A review of recent advances in thermal-catalytic cracking of plastic waste
Zhongxu
Wang
,
Jiahui
Zhang
,
Qihao
Wu
,
Quanhua
Wang
 ,
Yi
Liu
,
Jiajun
Zheng
,
Yi
Liu
,
Jiajun
Zheng
 *,
Yan
Wang
*,
Yan
Wang
 ,
Weijiong
Dai
,
Weijiong
Dai
 and
Ruifeng
Li
and
Ruifeng
Li
 *
*
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, College of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Research Centre of Energy Chemical & Catalytic Technology, Taiyuan University of Technology, 79# West Yingze Street, Taiyuan 030024, China. E-mail: zhengjiajun@tyut.edu.cn; rfli@tyut.edu.cn; Tel: +86 03516018384
First published on 27th November 2025
Abstract
The extensive use of plastics has resulted in severe environmental pollution, making the valorization of plastic waste not only a strategy for value recovery but also an effective approach to mitigate its environmental impact. Consequently, this topic has become a focal point of research in industry and academia. Pyrolysis is a key step in the carbon resource conversion of plastic waste, facilitating the degradation of complex polymeric materials into high value products such as alkanes, olefins, and BTX. This review summarizes recent advancements in plastic pyrolysis technologies, as a focus on scientific challenges and technological breakthroughs in this domain. Through a systematic analysis, the study examines the pyrolysis mechanisms and current research status of the most widely used plastics, exploring the critical factors influencing the pyrolysis process including reaction conditions, such as temperature, residence time, and catalyst dosage, and the reactor design which has a significant role in improving the pyrolysis efficiency and product selection. This review provides a summary of commonly used catalyst types, with emphasis on the exceptional performance of zeolite based catalysts and their metal modified productions. Research indicates that zeolite catalysts, owing to their strong acidity and stable pore structures, markedly enhance the activity and selectivity of pyrolysis reactions. Other catalysts such as FCC catalysts, clay catalysts and metal oxides have shown promising catalytic performance under certain conditions, offering potential for the industrial applicability of plastic pyrolysis technologies. However, plastic waste pyrolysis research remains a challenge, including regulation of reaction pathways for co-pyrolysis of multi-component plastics, reducing catalyst deactivation, and optimization of energy efficiency. These challenges not only limit further promotion of pyrolysis technologies but also demand more fundamental scientific research and engineering advances. Finally, we conclude with future research directions, with suggestions for theoretical guidance and technology support for plastic waste pyrolysis development and industrial applications.
1 Introduction
Since the early 20th century, plastics have become essential due to their lightweight, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Today, various plastics, including polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), and polystyrene (PS), are used widely in commercial applications.1 Driven by enormous demand, global plastic production has surged exponentially in recent decades, generating vast amounts of waste. In 2025, over 400 million tons of plastic waste will be generated annually, with the majority being sent to landfills. The lifecycle of plastics will emit 20 billion tons of greenhouse gases, and over 24 million tons of plastics will leak into land, rivers, and oceans.2 These plastics are slow to degrade in the natural environment, leading to widespread “white pollution”. Moreover, once plastic waste enters ecosystems, it undergoes mechanical and chemical weathering, breaking down into micro- and nanoplastics. These particles are now found in oceans, rivers, soils, and even within organisms, causing irreversible ecological damage and posing significant risks to human health.3 Despite these challenges, plastic waste is highly regarded as a valuable resource, complementing non-renewable fossil fuels, and needs efficient treatment and recycling methods.Although plastic waste is increasing worldwide, only a small fraction is recycled.4 Most plastic waste is recycled using landfilling and incineration. Landfilling consumes space and is contaminating, while incineration emits harmful emissions that pollute the air and harm human health.5 To address these problems, four recycling approaches have been developed: primary recycling (reuse), secondary recycling (mechanical processing), tertiary recycling (chemical conversion), and quaternary recycling (energy recovery).6 Primary recycling directly reprocesses clean plastics into new products suitable for single type plastics. Secondary recycling reprocesses used plastics into lower grade products, but often degrades the properties of the material. Tertiary or chemical recycling breaks plastics into monomers or other valuable chemicals such as fuels, waxes, or raw materials for new plastic production. This method is useful for complex or mixed plastics, offering high economic value and garnering significant interest. Quaternary recycling recovers energy through incineration, suitable for heavily contaminated plastics. Fig. 1(a) summarizes the life cycle of plastics.
 | ||
| Fig. 1 The lifecycle trajectory of plastics, encompassing production to post-consumer disposal (a). An elucidation of recycling strategies for post-consumer plastic waste (b).7–9 | ||
Chemical recycling is one of the most effective ways to turn plastic waste into valuable resources. High energy products such as fuel oil, olefins, BTX (benzene, toluene, and xylene), carbon materials, hydrogen, syngas, and other value added chemicals can be recovered from plastic waste.10,11 This process includes pyrolysis, rearrangement, isomerization, cyclization, hydrogen transfer, and β-scission.7 Given the chemical inertness of plastics at room temperature, these reactions typically occur at elevated temperatures. Catalysts can improve reaction kinetics and product selectivity, improve overall process efficiency and allow selective recovery of high value products.12 However, industrial implementation is still difficult due to difficulties in sorting contaminated plastic waste and development of highly active, selective and stable catalysts.
Among the methods involving chemical recycling, common approaches include: pyrolysis,13 gasification,14 steam cracking,15,16 and hydrothermal liquefaction.17,18 Pyrolysis involves treating plastic waste at high temperatures in the absence of air, breaking down large polymer chains into smaller molecules of oil, gas, and solid residues. Gasification aims to produce syngas by partially burning plastics under oxygen-limited conditions, generating a mixture rich in CO and H2, which can be used for power generation or synthesizing methanol, diesel, and other products. Steam cracking is industrially applied to produce high-value light olefins, and some researchers are exploring its adaptation for plastic cracking processes.19,20 Hydrothermal liquefaction involves the depolymerization and reorganization of plastic molecules in high-temperature and high-pressure water, forming crude oil-like “bio-crude”. Its greatest advantage is the ability to process plastics with high moisture content. Currently, researchers are focusing primarily on pyrolysis due to its higher product value and flexibility compared to other processes. Unlike low-value syngas, pyrolysis produces pyrolysis oil, a liquid with higher energy density that can be refined into diesel, naphtha, and other clean fuels or used as a chemical feedstock, offering broader applications and greater economic benefits. Additionally, pyrolysis operates under relatively milder conditions, at atmospheric or low pressure and moderate temperatures. For plastic cracking research, a standout advantage of pyrolysis is its capability to process mixed and lightly contaminated plastics. Although the presence of elements like Cl and N can affect catalyst lifespan and product quality, pretreatment can significantly mitigate these issues (Table 1).
| Technical characteristic | Pyrolysis | Gasification | Steam cracking | Hydrothermal liquefaction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Process nature | Thermal decomposition in the absence or near-absence of oxygen | Reaction with a gasifying agent (e.g., steam and O2) under oxygen-limited conditions | High-temperature cracking in a steam atmosphere | Thermal conversion in sub/supercritical water |
| Reaction environment | Oxygen-deficient/inert atmosphere | Limited oxygen, air, steam, or pure oxygen | High-temperature steam, typically oxygen-free | High-temperature and high-pressure aqueous medium |
| Main products | Pyrolysis oil, pyrolysis gas, solid char | Syngas (mainly CO + H2) | Light olefins (e.g., ethylene and propylene) | Bio-crude |
| Product state | Primarily liquid | Gaseous | Gaseous | Primarily liquid |
| Product value | Usable as a fuel or chemical feedstock | Fuel gas; feedstock for chemical synthesis | High-value chemical building blocks | Complex oil requiring further refining |
| Operating temperature | Medium (350–700 °C) | High (700–1500 °C) | Very high (750–900 °C) | Medium (300–400 °C) |
| Operating pressure | Atmospheric or slightly positive pressure | Atmospheric or pressurized | Atmospheric | Very high (10–25 MPa) |
| Pre-treatment requirements | Requires drying | Requires drying | Requires drying and high feedstock purity | Can process wet plastics directly |
Plastic pyrolysis is a non-catalytic process that requires high temperatures and energy consumption, yielding complex mixtures of low value products. Catalytic cracking allows more precise control of reaction conditions, allowing custom product compositions with low by-products.23,24 Catalytic plastic cracking can be traced back to the 1990s, when S. R. Ivanova used a MgCl2–AlCl3 catalyst to crack PE with an 88.2% gas yield, with isobutane as the main product.25 Given the challenge of catalyst separation, solid acid catalysts are considered optimal. Serrano et al. utilized nanocrystalline ZSM-5 zeolite to catalytically degrade LDPE at 420 °C, achieving complete conversion and yielding 60 wt.% C1–C5 hydrocarbons.26 Subsequently, H2 was introduced into plastic pyrolysis to obtain the highest yield of saturated hydrocarbons and reduce carbon deposition. Metal supported hydrogenolysis and hydrocracking strategies have been employed for plastic waste cracking. Metals such as Ru, Pt, Pd, and Ni have been used for this reaction.27–30 Rorrer et al. loaded Ru nanoparticles on carbon for hydrogenolysis of PP at 200–250 °C, with a yield of 68% isopropane.31 Wu et al. used CeO2 supported Ru and Pt for hydrogenolysis of polyamides.32 Hydrocracking uses bifunctional catalysts to improve the conversion of plastic waste into liquid isoparaffins. Therefore, researchers are developing more efficient methods for the chemical recycling of plastics.
