO3−x in Fig. 3(a) further confirmed the formation of nanowires with high aspect ratios, lengths ranging from hundreds of nanometres to several micrometers. The TEM micrographs of Pd/WO3−x, Pd-WO3–x-S, Pd colloids, Pd colloids/WO3−x, and Pd-WO3–x-S are shown in Fig. 3(b–h). The TEM image of Pd colloids/WO3−x revealed that Pd NPs were anchored on the nanowires. The HR-TEM images in Fig. 3(i–l) reveal clear lattice fringes with a 0.378 nm spacing corresponding to the (010) plane of WO3−x.41 The SAED pattern shows distinct diffraction spots/rings, confirming the polycrystalline nature of WO3−x. | ||
| Fig. 2 (a) SEM image of commercial WO3, (b and c) WO3−x, (d) Pd-WO3−x-S (PVP), (e and f) Pd-WO3−x-S, and (g and h) Pd colloids/WO3−x. | ||
The N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms for the synthesized samples are displayed in Fig. 4(a). The adsorption isotherms of all samples corresponded to type IV, which features mesoporous structures except commercial WO3 and Pd-WO3−x-S. The determined surface area and total pore volume were evaluated through the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) and Barrett–Joyner–Halenda (BJH) methods, with detailed values summarized in Table S1. The Pore size distribution is shown in Fig. S3 (a), confirming that the pores range from 2 to 50 nm, further supporting the mesoporous features of the materials. The WO3−x sample exhibits a significantly higher specific surface area of 66.51 m2 g−1, 30 times higher in comparison to commercial WO3 (2.03 m2 g−1), indicating a substantial increase in available active sites. This enhancement is expected to improve both photocatalytic efficiency and adsorption capacity, owing to the increased accessibility of reactant molecules. After Pd deposition, the BET surface areas of Pd/WO3−x and Pd colloids/WO3−x were reduced to 56.83 m2 g−1 and 22.2 m2 g−1, respectively. This decrease is attributed to the partial occupancy of surface sites with Pd NPs, thus confirming the successful loading of Pd. The samples synthesized via the solvothermal method, Pd-WO3−x-S (5.9 m2 g−1) and Pd-WO3−x-S (PVP) (8.0 m2 g−1), exhibited significantly lower surface areas than Pd/WO3−x prepared via impregnation. This reduction can be attributed to the dense particle aggregation and limited porosity often associated with solvothermal synthesis, especially in the presence of polymeric surfactants such as PVP.
 | ||
| Fig. 4 (a) Nitrogen adsorption–desorption isotherm of synthesized samples (b) EPR spectra of commercial WO3, Pd colloids/WO3−x measured at room temperature conditions. | ||
To examine the existence of paramagnetic centres and oxygen vacancies in Pd colloids/WO3−x, electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) analysis was performed, as shown in Fig. 4(b).42,43 The commercial WO3 sample displayed a broad and relatively weaker EPR signal, indicating a lower concentration of unpaired electrons and minimal oxygen vacancies. A signal observed around g ≈ 2.00 is probably associated with W5+ centres or isolated oxygen-deficient defects. In contrast, Pd colloids/WO3−x show a stronger EPR signal, indicating abundant oxygen vacancies and unpaired electrons, compared to commercial WO3. The EPR spectrum of Pd/WO3−x, Pd-WO3−x-S, and Pd-WO3−x-S (PVP) is displayed in Fig. S3 (b). The Pd/WO3−x exhibited a stronger EPR signal, suggesting a larger amount of oxygen vacancies, which probably trap electrons and form W5+ species. There may also be some contribution from palladium species in specific oxidation states, although palladium is typically EPR-silent unless under certain conditions.42 The asymmetry and splitting of the signal point toward possible interactions between Pd and defect centres within WO3−x. The Pd-WO3−x-S, Pd-WO3−x-S (PVP) shows enhanced electron delocalization or more isolated paramagnetic centres, confirming the preservation of oxygen vacancies following the incorporation of Pd NPs.