Recently, many new chemical methods have been proposed for C–C cleavage, C–H functionalization and aromatic ring functionalization for upcycling of plastic waste. Wang et al.33 used β zeolite and silicalite-1 encapsulated Pt particles (Pt@S-1) for tandem catalytic conversion of LDPE into naphtha at 250 °C, and the naphtha yield reached 89.5%, with a C5–C9 hydrocarbon selectivity of 96.8%. In this process, acid sites cleaved the long-chain LDPE into olefin intermediates, which were selectively converted into appropriately sized olefins and alkanes within the Pt@S-1 channels. Yan et al.34 developed a multifunctional Ru/Nb2O5 catalyst for directly upgrading aromatic plastic waste to aromatic hydrocarbons. This catalyst catalyzes single component plastic waste and mixed aromatic plastics into aromatics. NbOX is used for C–O bond activation, Brønsted acid sites for C–C bond activation, and Ru to prevent hydrogenation of the benzene ring. Liu et al.35 designed a RuReOX/SiO2 + HZSM-5 catalytic system for the hydrodeoxygenation (HDO) of aromatic plastic waste such as PET, PBT, PC, and PPO, and demonstrated the potential of HDO products as liquid organic hydrogen carriers (LOHCs). Liu et al.36 employed mesoporous SBA-15 as a precursor to synthesize a series of embryonic stage, partially crystalline, and fully crystalline β zeolites with tunable porosity and acidity. The optimal balance of acidity and porosity enabled the controllable selective conversion of PE into either diesel or lubricant base oil. The study revealed that catalysts possessing mesoporous structures and suitable acidity facilitated the rapid diffusion of intermediate products and minimized undesirable cracking by-products, leading to a high yield of lubricant base oil. Conversely, a higher concentration of micropores and greater acid site density promoted multiple cracking events within the PE, favoring the formation of low carbon number hydrocarbons. Overall, Fig. 1(b) summarizes the recycling technologies for plastic waste. Although many new methods have been developed, due to high equipment costs and difficulties in catalyst preparation, widespread industrial application remains challenging. Therefore, plastic waste upcycling still holds great potential for future development.
Plastic waste pyrolysis has become a major topic in academia. Research was extensive and in-depth, leading to important results. In this paper, we analyze current results, present differences between the pyrolysis processes of different types of plastics, explain pyrolysis reactions, classify the catalysts, and summarize the key parameters of pyrolysis reactions, including temperature, the reactor type, residence time, pressure, the type and flow rate of fluidizing gases and the impact of the by-products. In addition, we analyze current challenges and future development, providing scientific support and technical guidance for efficient pyrolysis of plastic waste.
2 The impact of plastic waste structures on pyrolytic degradation
To analyze the thermal cracking performance of various plastics, we have developed a method using the measurement of four elements of the chemical properties of plastics. These four elements are moisture content, fixed carbon, volatile matter and ash content.37 Volatile matter and ash content play an important role in the yield of liquid oil. Higher volatility content favours the production of liquid oil while higher ash content reduces the yield of liquid oil and increases the yield of gases and coke.38Table 2 summarizes the chemical structures of common plastics and the volatile matter and ash content of the polymers. All plastics have high volatile matter content and low ash content, indicating that plastics can be used as feedstocks for cracking oil. However, because different plastics have different compositions and chemical properties, their cracking processes differ. This chapter will summarize the impact of different plastic properties.| SPI code | Type of plastic | Chemical structure | Moisture (wt%) | Fixed carbon (wt%) | Volatile (wt%) | Ash (wt%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) |

|
0.46 | 7.7 | 91.75 | 0.02 | 39, 40 |
| 0.61 | 13.17 | 86.83 | 0.00 | ||||
| 2 | High-density polyethylene (HDPE) |
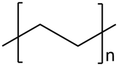
|
0.00 | 0.01 | 99.81 | 0.18 | 40, 41 |
| 0.00 | 0.03 | 98.57 | 1.40 | ||||
| 3 | Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) |

|
0.80 | 6.30 | 93.70 | 0.00 | 40, 42 |
| 0.74 | 5.19 | 94.82 | 0.00 | ||||
| 4 | Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) |
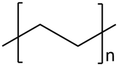
|
0.30 | 0.00 | 99.70 | 0.00 | 43, 44 |
| — | — | 99.60 | 0.40 | ||||
| 5 | Polypropylene (PP) |
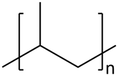
|
0.15 | 1.22 | 95.08 | 3.55 | 40, 45 |
| 0.18 | 0.16 | 97.85 | 1.99 | ||||
| 6 | Polystyrene (PS) |
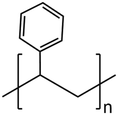
|
0.25 | 0.12 | 99.63 | 0.00 | 43, 46 |
| 0.30 | 0.20 | 99.50 | 0.00 | ||||
| Others | Polyethylene (PE) | — | 0.10 | 0.04 | 98.87 | 0.99 | 40, 45, 47 |
| Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) | — | 0.00 | 1.12 | 97.88 | 1.01 | ||
| Polyamide (PA) or nylon | — | 0.00 | 0.69 | 99.78 | 0.00 | ||
| Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) | — | 0.16 | 2.88 | 97.12 | 0.00 |
2.1 Polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a semicrystalline polymer formed by polycondensation of TPA and EG to produce a linear polyester with ester linkages (–COO–) in its structure. These ester linkages can be easily cleaved at high temperatures or using catalysts, leading to PET degradation at the surface. Because of its high molecular weight and the stability of aromatic rings, PET degradation requires considerable energy.48,49 As a polyester possessing β-H, the thermal degradation of PET predominantly proceeds through a cyclic transition state.50 The thermal decomposition of PET between 500 and 700 °C usually does not yield valuable chemicals. PET has a relatively low volatile content (86.83%), lower than most other plastics (generally over 90%). The gas yield from PET pyrolysis tends to be quite high, while pyrolysis oil typically contains terephthalic acid and benzoic acid, which can corrode and block process equipment due to their acidic nature.51,52 As such, further development of the pyrolysis products is required. Currently, the main products of PET pyrolysis are terephthalic acid and vinyl benzoate, which can be converted into aromatic hydrocarbons using oxidative catalysts.53 Many catalysts have been used in PET pyrolysis, including ZSM-5,54 FeOOH,55 and metal oxides such as CaO, ZnO, MgO, and TiO2.56,57 Masuda et al.58 reported that PET pyrolysis at 500 °C with steam produced 56 wt% pyrolysis oil, composed of 46 wt% acetophenone, 28 wt% benzene and 14 wt% phenol.Current researchers are no longer satisfied with simply producing fuels or basic chemicals from PET pyrolysis, but are focusing on high-value, functionalized specific chemicals and committed to developing greener and more efficient conversion pathways. The closed-loop recycling route for PET, achieved through the precise recovery of terephthalic acid (TPA) and ethylene glycol (EG) monomers using tandem reactors, represents an efficient recycling pathway. Cao et al.59 developed a reconstructed defective metal–organic framework catalyst, where the zinc-rich defect sites formed on its surface enabled efficient generation of BHET (bis(2-hydroxyethyl) terephthalate) products.
2.2 High density polyethylene (HDPE)
High density polyethylene (HDPE) is a linear low-branch polymer, made from polymerization of ethylene monomers, which is crystallized with high crystallinity, high strength, and excellent chemical stability. HDPE is the third largest type of plastic found in MSW, and a high liquid yield can be obtained by selecting appropriate reaction conditions. Hence, researchers tested HDPE pyrolysis under different reaction conditions.60 Artetxe et al.61 used HZSM-5 zeolite as a catalyst in a two-step reaction system for HDPE pyrolysis, achieving a light olefin yield of 62.9 wt% at 550 °C and a catalyst-to-HDPE ratio of 8 gcat min gHDPE−1.10,11 The yields of ethylene, propylene, and butene were 10.6%, 35.6% and 16.7%, respectively. A conical spouted bed reactor was used for continuous pyrolysis to produce wax products which were converted to olefins with high selectivity by HZSM-5 catalysis. Temperature (350–550 °C) and residence time changes increased the light olefin yield and reduced the C12+ hydrocarbon yield and non-aromatic C5–C11 fraction. Qian et al. synthesized Zn modified HZSM-5 to catalyze HDPE pyrolysis vapor and found that the modification promoted aromatization of HDPE vapor yielding 53% aromatics and 93% BTX products. The aromatization of HDPE vapor to monocyclic aromatics is believed to be mainly enabled by active species such as [ZnOH]+ and bridged Zn2+ species, and the selectivity to BTX is limited by the spatial constraints of zeolite pores and the size of olefin intermediates.62Research on HDPE pyrolysis primarily focuses on thermal cracking for fuel production and monomer extraction. For instance, Hu et al.63 developed a gradient porous pyrolysis technology that creates a “molecular gating effect,” where large-molecule intermediates become temporarily trapped when attempting to pass through small pores, thereby extending their residence time for sufficient cracking, while target-sized small molecules can pass through smoothly, avoiding over-cracking. This enables highly efficient conversion of HDPE into aviation fuel. Significant achievements have also been made in the production of high-value chemicals from HDPE. Recently, Han et al.,64 under a kinetic decoupling–recoupling (KDRC) strategy, utilized dual catalysts and segmented temperature control to efficiently convert reaction intermediates into ethylene and propylene. This entire process operates without metals or external hydrogen, representing a breakthrough in the production of high-value chemicals from HDPE.
2.3 Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is synthesized by polymerization of vinyl chloride monomer and has a linear structure with chlorine atoms evenly distributed along the chain. Chlorine is flame-retardant and is suitable for electrical insulation applications. Due to keto allyl chloride, tertiary chloride and allyl chloride structures, PVC has poor thermal stability. After heating to a certain temperature, PVC releases HCl which triggers chain reactions that accelerate further degradation of PVC.65,66 The release of HCl during the pyrolysis of PVC introduces additional challenges, such as equipment corrosion and catalyst poisoning, making the degradation process more complex. PVC pyrolysis occurs in three consecutive stages: (1) decomposition into intermediates and HCl; (2) further degradation of intermediates into polyene chains and other volatiles; (3) decomposition of the polyene chains into toluene and other aromatics.67 TGA shows that pre-dechlorination in the temperature range of 200–340 °C decreases the chlorine content in the final pyrolysis oil. Once the temperature increases, C–C bonds are broken. However, chlorine removal is not complete due to (a) a small number of isolated chlorine atoms (2 wt%) locked in the residues due to cyclization and cross linking in the pyrolysis; (b) long reaction times which often result in HCl becoming chlorinated hydrocarbons interacting with pyrolysis gas products; (c) other molten plastics which hinder the release of HCl from solid residues; (d) the formation of chlorinated hydrocarbons. PVC pyrolysis can be divided into catalytic dechlorination and cracking. Dechlorination can be achieved by stepwise pyrolysis, catalytic cracking, and pyrolysis with added adsorbents.68 Researchers typically divide PVC pyrolysis into two processes: catalytic dechlorination and subsequent cracking of the dechlorinated products. This dechlorination step can be achieved through several methods, such as stepwise pyrolysis, catalytic cracking, and pyrolysis in the presence of adsorbents added to the PVC samples.69 Therefore, PVC pyrolysis is significantly more difficult than other plastics because an additional dechlorination step is needed. Fortunately, the accumulation of PVC in municipal solid waste (MSW) is relatively small, comprising less than 3% of plastic waste categories, which is a fairly limited proportion.60Research on PVC pyrolysis remains centered on addressing the challenges posed by its high chlorine content, with the goal of achieving high-value resource utilization under safe and environmentally friendly premises. Various strategies have been employed for precise control and resource utilization of chlorine, including co-pyrolysis synergetic conversion,70in situ chlorine fixation and conversion technology,71 and one-step integrated processes.72 Given the complex and mixed nature of real-world plastic waste, co-pyrolysis research holds significant practical relevance. Studies demonstrate pronounced synergistic effects in PVC/PS co-pyrolysis. Compared to individual PVC pyrolysis, co-pyrolysis effectively suppresses HCl emissions and reduces the formation of chlorinated hydrocarbons. Concurrently, chlorine release behavior shifts, with more chlorine remaining in the solid residues, facilitating subsequent centralized treatment. This provides a novel approach for the safe processing of mixed plastic waste.
2.4 Low density polyethylene (LDPE)
Low density polyethylene (LDPE) is characterized by a greater number of branched chains compared to HDPE, which leads to weaker intermolecular forces and thus lower tensile strength and hardness.37 But it is ductile and water resistant and used in everyday products such as plastic bags, packaging, and garbage bags. Therefore, LDPE is the second largest solid waste in volume. Recycling and valorization of LDPE have also been studied. Li et al.33 employed Pt nanoparticles encapsulated in silicalite-1 (Pt@S-1) and β zeolite to catalyzed LDPE naphtha yield of 89.5% at 250 °C with C5–C9 hydrocarbons representing 96.8% of product selectivity. In another study, Wang et al.73 synthesized ZSM-5 zeolite with varied acid concentrations by modulating Al sites to catalyze the pyrolysis of LDPE. The increased presence of Al pairs at the channel intersections of the zeolite provides both a spacious environment and active sites, facilitating secondary reactions such as Diels–Alder reactions, cyclization, and dehydrogenation. This consequently results in a low light olefin yield of only 10.6 wt% and gives rise to conversion to light alkanes and aromatics.LDPE shares similar characteristics with HDPE in thermal pyrolysis, with the goal remaining efficient, highly selective conversion to produce fuels and chemicals of higher economic value. Researchers achieve the generation of high-value target products through precise design and optimization of catalysts. In one study, investigators constructed mesopores in Y zeolite using zeolite dissolution–gelation skeleton reinforcement (ZDGSR) technology, forming a macro–meso–microporous hierarchical pore architecture that provides smoother diffusion pathways for LDPE macromolecules and their cracking intermediates.74 In another approach, Yu et al.75 achieved efficient conversion of LDPE at a low temperature of 180 °C by precisely controlling the location of Pt clusters on Hβ zeolite. When Pt subnanoclusters were positioned inside the zeolite channels, they worked in close synergy with acid sites to first induce branching modification of LDPE chains followed by deep cracking. This mechanism enhanced catalyst activity by 5-fold compared to conventional Pt catalysts and enabled a 98% yield of gasoline components.
2.5 Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene (PP) is a lightweight, chemically resistant, electrically insulating, and impact-resistant thermoplastic saturated polymer synthesized from the polymerization of propylene monomers. Compared to other plastics, PP exhibits a higher melting point, indicating superior thermal stability.76 It has a lower density than HDPE, yet possesses greater hardness and rigidity, making it more favorable in the plastics industry.77 Representing approximately 24.3% of plastic waste, PP is the most prevalent type of plastic. Consequently, PP pyrolysis has emerged as a viable method for energy recovery. The pyrolytic mechanism of PP is analogous to that of PE, involving random cleavage to produce olefins. However, the activation energy (Ea) required for C–C bond cleavage in PP is lower than that in PE, at 176 kJ mol−1versus 225 kJ mol−1, respectively. This discrepancy is attributable to the presence of tertiary carbon atoms in PP, which facilitates easier cleavage and renders tertiary radicals more stable compared to the secondary radicals found in PE.45 In a study by Streitwieser et al.,78 pyrolysis of PP, HDPE, and LDPE in a batch reactor indicates that the Ea for materials follows the order PP < HDPE < LDPE. Additionally, the products derived from HDPE and LDPE are more akin to diesel fractions, while those from PP are more similar to gasoline fractions, reflecting a lower degree of chain scission difficulty for PP. Furthermore, the product distribution in liquid oils from PP pyrolysis frequently includes branched alkanes, olefins, and various aromatics and isoprene.79,80Similar to polyethylene, research on PP pyrolysis has primarily focused on fuel production and monomer extraction, though current investigator interest has largely shifted toward monomer recovery. Researchers guide PP's cracking pathways by modulating the pore structure and acidity (strength/density) of zeolite catalysts. In monomer recovery, Wang et al.81 utilized a core–shell ZSM-5@SBA-15 composite to enhance light aromatic (BTEX) production during catalytic pyrolysis of polypropylene. The SBA-15 shell precracks heavy paraffins into light aliphatics, and the enriched intermediates subsequently diffuse through the tandem meso–micro interface to the ZSM-5 core micropores. This architectural design boosted the BTEX yield by 49.1% while reducing heavy hydrocarbon content by 42.2%. In another study, Yuan et al.82 employed a flash Joule heating (FJH) approach that efficiently depolymerizes PP plastic within millisecond residence times, achieving an 84% yield of light olefins.
2.6 Polystyrene (PS)
Polystyrene (PS) is a polymer formed from polymers of styrene monomers by free radical polymerization. Due to its glass transition temperature above 100 °C, PS is used widely in the production of disposable containers that can tolerate boiling water such as foam food containers.83 Consequently, PS contributes significantly to waste accumulation. However, PS is not commonly included in curbside recycling programs, and thus is not separated and is not economically collected for recycling. The most efficient way to recycle PS waste is pyrolysis, converting it into valuable petroleum products.84 Previous research on the catalytic cracking of PS has primarily focused on two areas: obtaining fuel fractions from PS pyrolysis or recovering monomers/chemicals from the process. Due to its relatively simple structure compared to PE and PP, PS exhibits a high conversion rate (80.8%) at both lower and higher temperatures, along with minimal gas (13%) and coke (6.2%) production, making PS pyrolysis achievable with lower energy consumption.85 Furthermore, PS pyrolysis also allows direct recovery of monomers from waste with maximum recovery yields of 55–85 wt% depending on the PS type, degradation temperature and operating time. The yield of recovered monomers during PS thermal degradation depends on the reactor design. During the reaction process, the type of reactor determines the temperature distribution and residence time, with efficient reactors potentially achieving shorter reaction residence times.86–88Due to its molecular structure, the primary objective of polystyrene (PS) pyrolysis is the highly selective conversion of waste PS into high-value chemicals and fuels to maximize resource utilization. Through targeted catalytic conversion technologies, PS macromolecules can be precisely tailored into specific high-value chemicals. Huang et al.84 developed a pre-oxidation-induced nitrogen assembly strategy that converts PS into benzonitrile and benzamide using acetonitrile as a nitrogen source under thermal catalytic conditions. Sun et al.89 created a tandem Joule heating strategy that rapidly pyrolyzes PS within 2.5 seconds, achieving a remarkable hydrogen yield of up to 99% while simultaneously converting residual carbon into high-value turbostratic graphene, enabling simultaneous valorization of both gaseous and solid products.
2.7 Mixed plastics
In everyday life, the classification of plastics introduces additional costs, and it is challenging to strictly differentiate plastic types. During the recycling process, many plastics are incompatible and cannot be processed together. For instance, PVC releases HCl gas, which causes degradation, yellowing, and brittleness in other plastics, necessitating further treatment.90 This highlights the recycling process sensitivity to contaminants, thereby increasing its complexity. Consequently, many researchers have shifted their focus towards the pyrolysis of mixed plastics. Compared to individual types of plastics, mixed plastics exhibit interactions that significantly impact the pyrolysis process. Williams91 demonstrated that mixing PS with a 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 combination of HDPE, LDPE, PP, PVC, and PET resulted in a much higher gas yield than predicted based on the pyrolysis of single plastics. The mixing process led to an increased concentration of olefin gases. However, the liquid products from the pyrolysis of mixed plastics were primarily oils. Due to the mixing, the molecular weight distribution, as well as the number average molecular weight (Mn) and weight average molecular weight (Mw) of the oils produced from mixed plastic pyrolysis, was significantly reduced.