Thermal decomposition characteristics of the materials were evaluated using thermogravimetric analysis (TGA).42,44–46 The inert atmosphere (N2) was maintained during the measurements, with the temperature ramped at 10 °C min−1, as illustrated in Fig. S4(a). The commercial WO3 sample exhibited minimal weight loss up to 700 °C, indicating excellent thermal stability. In contrast, WO3−x showed a weight loss of approximately 10% below 300 °C, likely due to the evaporation of residual solvents.47 The Pd-WO3−x-S (PVP) exhibited the highest weight loss (∼35%) throughout the temperature range of 100–450 °C, primarily due to thermal decomposition of PVP, which was used as a surfactant during synthesis. Similarly, the Pd colloids/WO3−x demonstrated a weight loss of around 10% between 100 °C and 300 °C, resulting from residual PVP decomposition, while still maintaining good thermal stability beyond 350 °C. The Pd-WO3−x-S sample, synthesized without surfactant, exhibited a lower weight loss (∼5%) mainly below 250 °C, possibly resulting from desorption of moisture. The Pd/Commercial WO3 sample showed a slight weight loss of approximately 2–3% at 250 °C.
Subsequently, various characterizations were conducted to explore the electronic properties of the synthesized materials. Fig. S4(b) presents the FT-IR (Fourier-transform infrared) spectra of commercial WO3, WO3−x, and Pd-deposited samples. In commercial WO3, distinct absorption bands were observed (800–900 cm−1), which are typically ascribed to W–O–W stretching vibrations in a well-ordered WO6 octahedral network.47 In contrast, WO3−x displayed noticeable changes in the intensity and position of these bands, suggesting structural modifications associated with the introduction of oxygen vacancy. These spectral differences confirm the surface modifications in WO3−x compared to the commercial WO3.44,48 The peak observed around 2850–2950 cm−1 indicates the stretching vibrations associated with the PVP.
The Mott–Schottky curves (1/C2vs. V) shown in Fig. S5(a) were performed for commercial WO3, WO3−x, and Pd colloids/WO3−x, exhibiting positive slope, confirmed their n-type semiconducting nature.49 The flat-band potentials (approximating the conduction band edge) were obtained by linearly extrapolating the curve to the voltage X-axis. Commercial WO3 shows an ECB (conduction band edge potential) of approximately −0.11 V, while WO3−x exhibits a slightly less negative ECB of −0.02 V vs. Ag/AgCl.50 Notably, Pd colloids/WO3−x displays a significantly shifted conduction band edge at −0.99 V, indicating enhanced electron density and strong electronic interaction between Pd and WO3−x.51 The Tauc plots ((αhν)1/2versus photon energy (hν)), shown in Fig. S5(b), confirm indirect band-gap transitions for commercial WO3, WO3−x, and Pd colloids/WO3−x. Commercial WO3 exhibits an optical band gap of approximately 2.58 eV, whereas WO3−x displays a reduced band gap of about 2.45 eV, consistent with the formation of oxygen-vacancy defect states that extend light absorption into the visible region. The Pd colloids/WO3−x composite shows a further decrease in the band gap to around 1.64 eV, along with enhanced sub-band-gap absorption, indicating the introduction of additional electronic states and strong metal–semiconductor interactions that promote improved light harvesting and facilitate interfacial charge-transfer processes.
XPS analysis
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was utilized to determine the surface chemical environment of Pd-deposited WO3−x nanomaterial. The obtained W 4f and Pd 3d spectra for Pd colloids/WO3−x are shown in Fig. 5(a and b), respectively. This study concentrated on the elements W, O, and Pd to analyze the variations in oxidation states and verify the existence of oxygen vacancies.38,52 XPS also helps in examining how Pd NPs interact with the WO3−x surface and how defect engineering affects the electronic structure of the nanomaterial.42,44 The two characteristic peaks emerged at 37.7 eV (W 4f5/2) and 35.5 eV (W 4f7/2), corresponding to W6+, which is characteristic of stoichiometric WO3. Additionally, a second set of peaks at slightly lower binding energies was observed, attributed to W5+ species, suggesting oxygen deficiency within the lattice and the formation of non-stoichiometric WO3−x. The peak area ratio of W6+/W5+ was found to be 9.99. The Pd 3d XPS spectrum displays two prominent peaks at binding energies of 335.4 eV and 340.7 eV, corresponding to Pd 3d5/2 and Pd 3d3/2, respectively. These peaks exhibit the characteristic spin–orbit splitting of 5.3 eV and are associated with metallic palladium (Pd0). The XPS spectrum of commercial WO3, WO3−x, and Pd/WO3−x is shown in Fig. S6. The Pd 3d XPS spectra of the solvothermal samples (Pd-WO3−x-S and Pd-WO3−x-S-PVP) shown in Fig. S7 reveal relatively very low-intense signals of Pd, indicating that Pd is not on the surface but likely trapped within WO3−x. Overall, the XPS study confirms the successful deposition of palladium within the WO3−x matrix and reveals a mixed valence state of both W and Pd.X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS)