1 combination of HDPE, LDPE, PP, PVC, and PET resulted in a much higher gas yield than predicted based on the pyrolysis of single plastics. The mixing process led to an increased concentration of olefin gases. However, the liquid products from the pyrolysis of mixed plastics were primarily oils. Due to the mixing, the molecular weight distribution, as well as the number average molecular weight (Mn) and weight average molecular weight (Mw) of the oils produced from mixed plastic pyrolysis, was significantly reduced.
Currently, extensive research has been conducted on the pyrolysis of mixed plastics. Kameda et al.92 reported that the liquid oil yield from the pyrolysis of a plastic mixture (comprising 45% PE, 20% PP, 20% PS, and 15% PET) was about 45 wt%. Previous studies on mixed feedstock pyrolysis have struggled to achieve oil yields exceeding 50 wt%, with comparable quality.93,94 Recent advances in the pyrolysis of mixed plastics have resulted in significant breakthroughs. Ma and colleagues95 designed a catalytic process using chlorinated ionic liquids (ILs), solvents and catalysts and ZnCl2 as a Lewis acid catalyst, and upgraded PVC and PET simultaneously. This innovative recycling strategy allows for the conversion of PVC and PET into high-yield dehydrochlorinated PVC (DHPVC), terephthalic acid, and 1,2-dichloroethane, which exploits the chemical reaction of high chlorine content of PVC instead of treating the resulting toxicity. Additionally, Zhang et al.96 developed a single atom Ru catalyst that allowed rapid and continuous degradation of mixed plastics in a tandem fixed bed reactor with methane as the sole product. The Ru element played a key role in hydrogenolytic plastic pyrolysis, achieving a methane yield of over 91%, with remarkable stability even after 150 catalytic cycles.
3 Mechanism analysis of plastic waste during pyrolysis
Plastic waste can be reclaimed as energy using advanced thermochemical conversion processes to reduce dependence on fossil fuels such as petroleum. Thermally and chemically broken polymers in small molecules are used to recover resources and energy. High temperature pyrolysis and catalytic cracking are two of the most promising technologies. High temperature pyrolysis operates in an oxygen-deprived environment where plastics are thermally broken into syngas, liquid hydrocarbons and solid residues. Catalytic cracking, using specific catalysts, accelerates degradation reactions at lower temperature and yields high value fuels and chemical products. Polymer pyrolysis, partial oxidation or catalytic pathways transform plastic waste into valuable resources to alleviate environmental pressures while providing renewable energy and feedstocks for further industrial use.3.1 Thermal pyrolysis
The pyrolysis process for converting plastic waste can be achieved through anaerobic heating at typically above 500 °C high temperatures. By supplying energy for thermal degradation, plastic waste can be transformed into combustible gases and liquid oils.97 Due to the different types of plastic waste structures, the resulting products differ significantly. Polyolefins and PS are suitable for producing high-energy liquid fuels; however, incomplete reactions can lead to significant wax formation. While PET can be utilized to recover valuable chemicals, secondary reactions may cause partial conversion of products into CO2 and H2.98–101Fig. 2 illustrates the distribution of products at different temperatures, using PE as an example. Under identical conditions, PS produces fewer gas components compared to PP and PE, while PE generates more wax in the liquid oil fraction than PP.102,103 This is attributed to the high crystallinity and stronger thermal and chemical stability. Tertiary carbon centers in PP are activated by C–H activation and provide free radical sites to enhance C–C bond cleavage, making PP more susceptible to oxidation and thermal degradation.103,104 In contrast, PVC is more thermally stable and its pyrolysis is slower, but it produces high amounts of HCl gas which corrodes equipment and requires pre- or post-treatment to remove Cl.65 | ||
| Fig. 2 The temperature-dependent selective products of polyethylene pyrolysis.105 | ||
The distribution and characteristics of pyrolysis products are largely governed by key process parameters, such as heating rate, reaction temperature, and residence time. By precisely controlling these conditions, high-selectivity conversion of plastic waste into high-value chemicals (e.g., monomers or olefins) or waxes can be achieved. The heating rate significantly influences the trade-off between wax and monomer yields during the reaction process. For polyolefins, fast pyrolysis causes rapid random scission of macromolecular polymer chains, generating linear alkanes and olefins with a broad molecular weight distribution.106 When the reaction extent is insufficient or the temperature is relatively low, these products primarily accumulate as waxy solids or high-boiling-point liquids. In contrast, slow pyrolysis provides longer reaction times for intermediate products, promoting secondary cracking reactions. This is particularly important for high-molecular-weight plastics like PS.107 Under slow heating conditions, the backbone of PS undergoes more ordered depolymerization dominated by end-chain scission, thereby significantly increasing the yield of its styrene monomer.108 Singh et al.109 observed that slower heating rates favor aromatic formation, whereas faster heating rates produce more gaseous products, as slow heating promotes secondary reactions, such as prolonged residence time.
Reaction temperature is the most direct factor controlling pyrolysis depth and product selectivity. At relatively low temperatures, the pyrolysis of polyolefins typically remains in the primary stage, mainly generating long-chain alkanes and olefins, resulting in a high wax yield. At this stage, random scission of molecular chains dominates, but the energy is insufficient to further crack the long-chain products into small gas molecules.110,111 As the temperature increases, the provided energy becomes sufficient to induce thorough cleavage of C–C and C–H bonds. Under these conditions, not only do the primary pyrolysis products undergo vigorous secondary reactions, but the polymer molecules themselves can also undergo deep cracking via free-radical mechanisms.112,113 For polyolefins, this means that a selective shift in products from waxes toward light olefins determines the extent of secondary reactions. Longer residence times allow initial pyrolysis products to undergo further cracking, aromatization, and condensation within the reaction zone.82,114 High temperatures combined with long residence times favor the production of olefins, but excessive reactions can also lead to increased coke formation and higher gas yields. Therefore, for processes aimed at monomer recovery, it is essential to optimize the residence time to suppress excessive decomposition.
Random chain scission in non-catalytic cracking is usually controlled by free radicals. Chain initiation, propagation and termination are the reactions involved in the plastic pyrolysis at high temperature.115–118Table 3 shows the specific reactions involved in the plastic pyrolysis at high temperatures, with Fig. 3(a) illustrating PE pyrolysis reaction processes. As shown in Fig. 3(a), chain initiation begins with random cleavage of C–C bonds along long PE chains under thermal influence to produce primary free radicals.119,120 Primary radicals may undergo intramolecular hydrogen transfer stabilizing as secondary radicals or undergo β-scission, and new primary or alkyl radicals may undergo intermolecular hydrogen transfer to obtain normal alkanes and new primary radicals, or they may react with other radicals to form isoalkanes or normal alkanes as end products.121,122 This process can continue repeatedly, ultimately yielding low molecular products. Due to the characteristics of PE, the significant presence of wax in pyrolysis products is explained. Following the free radical mechanism, primary reactions in pyrolysis involve the formation of olefins, while growth and coupling reactions produce alkanes.123
 | ||
| Fig. 3 (a) Reaction mechanism scheme of pyrolysis and (b) catalytic cracking of PE on a Brønsted acid site in the zeolite.7 Adapted with permission from American Chemical Society, copyright 2022. | ||
3.2 Catalytic cracking
Unlike thermal pyrolysis, catalytic pyrolysis uses heating plastic waste with mixed catalysts to produce pyrolysis oil. Adding catalysts reduces the activation energy of the reaction and allows for lower temperature and shorter reaction times (Table 5). This improves the overall pyrolysis process, facilitates plastic waste breakdown and increases the liquid oil yield. Pyrolysis oil has high calorific value and good performance, and can be used as an alternative fuel to petroleum and diesel. Catalytic pyrolysis uses the carbocation mechanism which differs fundamentally from the free radical mechanism of thermal pyrolysis. Table 4 summarizes the carbocation mechanism in plastic waste catalytic cracking. The carbocation mechanism for the catalytic cracking of PE—a long-chain hydrocarbon—provides deeper insights into the breakdown of polymer chains. As illustrated in Fig. 3(b), the catalytic cracking of PE occurs via Brønsted acid sites. In this process, alkane molecules first adsorb onto Brønsted acid sites and become protonated, forming carbocation intermediates. These intermediates then undergo cracking, resulting in smaller alkane molecules and carbocations. The carbocations undergo intramolecular hydrogen transfer, leading to skeletal rearrangement and the formation of isomerized carbocations. This is followed by β-scission, producing shorter chain carbocations, terminal alkenes, or isoalkenes, depending on the structure of the carbocation intermediates and products.120 The long chain carbocations derived from alkanes or alkenes undergo multiple rearrangements and β-scission, eventually to low molecular hydrocarbons. In addition to random chain scission, the branch chains of polyolefin molecules can undergo terminal cleavage, directly to low molecular products.120,124–126Research on catalytic cracking primarily focuses on catalyst development and the optimization of reaction conditions. Systematic investigation of the detailed chemical composition, distribution patterns, and physicochemical properties of products across catalytic systems will elucidate the mechanisms by which catalysts direct the selectivity towards target products. Concurrent optimization of reaction conditions will facilitate a deeper understanding of the reaction mechanism and kinetics, alongside the study of energy conversion pathways to the plastic cracking process. A study comparing two catalysts for plastic pyrolysis revealed that ZSM-5 produced higher yields of gaseous and liquid products with elevated aromatic content, while red mud required higher pyrolysis temperatures. The tests used a plastic mixture simulating municipal plastic waste.127 Several factors affect the conversion of plastic waste during catalytic pyrolysis, including temperature, residence time, the type of quencher and scrubber, the flow rate, the plastic to catalyst ratio, and catalyst properties. As shown in Table 5, with ZSM-5 as the catalyst, increasing the temperature from 400 °C to 450 °C resulted in a reduction of residues from 73.7% to 3.9%, while the liquid product yield increased from 14.3% to 81.0%.128 Another study showed that ZSM-5 zeolite is used for pyrolysis of plastic mixtures at 440 °C, producing more gas and lighter, more aromatic liquid products.129 Compared to thermal pyrolysis, catalytic pyrolysis allows for the production of more low chain hydrocarbons at lower temperatures, resulting in a more energy efficient process. Anene et al.130 studied pyrolysis and catalytic pyrolysis of LDPE, HDPE, PP and LDPE/PP mixtures and found that products concentrated in the C7–C12 range with CAT-2, compared to the C13–C20 fraction obtained in thermal pyrolysis. Catalytic pyrolysis is more energy efficient.
| Type of plastic | Catalyst | Reaction conditions | Ambient gases | Yield (%) | Ref. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reactor type | Feed/catalyst ratio (m m−1) | Temp (°C) | Time | Gas | Oil | Wax | Residue | ||||
| Thermal pyrolysis | |||||||||||
| HDPE | — | Fluidized bed reactor | — | 650 | Residence time = 0.8 s | — | 20.3 | — | 51.9 | — | 131 |
| 650 | Residence time = 1.5 s | 31.5 | — | 34.1 | — | ||||||
| 780 | Residence time = 1.5 s | 90.4 | — | — | — | ||||||
| PET | — | TGA | — | Room temperature to 800 °C at 10 °C min−1 | — | N2 | 76.9 | 23.1 | — | — | 132 |
| PP | — | Heated wire mesh | — | 746 | Residence time = 10 s | — | 65.9 | 29.6 | — | 4.5 | 45 |
| PS | — | Batch reactor | — | 450 | 1 h | N2 | 0.4 | 80 | — | 19.6 | 133 |
| 70% LDPE + PS | — | 12.8 | 93.7 | — | 3.5 | ||||||
| 45% PE + 20% PP + 20% PS + 15% PET | — | Fluidized bed reactor | — | 600 | Residence time = 2.2 s | N2 | 18 | 45 | 36 | 1.8 | 92 |
| Catalytic cracking | |||||||||||
| PE | Natural zeolite | Pyrolysis reactor | 10/1 | 450 | 75 min | N2 | 34.2 | 16.0 | 49.8 | — | 134 |
| PP | 75.4 | 14.0 | 10.6 | — | |||||||
| PS | 12.8 | 54.0 | 33.2 | — | |||||||
| HDPE | Hierarchical beta zeolite (PHAPTMS) | Batch reactor | 100/1 | 380 | 2 h | — | 15.1 | 81.9 | 3.0 | — | 135 |
| PE/PP = 6/5 | Al-MCM-41 | 500 | 34.8 | 64.9 | 0.3 | — | |||||
| PP | USY | Batch reactor | 10/1 | 450 | 50 min | N2 | 16.8 | 82.0 | 1.2 | — | 103 |
| PE | 26.8 | 71.0 | 2.2 | — | |||||||
| 20% PET + PS | 20% Al–Al2O3 | Quartz tube reactor | 5/1 | 450 | 1 h | — | 50.51 | 44.60 | — | 3.89 | 136 |
| 42% HDPE + 35% PP + 18% PS + 5% PET | Fe-PILC | Conical pouted bed reactor | 1 g min−1 of plastic into the reactor | 500 | 30 min | N2 | 18.0 | 79.3 | — | 2.7 | 137 |
| PP | FCC | Autoclave reactor | 2/1 | 450 | 30 min | N2 | 66 | 29 | 5 | — | 138 |
| PE/PP = 6/5 | Al-SBA-15 | Batch reactor | 33/1 | 500 | 30 min | N2 | 10.9 | 89.1 | — | — | 139 |
| HDPE | MgCO3 | Glass reactor | 5/1 | 450 | 1 h | — | — | 33.6 | — | — | 140 |
| CaCO3 | — | 32.2 | — | — | |||||||
| BaCO3 | — | 29.6 | — | — | |||||||
| PE | Ni/NbOx | Batch reactor | 20/1 | 240 | 5 h | H2 | 4.0 | 95.0 | — | 1.0 | 141 |
| HDPE | Ni/Al2O3 | Batch reactor | 50/1 | 400 | 2 h | N2 | — | 78.1 | — | — | 142 |
| HDPE | HZSM-5 | Batch reactor | 100/3 | 400 | 1 h | N2 | 12.0 | 14.3 | — | 73.7 | 128 |
| 450 | 15.1 | 81.0 | — | 3.9 | |||||||
| PP | Ru/beta | Batch reactor | 14/1 | 215 | 16 h | H2 | 10.5 | 67.0 | 22.5 | 0 | 8 |
| Ru/FAU | 3.2 | 52.0 | 44.8 | 0 | |||||||
| Plastic waste | Ni/ZSM-5 | Batch reactor | 25/1 | 510 | 2 h | N2 | 26 | 63 | 11 | — | 143 |
| Ni/SAPO-11 | 23 | 64 | 13 | — | |||||||
| LDPE | AlCl3 | Glass tube | 200 mg/1 mmol | 60 | 30 min | Air | 18.0 | 80 | 2.0 | — | 144 |
| PE/PP/PS/PET/PVC | Red mud | Semi-batch reactor | 10/1 | 500 | 30 min | N2 | 41.3 | 57.0 | 1.7 | — | 145 |
| LDPE | Cu@TiO2 | High-pressure autoclave reactor | 50/1 | 300 | 30 min | — | — | 86.4 | — | — | 146 |
| HDPE | ZSM-5 | Fluidized bed reactor | 1.41 | 500 | 35 min | N2 | 42.5 | 36.0 | 21.5 | — | 147 |
| LDPE | MCM-41 | Batch reactor | 10/1 | 380 | 30 min | N2 | 41.6 | 34.1 | — | 24.3 | 148 |
| HDPE | 37.3 | 23.2 | — | 39.5 | |||||||
| HDPE/LDPE/PP | FCC | Fixed bed reactor/batch reactor | 15/7 | 450/450 | 17 min | N2 | 0.6–6.2 | 38.5–67.3 | — | 26.5–61.0 | 149 |
| Polyolefin mixture (84%) + PS + ABS + PET | HZSM-5 | Screw kiln reactor | 10/3 | 450/480 | 2 h | N2 | 28.7 | 48.3 | 18.0 | — | 150 |
| PP | HUSY | Stirred reactor | 70/3 | 380 | 72 min | N2 | 9.5 | 90.0(78.8 gasoline) | — | — | 151 |
| PP | Silica–alumina | 6.7 | 93.3(70.3 gasoline) | — | — | ||||||
| PE | Ru/ZrO2 | Batch reactor | 10/1 | 250 | 8 h | H2 | 28.0 | 69.0 | 3.0 | — | 152 |
| PP | 27.0 | 71.0 | 2.0 | — | |||||||
| LDPE | Pt/WO3/ZrO3 + HY | Batch reactor | 10/1 | 250 | 2 h | H2 | 11.0 | 89.0 | _ | 5.0 | 153 |
| LDPE | HY (30) | 9.0 | 83.0 | — | 6.0 | ||||||
| PE | L-ZrO2@mSiO2 | Batch reactor | 545/1 | 300 | 20 h | H2 | 14.0 | 86.0 | — | — | 154 |
| HDPE | LSP-Z100 | Batch reactor | 5/1 | 240 | 4 h | N2 | 0.6 | 81.2 | — | 18.2 | 155 |
| PE | Ni–WO3/Al2O3 + beta | Batch reactor | 20/1 | 280 | 4 h | H2 | 8.0.4 | 77.8 | — | 13.8 | 156 |
| PE | ZSM-5 nanosheets | Fixed-bed reactor | 5/1 | 280 | 600 mL h−1 | 1% H2, 9% Ar, 90% N2 | 74.6% C1–C7, where 83.9% is C3–C6 olefins | 157 | |||
The addition of gases can also affect product distribution. N2 is often used as an inert gas to prevent plastics from oxidizing at high temperature. Table 4 shows that N2 is the most common choice for researchers. H2 is another gas that reduces the unsaturation of pyrolysis products, promoting aromatic and alkane formation. Liu et al.36 studied pyrolysis of plastic waste in N2 and H2 atmospheres, and found that the relative content of olefins in the gaseous products decreased significantly under the H2 atmosphere. Some studies used steam as a pyrolysis atmosphere. Steam can lower the reaction temperature, increase the reaction rate and reduce the tendency for coke formation. It also contributes to light gases such as hydrogen and carbon monoxide, particularly under water–gas shift reaction conditions.158–160
The type of catalyst and the feed ratio between the catalyst and plastic waste have a significant impact on the efficiency of plastic pyrolysis. While a detailed discussion on the types of catalysts used in plastic pyrolysis will be presented in section 4, this section focuses on the effect of the catalyst to plastic feed ratio on the pyrolysis process. Firstly, the plastic to catalyst mass ratio directly influences product distribution and selectivity. A higher catalyst loading can substantially enhance the selective cracking capability of the catalyst, thereby increasing the yield of light hydrocarbons, such as gaseous hydrocarbons and light oils. Further, a higher catalyst proportion can suppress the formation of heavy waxy compounds and yield light hydrocarbons such as gasoline and diesel-range liquid products. Lin et al.161 investigated the conversion of blended plastics (PE/PP/PS) at 400 °C with different catalyst to plastic mass ratios. The study revealed that as the ECat-1 plastic waste to catalyst mass ratio decreased from 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 to 60
1 to 60![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, the yields of C5–C9 gasoline and C1–C4 hydrocarbon gases decreased by 5.3% and 0.6%, respectively. Similarly, Owusu et al.162 reported the catalytic cracking of PS using a SiO2/Al2O3 catalyst at 300 °C. It was observed that as the PS to catalyst mass ratio increased from 20
1, the yields of C5–C9 gasoline and C1–C4 hydrocarbon gases decreased by 5.3% and 0.6%, respectively. Similarly, Owusu et al.162 reported the catalytic cracking of PS using a SiO2/Al2O3 catalyst at 300 °C. It was observed that as the PS to catalyst mass ratio increased from 20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 to 10
1 to 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, the yield of styrene decreased by 9.1%. It is important to note that there is an optimal mass ratio for plastics and catalysts. When the catalyst loading exceeds a certain threshold, catalyst particles may agglomerate, reducing the surface area available for the reaction, thereby lowering catalytic efficiency and leading to increased coke formation.163 As shown in Table 4, the commonly employed plastic waste to catalyst mass ratios range from 5
1, the yield of styrene decreased by 9.1%. It is important to note that there is an optimal mass ratio for plastics and catalysts. When the catalyst loading exceeds a certain threshold, catalyst particles may agglomerate, reducing the surface area available for the reaction, thereby lowering catalytic efficiency and leading to increased coke formation.163 As shown in Table 4, the commonly employed plastic waste to catalyst mass ratios range from 5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 to 20
1 to 20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1. Besides, lower mass ratios are typically suited for processes aiming to maximize the yield of light hydrocarbons, particularly for the production of high value olefins such as ethylene and propylene, whereas higher mass ratios are used in scenarios where catalyst activity requirements are lower, but higher yields of heavy hydrocarbons are desired.