To analyze the coordination environment, XAS analyses were carried out at the W L3-edge and Pd K-edge, revealing key insights into metal-support interactions.42,53,54Fig. 6(a and c) presents the normalized W L3-edge XANES and FT-EXAFS spectra of the reference WO3 sample and the Pd-loaded WO3-based catalysts. All samples exhibited spectral features comparable to WO3, confirming the predominance of W(VI). Notably, variations in the intensity of the white line were observed. The reference WO3 displayed a broad white-line peak with a characteristic plateau. In contrast, other WO3−x samples showed narrower peaks shifted slightly toward lower energy with enhanced intensity, indicating distortions in the local coordination environment of W. Such distortions are typically associated with oxygen vacancies in non-stoichiometric WO3. Importantly, no appreciable changes in XANES were observed upon Pd loading. | ||
| Fig. 6 XANES of (a) W L3-edge and (b) Pd K-edge and FT-EXAFS of (c) W L3-edge (d) Pd K-edge for prepared samples. | ||
The Pd K-edge XANES and FT-EXAFS of the prepared samples are shown in Fig. 6(b and d) along with the reference Pd foil and PdO. All samples exhibited absorption features closely resembling metallic Pd foil, confirming that Pd predominantly exists in the metallic state. However, Pd colloids/WO3−x and Pd-WO3−x-S (PVP) displayed slight deviations in white-line intensity compared to Pd foil, suggesting partial oxidation of Pd. The absence of distinct PdO-like features in other samples indicates a stable metallic Pd environment. These findings confirm that the co-catalyst maintains its metallic state, with minor oxidation effects.
Evaluation of photocatalytic performance
4-Nitrophenol (4-NP) is a toxic organic contaminant frequently detected in industrial and agricultural wastewater, resulting in environmental and health concerns. In contrast, an important chemical intermediate, 4-aminophenol (4-AP), is widely utilized in the production of pharmaceuticals like analgesics and antipyretics, as well as dyes, polymers, and natural products.55 Several treatment methods, including oxidation, degradation, adsorption, and coagulation, have been developed to remove or convert 4-NP.56,57 To address these issues, greener and more efficient methods are being explored for the catalytic reduction of 4-NP into 4-AP.56,58 Herein, we used the catalytic conversion of 4-NP to 4-AP (Fig. 7a) as a model reaction to evaluate the catalytic activity in the presence and absence of light irradiation. AB was used as the source of in situ hydrogen generation due to its high stability, non-toxic nature, and ease of handling, offering a safer and more sustainable alternative.59Fig. 7(b and c) illustrates the kinetics of the catalytic conversion for the catalytic reduction of 4-NP to 4-AP in dark and light irradiation conditions, plotted as −ln(C/C0) versus time, where C0 denotes the initial concentration of 4-NP, while C refers to its concentration at a given reaction time. The reduction efficiency varied with the nature of the catalyst employed, highlighting the significance of structural properties and material composition on the catalytic performance. The reaction rate in dark conditions (Fig. 7(b)) follows the order: Pd colloids/WO3−x > Pd/WO3−x > Pd/Commercial WO3. Pd-WO3−x-S and Pd-WO3−x-S (PVP) prepared via the solvothermal method did not show any catalytic activity. Also, bare WO3−x and commercial WO3 were inactive in this reaction. The hydrogen evolution in the dark arises solely from the catalytic contributions of Pd and defect-rich WO3−x. In this system, Pd acts as the primary active site for AB decomposition due to its well-known intrinsic catalytic activity under dark conditions. The hydrogenation of 4-NP predominantly occurs on Pd NPs, where activated hydrogen is transferred to the nitro group. Fig. 7(d) shows that WO3−x alone is inactive for 4-NP reduction, while Pd/WO3−x exhibits a much faster reaction rate. This confirms that Pd acts as the hydrogen-activating site. Metallic Pd0 dissociates H2 or forms surface hydrides, which transfer hydrogen to the –NO2 group, enabling efficient conversion of 4-NP to 4-AP.60
The same trend in the catalytic performance with enhanced reaction rates was obtained under light irradiation, as shown in Fig. 7(c).
The reaction was assumed to follow pseudo-first-order kinetics. The rate constant (min−1) under light irradiation follows the order (Pd colloids/WO3−x (0.75) > Pd/WO3−x (0.61) > Pd/commercial WO3 (0.35)). Under dark conditions, the corresponding values are 0.30, 0.32, and 0.21 for Pd colloids/WO3−x, Pd/WO3−x, and Pd/Commercial WO3, respectively. The comparison of the reaction rate constant in dark and light irradiation is shown in Fig. 7(d). From the obtained values, we conclude that the catalyst prepared via the impregnation method shows significantly higher activity in comparison to the solvothermal method. The sample prepared via the solvothermal method using PVP surfactant (Pd-WO3−x-S (PVP)) and without using surfactant (Pd-WO3−x-S), showed no observable activity either in dark or light irradiation conditions. The XPS analysis of these samples shows a very weak Pd signal, indicating that only a small amount of Pd is exposed on the surface. This limits the exposed Pd sites, resulting in poor catalytic activity. The kinetics of catalysis in dark and under light irradiation conditions measured via UV-vis absorption for the most active sample, Pd colloids/WO3−x, are shown in Fig. S8.
We expect that the impregnation method facilitated a more uniform distribution of metal NPs on the photocatalyst support, enhancing active sites for the reaction. In contrast, the solvothermal method, especially when performed in the presence of surfactant, may partially encapsulate active metal NPs, limiting their accessibility during the reaction. Moreover, the solvothermal conditions often lead to the formation of larger-sized/agglomerated particles that subsequently reduce surface area and catalytic efficiency. Additionally, catalysts prepared by impregnation tend to exhibit better metal-support interaction, promoting effective separation of photogenerated charge carriers. Overall, the structural and morphological advantages achieved by the impregnation method provide a more favourable system, leading to improved conversion efficiency in the reduction of 4-NP.
Commercial WO3 has a wide band gap with limited visible-light absorption, whereas WO3−x shows band-gap narrowing due to oxygen vacancies, which introduce defects, extend visible-light absorption, and act as electron traps that suppress recombination and enhance electron transfer. The increased surface electron density also improves 4-NP adsorption and activation. Pd nanoparticles serve as an active site and facilitate catalytic reaction by acting as an electron sink, enabling rapid transfer of photogenerated electrons from WO3−x and promoting strong charge separation.
The photocatalytic activity of Pd colloids/WO3−x with 1.0, 2.5, and 5.0 wt% Pd was also investigated (Fig. S9). The 2.5 wt% sample showed much faster reaction rate than 1.0 wt%, confirming that additional Pd sites enhance electron trapping and accelerate reaction kinetics. At 5.0 wt%, the activity became extremely rapid, completing the reaction within 5 minutes in the dark and 2 minutes under light irradiation conditions, making kinetic analysis difficult. These results clearly demonstrate that increasing the Pd loading steadily enhances both dark and light-driven reduction pathways. Table S2 provides a comparative overview of reported plasmonic photocatalysts and their kinetic performance toward 4-NP reduction, enabling direct assessment of their relative catalytic efficiencies.