1. Besides, lower mass ratios are typically suited for processes aiming to maximize the yield of light hydrocarbons, particularly for the production of high value olefins such as ethylene and propylene, whereas higher mass ratios are used in scenarios where catalyst activity requirements are lower, but higher yields of heavy hydrocarbons are desired.
4 Reactors for plastic catalysis cracking
Plastics have low thermal conductivity, high viscosity and high melting temperatures, which make design of pyrolysis reactors difficult. High viscosity, along with solid residue formation from side reactions, can block reactor pipelines. The reactor type plays a crucial role in heat transfer efficiency, reaction rate, and product distribution during pyrolysis of plastics, hence the catalytic reactor design must emphasize heat transfer efficiency, mass transfer efficiency and product selection. As shown in Table 6, current work focuses on six types of reactors.| Reactor types | Advantages | Disadvantages | Real applications | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-pressure autoclave | Simple construction and operation; low investment | Low processing capacity; long residence time; low heat transfer rate | Operating conditions: 3.5 L high-pressure autoclave, 100 g plastic mixture, pyrolysis temperature of 500 °C, reaction time of 30 min | 145, 164, 165 |
| Result: 65.2 wt% liquid yield with 69.7 wt% of monoaromatics; a positive energy balance (+700 kJ kg−1) | ||||
| Fixed bed reactor | Simple operation with relatively low capital investment; straightforward reactor design, ensuring easy maintenance | Catalyst deactivation; low pyrolysis efficiency; unsuitable for large-scale processing | Operating conditions: 280 g of PP was pyrolyzed at 520 °C with a 5 cc min−1 N2 flow and a 30 min reaction time | 166, 167, 168 |
| Result: pyrolysis yielded 61–63 wt% with over 40% C3H6 | ||||
| Fluidized bed reactor | High heat transfer efficiency; rapid pyrolysis rate; suitable for large-scale plastic processing with continuous feed and discharge capabilities | Requires stringent control over plastic feedstock particle size | Operating conditions: the reactor is 107 cm long with a 3.49 cm internal diameter, operating at 797 °C with 400 ms residence time, LDPE feed rate of 50 g min−1 | 169–171 |
| Result: total gas yield exceeds 90 wt% with olefins at 75 wt% | ||||
| Conical spouted bed reactor | Minimal residence time; enhanced heat transfer efficiency; superior mixing performance; precise regulation of operational parameters | Scale up; bed material with a very fine particle size is required; catalyst circulation | Operating conditions: 30 g of sands, LDPE flow rate of 60 g h−1; pyrolysis temperature of 500 °C; N2 flow rate of 11 L min−1 | 105, 172, 173 |
| Result: 69 wt% of wax with a Mw of 1534 Da; HHV of 35.55 MJ kg−1 | ||||
| Rotary kiln reactor | Uniform heat transfer; controllable residence time; broad particle size compatibility | Blockage risk; heat transfer issues at scale; poor radial mixing | Operating conditions: the reactor size of 300 mm in diameter and 65 mm in length, pyrolysis temperature of 500 °C, 6 rpm rotation speed, 90 g plastic mixture per h, residence time of 10 min | 174, 175 |
| Result: 45 wt% liquid oil and 47.5% BTX selectivity | ||||
| Microwave reactor | Rapid, uniform heating; energy-efficient with fast reaction rates; allows precise control of the heating rate and temperature | Not suitable for low-conductivity plastics; high cost with limited scalability; complex design hinders large-scale processing | Operating conditions: microwave power: 9 kW, HDPE feed rate: 2 kg h−1, 200 g ZSM-5 catalyst, WHSV: 10 h−1, reaction temperature: 560 °C | 176, 177, 178 |
| Result: liquid product yield: 47.4%, wax yield: 24.5%, energy efficiency: 89.6% |
High-pressure autoclaves are simple in design, usually having a sealed vessel to allow reactions at high temperature and high pressure. This allows for reactions to occur under controlled parameters, which is beneficial for studying reactions and encouraging formation of pyrolysis oil. However, this batch reactor has not been applied at an industrial scale due to the complexity of material handling. The feedstock addition and separation are slow and the catalytic cracking often results in a small production loss. The catalytic cracking in high-pressure autoclaves is often due to severe carbon deposited on the catalyst surfaces, which prevents catalyst recovery and reusability. Mechanical stirring is often used to increase heat transfer efficiency in high-pressure autoclaves. Additional heat carriers such as metals or sand can further increase the heat distribution in the reactor. High-pressure autoclaves are best suited for small scale operations (especially in laboratories), where they provide valuable insights into the catalytic cracking of plastic waste.
Fixed bed reactors are designed with catalyst particles packed in a stationary configuration, forming a static bed through which reactants flow at a controlled rate and make contact with the catalyst for effective reactions. Fixed bed reactors address the problem of batch reactors with limited capacity to introduce feedstocks continuously.179 During operation, critical parameters such as temperature, pressure, flow rate, and residence time govern the catalytic process. However, large particle sizes of the plastic feedstock tend to cause difficulties in feeding and do not provide sufficient catalyst surface area for contact with plastic molecules. This limitation necessitates the use of dual section fixed bed reactors. In the first section, solid feedstock particles undergo thermochemical conditioning via partial pyrolysis at elevated temperatures. The resulting pyrolysis vapors are subsequently directed through the catalyst bed within the second section. This configuration enables catalytic vapor-phase contact, facilitating the decomposition of polymeric structures into lower molecular hydrocarbons. Despite energetic constraints, this approach exhibits significant limitations for industrial applications.180
Fluidized bed reactors are designed based on that catalyst particles are not packed in a static bed but on a distributor plate by which a fluidizing gas flows through the bed. Fluidized bed reactors can exhibit better catalyst contact efficiency and have much larger active surface area.181 In plastic pyrolysis, N2 is commonly used as the fluidizing medium. This design endows fluidized bed reactors with excellent heat and mass transfer properties, making them particularly advantageous for pyrolysis processes.45,181 Fluidized bed reactors are a highly advantageous technology for catalytic cracking of plastic waste, due to their capacity for efficient catalyst regeneration and suitability for continuous, large-scale operations. Compared to fixed bed reactors, fluidized bed reactors are more widely favored by researchers for plastic pyrolysis reactions. Hwang et al.166 compared thermal degradation of PP, LDPE, and ABS in fixed bed and fluidized bed reactors. While the yields of the three plastics were similar in both systems, fluidized bed reactors produced higher middle-to-light fractions (C5–C22) from ABS and PP, and the improved heat transfer efficiency of fluidized bed reactors resulted in higher light gas yields (C1–C2).
The conical spouted bed reactor (CSBR) is a variation of the fluidized bed reactor where a small inlet is connected to a fixed diameter column in a conical section and static spouted particles packed inside the column for spouting.182 To achieve spouting conditions, the inlet diameter typically exceeds the particle diameter by 20–30 times. However, draft tubes negate this restriction and affect other parameters like spouting speed, pressure drop and gas distribution. CSBRs can mix well and can accommodate a large size particle.183,184 Compared to fluidized bed reactors, CSBRs offer the additional advantage of significantly reducing the residence time of reactants to as little as 20 ms. This minimizes undesired secondary reactions and coke formation.172,185 In previous studies, CSBRs have been applied in plastic pyrolysis. Elordi et al.185 studied the pyrolysis of HDPE in a CSBR at 500 to 700 °C. The fractions were compared with the fractions obtained by discontinuous pyrolysis and pyrolysis in fluidized bed reactors. The result showed that the CSBRs yield high waxes and fuels with low aromatic content due to improved mass and heat transfer, and suppression of secondary reactions.