To identify the reactive species that drive the conversion of 4-NP reduction to 4-AP over Pd-colloids/WO3−x catalyst, a systematic scavenger study was performed. All reactions were carried out under the standard conditions as described earlier, with the addition of 2.5 mM of scavenger. As illustrated in Fig. 7(e), without using any scavenger, the reaction rate was not affected. However, by adding a hydroxyl radical scavenger, isopropanol (IPA), the reaction rate was not much affected, suggesting ·OH radicals may contribute to the reaction, but are not the dominant species. Ethanol, a hole scavenger, led to a noticeable decrease in the rate, indicating that photogenerated holes indirectly affect the reaction by influencing charge recombination dynamics. In contrast, a significant decrease in the reaction rate was observed with the addition of electron scavengers, DMSO and O2. These findings confirm that photogenerated electrons are the dominant species driving 4-NP reduction, while the ·OH radicals and holes play supportive roles.61,62
To investigate the structural and morphological changes leading to catalyst deactivation, an increased amount of catalyst (20 mg instead of the standard 5 mg) was used in subsequent cycles under the same reaction conditions as shown in Fig. 8(a). After each cycle, nitrogen gas was introduced into the reactor for 10 min to eliminate the hydrogen generated from AB. The catalyst was not separated or washed; instead, fresh 4-NP and AB solutions were added directly to the existing catalyst suspension to initiate the next cycle. The reaction was repeated under the same conditions for three cycles. The catalytic activity was maintained up to two cycles, and a decrease in activity was observed in the third cycle, indicating catalyst deactivation. The gradual decrease in activity may be due to changes on the catalyst surface, such as nanoparticle aggregation or surface blocking. The post-reaction characterization using XRD and TEM was carried out to examine the crystal structure and morphological changes after recycling, as shown in Fig. 8(b–d). XRD analysis Fig. 8(b) confirmed that the monoclinic phase of WO3−x is preserved after the reaction, indicating structural stability. However, impurity peaks were also observed, probably due to the formation of by-products during the catalytic process. The TEM images before the reaction (Fig. 8(c)) exhibit a loosely arranged nanorod morphology with uniformly dispersed Pd NPs. After the reaction (Fig. 8(d)), the nanorods transform into more densely packed aggregates. This morphological change may reduce surface accessibility and hinder mass transport, potentially impacting catalytic performance.
The reduction of 4-NP facilitated by Pd colloids/WO3−x in the presence of AB proceeds through a synergistic photocatalytic pathway involving light absorption, hydrogen generation, and selective hydrogen transfer, as illustrated in Scheme 1(a). The photocatalytic efficiency arises from the readily accessible active Pd metal sites. The reduction of 4-NP proceeds through two key steps: (1) the mildly basic ammonia borane converts 4-NP to the nitrophenolate ion, forming a stable intermediate; and (2) the nitrophenolate ion is subsequently reduced to 4-AP on the catalyst surface, as illustrated in Scheme 1(a). Hydrogen generated in situ from ammonia borane is transferred to the adsorbed nitrophenolate species, reducing the nitro group to an amino group, after which 4-AP desorbs from the catalyst surface. Additionally, these reactive hydrogen species may synergistically interact with photogenerated electrons originating from WO3−x, contributing to the stepwise conversion of 4-NP to its 4-hydroxylaminophenol intermediate and finally to 4-AP.61,63 The combined effects of oxygen vacancy-mediated charge separation, plasmonic electron trapping at Pd sites, under visible light irradiation make this catalytic system efficient.49–51
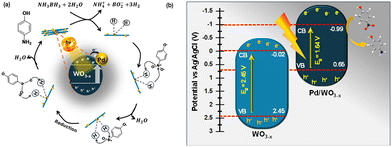 | ||
| Scheme 1 (a) Plausible reaction pathway and (b) band alignment of WO3−x and Pd/WO3−x illustrating electron transfer under illumination, enabling efficient photoreduction of 4-NP. | ||
The Mott–Schottky plots provide the conduction band edge positions, which were found to be −0.11 V (WO3), −0.02 V (WO3−x), and −0.99 V (Pd colloids/WO3−x) vs. Ag/AgCl. Using these values along with the experimentally determined band gaps (2.58 eV for WO3, 2.45 eV for WO3−x, and 1.64 eV for Pd colloids/WO3−x), the valence band positions were calculated as +2.47 V, +2.45 V, and +1.64 V, respectively, as shown in Scheme 1(b). Importantly, the conduction band of Pd colloids/WO3−x lies at −0.99 V, which is sufficiently negative to thermodynamically drive the reduction of 4-nitrophenol (−0.76 V to −0.80 V vs. Ag/AgCl).64 This confirms that electron transfer from the Pd colloids/WO3−x CB to nitrophenol is energetically feasible, whereas bare WO3 and WO3−x do not possess sufficiently negative CB positions. The significant CB shift and narrowed bandgap for Pd colloids/WO3−x also indicate enhanced electron density and improved charge separation at the interface. Therefore, the inclusion of band-edge positions directly supports our proposed redox mechanism and validates the claim that Pd colloids/WO3−x exhibits improved e−/h+ separation and is energetically favorable for nitrophenol reduction.65