The rotary kiln reactor is a cylindrical rotating device used in various industries for pyrolysis, calcination and thermal decomposition. It can operate continuously or in batch under controlled temperature and residence time conditions.186 It is usually composed of a gas supply unit, a rotary kiln, a gas–liquid separator, and a gas product collector. Heat transfer within the kiln is achieved by thermal fluid flowing upwards or downwards along its length. One of the main advantages of rotary kiln reactors is that they are flexible enough for processing mixed plastic waste of all shapes and sizes. Also, they are easy to design and operate.187,188 On the other hand, unlike fluidized bed reactors, rotary kilns require extended residence times within the kiln bed to achieve complete pyrolysis of plastics.189 Further innovations in rotary kiln technology resulted in screw kiln reactors that use a helical screw conveyor in the cylinder for material transport and processing. Screw kilns are particularly suitable for processes where precise residence time control and thermal treatment are required. For plastic pyrolysis, the reactor can handle complex mixtures of plastics.187
Conventional pyrolysis relies on surface heating of plastics by burning fuel to provide energy needed for thermal decomposition. Microwave electromagnetic radiation uses highly microwave-absorbent materials such as carbon particles or metals to interact with microwave radiation. The electric field is directly engaged with charged particles in the material, and they move out of the equilibrium position. Heat generation depends on two main mechanisms: dipolar polarization and dipolar rotation.176 When dielectric materials are mixed with plastics, they can directly transfer energy to the plastic decomposition process and thus convert energy into heat faster than absorbed energy into heat conversion. Microwave assisted pyrolysis also reduces side reactions and allows better control over product distribution.190 Additionally, microwave technology offers the advantages of rapid heating, enhanced production rates, and reduced operating costs. For instance, studies involving the pyrolysis of LDPE under conditions of 1.6 MPa and 425 °C achieved liquid oil yields of up to 89.5 wt%.117 Using such a setup, HDPE and PP waste materials were fully degraded within 2–4 min, demonstrating the efficiency of microwave technology in energy transfer. However, a significant limitation of this technology lies in the insufficient data available to quantify the dielectric properties of plastic waste during processing.37,191 This hinders the development and optimization of microwave assisted pyrolysis systems. This impedes development and optimization of microwave-assisted pyrolysis systems. Furthermore, the high electricity consumption of microwave technology is also an economic disadvantage.
5 The influence of catalysts in plastic waste cracking
In the non-catalytic plastic pyrolysis, the C–C bonds of polymer chains are randomly scissioned without fragment rearrangement, producing light olefins, gasoline-range components, diesel fractions and waxes.174,192 Higher temperatures can increase the light hydrocarbon fraction yield, but high selectivity for desired fuels and chemicals remains a challenge. Thus, suitable catalysts are needed to select targets. Firstly, catalysts reduce the activation energy of plastic pyrolysis and thus lower energy consumption. On the other hand, catalysts enhance product selectivity, allowing for the production of valuable chemicals, such as ethylene,193 aromatics,34 gasoline,194 and diesel,111 which are difficult to achieve in non-catalytic processes. In summary, the use of catalysts improves the product distribution of plastic pyrolysis, enabling a more refined product range. The catalyst properties, particularly the pore structure and acidity, significantly influence the composition of the final product yield. Fig. 4 summarizes the impact of catalyst characteristics on pyrolysis products. Catalytic cracking reactions (C–C bond scission) occur at Brønsted acid sites, and acid distribution and density are critical factors in catalyst design. The pores also play a role in accessing these acid sites, diffusion of reactants and shape selectivity, which may affect the catalyst activity, stability and selectivity.195,196 In conclusion, catalyst design for the pyrolysis of plastic waste is a multifaceted research endeavor. | ||
| Fig. 4 Main products obtained in the catalytic pyrolysis of polyolefins on different acid catalysts.105 Adapted with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2017. | ||
Results of catalytic cracking of plastic waste in current catalyst design show several important drawbacks. First, there is significant catalyst deactivation. When cracking plastics on highly acidic catalysts, certain cracking products polymerize and condense and form carbon deposits. These coke deposits cover the active sites of the catalyst and weaken its activity. Second, catalyst poisoning is also important. Plastic waste often contains impurities and additives (such as chlorine, sulfur and metals) which react with the catalyst during cracking and cause site poisoning. For example, the pyrolysis of PVC releases HCl gas that reacts irreversibly with acidic catalysts and deactivates the catalyst.7,197,198 Another challenge is that the activity and selectivity of the catalytic process are influenced by reaction parameters such as temperature, residence time, atmosphere, and reactor design. Based on prior research, acidic catalysts have been identified as the most promising candidates for catalytic cracking of plastics.199,200 Therefore, this section will focus on the use of different types of solid acids in the catalytic cracking of plastic waste.
5.1 Activity of zeolite catalysts in pyrolysis cracking
Zeolites represent the predominant class of solid acid catalysts, distinguished by their unique structural and chemical properties. Before examining their catalytic performance in the catalytic cracking, a foundational understanding of zeolite is essential. Zeolites are microporous materials consisting of regular Si–O tetrahedral and Al networks. Tetrahedral Al atoms replace Si atoms in the framework through isomorphic substitution. This results in Al–O tetrahedral structures with a negatively charged framework. To maintain charge balance, these structures require cations. Fig. 6 illustrates the Si–O(H)–Al structures, which are formed via the adsorption of protons onto the zeolite framework and function as the origin of Brønsted acid sites (BAS).201,202 Conversely, Lewis acid sites (LAS) can originate from the zeolite framework, forming coordinated Al structures like in Fig. 6 or from extra-framework distorted Al, four- or five-coordinated Al species.203,204 Additionally, zeolite channels are adjustable, with numerous synthesis and post-treatment modification methods available to tailor the pore structure or incorporate hierarchical pore channels.205,206 By combining their BAS, LAS, and tunable pore structure, zeolite catalysts exhibit significant advantages in plastic cracking applications, making them a preferred choice for researchers.The authors believe that the combination of these three properties makes zeolites extremely active in waste plastic cracking. Thus, it would be overly simplistic to study the effect of any single property on the plastic cracking process, although qualitative trend analysis based on acid strength, acid quantity and pore size will be useful to design suitable catalytic systems in future work. In the next section, we will use the pore structure as a main line, incorporating acidity characteristics for further evaluation of zeolite performance in plastic cracking applications.
Zeolites are widely used catalysts and microporous zeolites exhibit excellent deoxygenation performance and shape selectivity for hydrocarbons. They are also highly effective for aromatic production.207 Therefore, researchers have studied various types of zeolites for efficient catalysts. Different types of zeolites have been used to study catalytic pyrolysis of plastics, including HZSM-5, HUSY, Hβ, HMOR, and natural zeolites.208,209 In an earlier study, Manos et al.210 compared the catalytic performance of USY, Y, β, MOR, and ZSM-5 degradation of HDPE. The results showed that the zeolite structure had a significant impact on product distribution: alkanes were the main products on USY, Y, and β zeolites, while olefins were the main products on MOR and ZSM-5. Furthermore, compared to large pore zeolites, medium pore zeolites tend to produce lighter hydrocarbon products, following the trend ZSM-5 < MOR < β < Y < USY. This suggests that the pore structure plays a crucial role in the final products of plastic cracking. In subsequent studies, Manos et al. further analyzed the underlying mechanisms and attributed them to rapid bimolecular hydrogen transfer in the large channels, leading to an increased yield of saturated hydrocarbons.211 Similar research was conducted by Mordi et al., which tested the catalytic activity of H-MOR, H-Theta-1, and H-ZSM-5 in the catalytic degradation of LDPE.212 The main components from degradation on H-MOR or H-Theta-1 were C11–C19 hydrocarbons (mainly alkanes and olefins) and degradation on H-ZSM-5 was mostly aromatics with no longer than C14 chains. Cracking may occur on the outer surface or at the pore entrance of the zeolite catalysts since polymers are too large to enter the pores and enter the inner active sites.
Further studies have shown that zeolites with micropore diameters between 5.2 and 5.9 Å, especially ZSM-5, are the most suitable zeolites for aromatic hydrocarbon production, because catalytic pyrolysis reactions occur mostly at the active centers of the channels, where reactive intermediates need to diffuse into pores.207 Consequently, the pore structure of zeolites exhibits a strong shape selectivity toward reactants, intermediates, and products.213,214 For reactants, only those with molecular diameters smaller than the pore dimensions can diffuse into the zeolite channel structure. Once inside, as the reactants convert into a series of intermediates and final products, larger molecules may either crack into smaller ones and diffuse out or block the pores, leading to a decline in catalytic activity. Zhang et al.215 designed a one-step microwave-triggered tandem pyrolysis coupled with ZSM-5 catalytic reforming technique, which selectively converts polyolefin plastics through processes such as cracking, aromatization, and Diels–Alder reactions into petroleum products rich in benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylene (BTEX). The selectivity to and yield of BTEX were reported to be 70.53% and 24.17%, respectively, highlighting the potential of this method for producing high value BTEX. In another study, a process route was developed to degrade metallized food plastic packaging waste from materials such as potato chip and coffee packaging using microwave pyrolysis combined with ex situ catalytic reforming, following a NaOH treatment. This process was aimed at producing monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. In this work, NaOH pretreatment was used to break the chemical bonds between the plastic and Al layers, followed by the conversion of intermediates into liquid oils using an HZSM-5 zeolite catalyst. As shown in Fig. 5(c) and (d), the results revealed that the MAH content in the products reached as high as 80.50%, with toluene being the most abundant component among the MAHs.216 This further reinforces the potential of ZSM-5 in plastic cracking for the production of aromatic compounds.