Conclusions
In conclusion, Pd-deposited WO3−x photocatalysts were prepared via impregnation and solvothermal methods by tuning their morphology (nanorods, nanosheets, and nanoblocks). The prepared catalysts were characterized by XRD, SEM, HR-TEM, XAS, BET, Mott Schottky, XPS, and EPR to examine the crystallographic structure, morphological variations, surface area characteristics, and the presence of oxygen defects. The defect-engineered WO3−x showed an approximately 30 times enhancement in surface area compared to commercial WO3, demonstrating the effectiveness of defect introduction. The UV-vis analysis revealed improved light absorption in the visible to near-infrared region. Among all catalysts, Pd colloids/WO3−x and Pd/WO3−x exhibited superior catalytic performance for the reduction of 4-NP, with higher values of reaction rate constant 0.75 min−1 and 0.61 min−1, respectively, under light irradiation conditions. An approximate 2.5 times enhancement in the reaction rate was observed in comparison to dark conditions, with a reaction rate of 0.30 min−1 and 0.37 min−1 for Pd colloids/WO3−x and Pd/WO3−x, respectively. Additionally, the catalysts demonstrated stability and reusability in recycling tests. To understand the reaction mechanism, scavenger experiments were carried out, providing insight into the photocatalytic process. Overall, this work highlights the potential of Pd deposited oxygen-deficient WO3−x nanomaterials, engineered through controlled morphology, for enhanced photocatalytic applications under broad-spectrum light irradiation.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Data availability
The data supporting this article have been included as part of the supplementary information (SI).Supplementary information: synthesis of colloidal Pd nanoparticles, thermogravimetric analysis, FT-IR spectra, XPS, Mott–Schottky and Tauc plot. Reaction kinetics for nitroaromatic reduction reaction. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d5cy01196e.
Acknowledgements
Priyanka Verma thanks the seed and matching equipment grant supported by IIT Delhi (MI03052; MI03068), CSIR-ASPIRE scheme (01WS(10)/2023-2024/EMRII/ASPIRE), and the Research Fund by the Royal Society of Chemistry (R24-1159911204) for the financial support. Priyanka (Ref. No. 231610046924) thanks UGC for the PhD fellowship. SY thanks the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI (No. 24H02217 in Transformative Research Areas (A) JP24A202 Integrated Science of Synthesis by Chemical Structure Reprogramming). The authors thank the Central Research Facility (CRF) and Nanoscale Research Facility (NRF) at IIT Delhi for providing access to research infrastructure. XAFS measurements were performed at SPring-8 (Proposal number 2025A1655).References
- P. Verma, Y. Kuwahara, K. Mori, R. Watanabe, C. Fukuhara and H. Yamashita, Energy Fuels, 2023, 37, 17652–17666 CrossRef CAS
.
- J. Barber, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2009, 38, 185–196 RSC
.
- A. K. Nayak and D. Pradhan, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2018, 122, 3183–3193 CrossRef CAS
.
- H. Robatjazi, S. M. Bahauddin, C. Doiron and I. Thomann, Nano Lett., 2015, 15, 6155–6161 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- S. Linic, P. Christopher and D. B. Ingram, Nat. Mater., 2011, 10, 911–921 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- J. Lee, S. Mubeen, X. Ji, G. D. Stucky and M. Moskovits, Nano Lett., 2012, 12, 5014–5019 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- J. A. Faucheaux, A. L. D. Stanton and P. K. Jain, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2014, 5, 976–985 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- P. Verma, K. Mori, Y. Kuwahara, R. Raja and H. Yamashita, Mater. Adv., 2021, 2, 880–906 Search PubMed
.
- R. Jiang, B. Li, C. Fang and J. Wang, Adv. Mater., 2014, 26, 5274–5309 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- S. Luo, X. Ren, H. Lin, H. Song and J. Ye, Chem. Sci., 2021, 12, 5701–5719 RSC
.
- E. Petryayeva and U. J. Krull, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2011, 706, 8–24 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- S. J. A. Moniz, S. A. Shevlin, D. J. Martin, Z. X. Guo and J. Tang, Energy Environ. Sci., 2015, 8, 731–759 RSC
.
- S. Vikal, Y. K. Gautam, S. Meena, V. Parewa, A. Kumar, S. Meena, S. Kumar and B. P. Singh, Nanoscale Adv., 2023, 5, 805–819 RSC
.
- D. Chen, Y. Cheng, N. Zhou, P. Chen, Y. Wang, K. Li, S. Huo, P. Cheng, P. Peng, R. Zhang, L. Wang, H. Liu, Y. Liu and R. Ruan, J. Cleaner Prod., 2020, 268, 121725 CrossRef CAS
.
- A. Zarei, F. Hedayatinasab and H. Rezaei-Vahidian, Environ. Prog. Sustainable Energy, 2020, 39, e13386 CrossRef CAS
.
- S. Nishimoto, T. Mano, Y. Kameshima and M. Miyake, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2010, 500, 86–89 CrossRef CAS
.
- S. Singh, S. Parveen, L. Clarizia and P. Kumar, Catal. Rev.: Sci. Eng., 2025, 1–49 Search PubMed
.
- L. Wang, X. Xu, Z. Feng, L. Bian and Y. Wang, J. Solid State Chem., 2018, 266, 23–30 CrossRef CAS
.
- Y. Huang, Y. Yu, Y. Yu and B. Zhang, Sol. RRL, 2020, 4, 2000037 CrossRef CAS
.
- K. Pan, K. Shan, S. Wei, K. Li, J. Zhu, S. H. Siyal and H. H. Wu, Compos. Commun., 2019, 16, 106–110 CrossRef
.
- J. Chen, S. Shen, P. Guo, M. Wang, J. Su, D. Zhao and L. Guo, J. Mater. Res., 2014, 29, 64–70 CrossRef CAS
.
- T. Paik, M. Cargnello, T. R. Gordon, S. Zhang, H. Yun, J. D. Lee, H. Y. Woo, S. J. Oh, C. R. Kagan, P. Fornasiero and C. B. Murray, ACS Energy Lett., 2018, 3, 1904–1910 CrossRef CAS
.
- L. Zhang, H. Wang, J. Liu, Q. Zhang and H. Yan, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron., 2020, 31, 861–873 CrossRef CAS
.
- H. Quan, Y. Gao and W. Wang, Inorg. Chem. Front., 2020, 7, 817–838 RSC
.
- Q. Liu, F. Wang, H. Lin, Y. Xie, N. Tong, J. Lin, X. Zhang, Z. Zhang and X. Wang, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2018, 8, 4399–4406 RSC
.
- H. Yin, Y. Kuwahara, K. Mori, H. Cheng, M. Wen, Y. Huo and H. Yamashita, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2017, 121, 23531–23540 CrossRef CAS
.
- H. Cheng, T. Kamegawa, K. Mori and H. Yamashita, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 2910–2914 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- S. Meena, M. Sethi, S. Meena, P. Saini, K. Kumar, S. Saini, S. Shekhawat, M. L. Meena, A. Dandia, S.-D. Lin and V. Parewa, Environ. Res., 2023, 231, 116181 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- Z. Lou, Q. Gu, Y. Liao, S. Yu and C. Xue, Appl. Catal., B, 2016, 184, 258–263 CrossRef CAS
.
- Dimple, Priyanka, R. Watanabe, C. Fukuhara, H. Yamashita and P. Verma, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2024, 14, 4775–4798 Search PubMed
.
- G. Xi, S. Ouyang, P. Li, J. Ye, Q. Ma, N. Su, H. Bai and C. Wang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 2395–2399 Search PubMed
.
- C. M. Wu, S. Naseem, M. H. Chou, J. H. Wang and Y. Q. Jian, Front. Mater., 2019, 6, 00049 CrossRef
.
- P. Verma, Y. Kuwahara, K. Mori and H. Yamashita, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2017, 7, 2551–2558 RSC
.
- M. Navlani-Garcia, M. Martis, D. Lozano-Castello, D. Cazorla-Amoros, K. Mori and H. Yamashita, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2015, 5, 364–371 RSC
.
- M. Navlani-Garcia, K. Mori, A. Nozaki, Y. Kuwahara and H. Yamashita, ChemistrySelect, 2016, 1, 1879–1886 Search PubMed
.
- T. Song, F. Gao, S. Guo, Y. Zhang, S. Li, H. You and Y. Du, Nanoscale, 2021, 13, 3895–3910 Search PubMed
.
- H. Asakura, S. Yamazoe, T. Misumi, A. Fujita, T. Tsukuda and T. Tanaka, Radiat. Phys. Chem., 2020, 175, 108270 CrossRef CAS
.
- Z. Lou, Q. Gu, L. Xu, Y. Liao and C. Xue, Chem. – Asian J., 2015, 10, 1291–1294 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- Dimple, S. Pratap Singh, F. Amano, K. Beppu, R. Watanabe, C. Fukuhara and P. Verma, ChemCatChem, 2025, e00795 CrossRef
.
- Y. Lu, Y. Jiang, X. Gao, X. Wang and W. Chen, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 11687–11697 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- G. Hai, J. Huang, L. Cao, Y. Jie, J. Li, X. Wang and G. Zhang, J. Alloys Compd., 2017, 690, 239–248 CrossRef CAS
.
- K. Zhang, Y. Li, Z. Fu, X. Chi, Y. Xiong, Y. Yao, X. Wang, Z. Tang, J. Wang, K. Nie, Z. Yang and Y. M. Yan, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2023, 15, 15024–15035 CAS
.
- W. Q. Zhao, Q. Zhao, Z. K. Song, L. Ma, X. B. Chen, S. J. Ding and L. Zhou, ACS Appl. Nano Mater., 2022, 5, 16440–16450 CrossRef CAS
.
- K. Shi, F. Wang, X. Li, W. Huang, K. Lu, C. Yu and K. Yang, J. Mater. Sci., 2023, 58, 16309–16321 CrossRef CAS
.
- P. Gholami, A. Khataee and A. Bhatnagar, J. Cleaner Prod., 2020, 275, 124157 CrossRef CAS
.
- P. Gholami, A. Khataee, A. Bhatnagar and B. Vahid, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13, 13072–13086 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- F. Liu, X. Chen, Q. Xia, L. Tian and X. Chen, RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 77423–77428 RSC
.
- K. Kumar Das, D. P. Sahoo, S. Mansingh and K. Parida, ACS Omega, 2021, 6, 30401–30418 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- A. Jaryal, V. Rao Battula and K. Kailasam, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2020, 3, 4669–4676 CrossRef CAS
.
- Y. Kong, H. Sun, W. Fan, L. Wang, H. Zhao, X. Zhao and S. Yuan, RSC Adv., 2017, 7, 15201–15210 RSC
.
- Y. Xia, X. Xia, S. Zhu, R. Liang, G. Yan, F. Chen and X. Wang, Molecules, 2023, 28, 8013 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- M. B. Cetin, T. Top, M. Yurderi, M. Zahmakıran and M. Rakap, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 72, 60–73 CrossRef CAS
.
- M. Takahashi, Y. Kitazaki, H. Oshima, M. Harada and S. Maenosono, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2023, 127, 8175–8185 CrossRef CAS
.
- A. Kuzmin, J. Purans and P. Parent, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 1993, 5, 9423–9430 CrossRef CAS
.
- Ajay, H. Jaipal, R. Watanabe, C. Fukuhara and P. Verma, J. Chem. Sci., 2025, 137, 14 CrossRef CAS
.
- S. Maged, O. M. El-Borady, H. El-Hosainy and M. El-Kemary, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., 2023, 30, 117909–117922 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- H. Zhang, Q. Niu, Y. Mou, Z. Bian, T. Zhang, C. Chu, D. Han, F. Wang, G. Wang and L. Bing, J. Environ. Chem. Eng., 2025, 13, 115936 CrossRef CAS
.
- Z. Yuan, X. Wang, Y. Liu, P. Zhou and R. Y. Liu, React. Chem. Eng., 2025, 10, 953–958 RSC
.
- P. Verma, M. Navlani-García, Y. Kuwahara, K. Mori and H. Yamashita, J. Chem. Sci., 2017, 129, 1661–1669 CrossRef CAS
.
- B. D. Adams and A. Chen, Mater. Today, 2011, 14, 6 CrossRef
.
- S. Velusamy, A. Roy, E. Mariam, S. Krishnamurthy, S. Sundaram and T. K. Mallick, Sci. Rep., 2023, 13, 1 CrossRef PubMed
.
- G. Naresh and T. K. Mandal, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, 6, 21000–21010 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- N. C. Para, A. Raj and M. Haukka, Nano Sel., 2025, e70074 CrossRef
.
- A. K. Samuel, Z. Ertekin, B. Moses Abraham, Z. Yang, M. D. Symes and A. Y. Ganin, Dalton Trans., 2025, 54, 16525–16534 RSC
.
- M. Ismael, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 2023, 439, 114576 CrossRef CAS
.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2026 |