 | ||
| Fig. 5 (a) Global “conversion” of HDPE, as a function of total acidity of the catalyst. Note: total acidity = 0 mmol NH3 per g corresponding to degradation of HDPE without a catalyst.217 (b) Product molar distribution for the thermal and catalytic (HZSM-5 and with different amounts of sodium) degradation of HDPE.217 Adapted with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2012. Yield and composition of products under different SARs: (c) GC/MS chromatograms of liquid oil; (d) liquid oil composition.216 Adapted with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2024. (e and f) Effect of the SiO2/Al2O3 ratio of the HZSM-5 zeolite on the TPO curves of the combustion of the coke deposited on the catalysts.218 Adapted with permission from American Chemical Society, copyright 2023. | ||
 | ||
| Fig. 6 The mechanisms underlying the formation of Brønsted and Lewis acid sites within the zeolite framework. | ||
Within the same class of microporous zeolites, variations in acidity exert a profound influence on product composition. First, an increase in acid density directly enhances the number of active sites, significantly lowering the cracking temperature of plastic waste and improving the conversion rate.217,219,220 Coelho et al.217 synthesized a series of HZSM-5 with varying Si/Al ratios to catalyze the cracking of HDPE. They observed that as the total acid density increased, the degradation temperature decreased, and conversion rates improved. They calculated the reaction Ea of zeolites with different Si/Al ratios, revealing that Ea decreased with increasing acid density. Similar behavior was observed in beta and ZSM-12 zeolites.219,220 Moreover, the acid strength of zeolite also impacts the distribution of final products. Generally, higher acid strength favors the production of lighter hydrocarbons. As shown in Fig. 5(b), Coelho et al.217 obtained more C3–C4 light olefins using an HZSM-5 catalyst compared to NaHZSM-5 with a larger Si/Al ratio. Similarly, López et al.127 compared a more acidic ZSM-5 zeolite with red mud, finding that the latter required higher reaction temperatures and produced heavier products. Increasing acid strength favors the cracking of plastic waste into low carbon products. However, excessive acid strength often leads to increased coke formation. Many aromatic products derived from high acidity zeolite catalysts easily form coke precursors, which, under the influence of strong acidity, can grow into large polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. For instance, as shown in Fig. 5(e) and (f), Elordi et al.218 found that when catalytically cracking HDPE with ZSM-5 zeolite, increasing the SiO2/Al2O3 ratio from 30 to 80 significantly reduced coke deposition both on the external surface of zeolite crystals (coke I) and inside the zeolite micropores (coke II).
In addition to microporous zeolites, mesoporous aluminosilicates such as Al-MCM-41 and Al-SBA-15 possess adjustable mesoporous channels ranging from 2 to 30 nm, which significantly enhance the mass transport of polymer molecules and intermediates, allowing them to directly access the internal active sites. This feature greatly reduces spatial and diffusion limitations. Al-MCM-41 exhibits a well-ordered hexagonal pore structure, while Al-SBA-15 features larger pore sizes and thicker walls, conferring superior mechanical stability. The incorporation of Al into the MCM-41 and SBA-15 frameworks endows these materials with both Brønsted and Lewis acidity, which underpins their applicability in catalytic reactions. In 1996, Aguado et al.221 first demonstrated the feasibility of utilizing Al-MCM-41 for PE pyrolysis. Despite its weaker acidity compared to microporous zeolites, which limits the activity of mesoporous materials in plastic pyrolysis, its unique porous architecture imparts significant advantages. Aguado et al.222 further conducted a comparative study between Al-MCM-41, SiO2–Al2O3, and ZSM-5, revealing that while Al-MCM-41 acidity is less than that of ZSM-5, its superior surface area and more ordered mesoporous structure enable a high conversion rate. Particularly in the degradation of highly branched polymers such as PP, the narrow pore structure of ZSM-5 induces remarkable steric hindrance, resulting in lower catalytic activity. Al-MCM-41 demonstrates higher selectivity towards gasoline range and middle distillates, reinforcing its potential in producing valuable liquid fuels. Socci et al.223 compared the catalytic behavior of ZSM-5 and Al-SBA-15. Al-SBA-15 overcomes diffusion constraints, exhibiting a stronger cracking propensity and yielding a higher selectivity for gasoline range products. This research highlighted that factors such as the strength and density of BAS, pore structure, and Al content influence the composition of pyrolysis products.
Some researchers have recognized that microporous zeolites with high active sites can be combined with mesoporous aluminosilicates with a high mass transport capability. The hybrid zeolite catalysts combine the advantages of first cleavage of reactants on weaker acid sites of mesoporous aluminosilicates, producing shorter chains, and preventing coke formation on the microporous zeolite surfaces. These shorter chains can be moved to the internal microporous region and crack again, resulting in light alkanes and alkenes. Thus, the optimal combination of different pores can maximize the efficiency and selectivity of the catalytic process. Ratnasari et al.180 showed high efficiency cracking of plastic waste into gasoline-range hydrocarbons. When the MCM-41 to ZSM-5 ratio is 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, the main gas products are ethylene, propylene, butene and butadiene. During catalytic pyrolysis of HDPE, the resultant oil yielded 97.72 wt% C8–C12 hydrocarbons with aromatic content as high as 95.85 wt%. These results demonstrate that the composite catalysts are promising candidates for valorization of plastic waste to high value hydrocarbon products.
1, the main gas products are ethylene, propylene, butene and butadiene. During catalytic pyrolysis of HDPE, the resultant oil yielded 97.72 wt% C8–C12 hydrocarbons with aromatic content as high as 95.85 wt%. These results demonstrate that the composite catalysts are promising candidates for valorization of plastic waste to high value hydrocarbon products.
Similar to composite zeolites, researchers have explored the application of hierarchical zeolites in plastic pyrolysis. In a zeolite catalyzed plastic pyrolysis reaction, the first step is to bring into contact the acid centers on the external surface or in the macropores of the zeolite. Then the smaller intermediates of the first step enter the micropores of the zeolite for further cracking or secondary reactions. This is determined by the acidity and the pores. Hierarchical zeolite catalysts have been introduced for plastic cracking reactions. Unlike micropores, hierarchical zeolites have interconnected micro–meso–macro pores, which can promote catalytic activity for waste plastic conversion and reduce coke formation. The development of hierarchical zeolites for plastic cracking has made a lot of progress. Recently, researchers have synthesised highly ordered multilayer nanosheet hierarchical Y zeolites (Fig. 7b and c).
 | ||
| Fig. 7 (a) The relative abundance of identified products from the thermal and catalytic cracking of LDPE analysed by Py-GC/MS, grouped by the number of carbon atoms.223 Adapted with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2019. (b) SEM images of commercial Y and Y-H zeolites after recrystallization.224 Adapted with permission from American Chemical Society, copyright 2024. (c) (i) Photograph of the powder PE and SEM image of s-ZSM-5 with a panel morphology; (ii) hydrocarbon distribution of the products from the conventional thermal depolymerization route at 440 °C and the catalytic depolymerization route on the s-ZSM-5 catalyst at 280 °C; (iii) schematic illustration of the cascade cracking steps on the external zeolite surface and within zeolite micropores on n-ZSM-5 and s-ZSM-5 catalysts.157 Adapted with permission from American Chemical Society, copyright 2022. | ||
The exterior surface area and porosity of hierarchical HY zeolites improved significantly with similar acidity to the parent Y zeolites and they achieved a very high PE conversion rate of 96.8% at 280 °C. The distribution of the products yielded a high selectivity of 90.8% for C5–C20 hydrocarbons due to better access of the acid sites, which allowed cascade cracking of macromolecular polyolefins into small branched alkanes.224 Furthermore, Tan et al.225 developed hierarchical MFI zeolites for metal free PE conversion with batch or continuous flow. These zeolites were prepared by treating MFI zeolite (Si/Al = 40) with 0.2 M NaOH at 60 °C for 15, 30 or 60 min, followed by comparison with MFI zeolites recrystallized with surfactant templates. In surfactant templated samples, 0.2 M TPABr was added to NaOH before desilication. As expected, increased desilication time led to larger mesopore volume and external surface area, but at the cost of lower microporosity. Surfactant templated recrystallization allowed controlled mesopore volume enhancement without significantly changing the functionality of the parent material. However, interactions between the catalyst surface and reactants resulted in contracted mesopores instead of open mesopores. However, the desilicated zeolites modified with NaOH + TPABr had the highest number of strong acids. The sample treated for 30 min with TPABr had the highest mesoporous specific surface area and the highest number of strong acids. Compared to the parent and other desilicated MFI zeolites, this sample had the highest catalytic cracking performance for PE. This further proves the importance of controlled desilication to preserve acid site density and improve cracking performance.
To enhance the interaction between plastics and the active centers of zeolites, we have proposed a zeolite synthesis technique by changing the shape of zeolites (nanoscale and lamellar) in order to reduce diffusion limits of reactants and thus improve the plastic cracking rate. Both nanoscale and lamellar zeolites have much larger external surface areas and more acidic sites. This substantially reduces the mass transfer resistance of reactants on the zeolite catalyst, which allows plastic polymer molecules to crack and undergo subsequent secondary reactions without entering pores. For instance, Xiao et al.157 developed ZSM-5 nanosheets (s-ZSM-5), which crack PE plastics first on the expansive external surface, followed by diffusion of intermediates into micropores, resulting in cracking into smaller molecules. The short diffusion path of the lamellar zeolites suppresses accumulation of intermediate products and reduces coke formation, as evidenced by TGA showing less than 1 wt% weight loss. The nanoscale ZSM-5 (n-ZSM-5) had 27% coke formation, suggesting that lamellar zeolites have lower diffusion constraints compared to nanocrystals. Smaller dimensions, such as cubic or spherical zeolites, can have higher mass transfer rates. In another study, Tang et al.226 demonstrated that nanosized ZSM-5, because of its larger external surface area, enables better contact between reactants and strong acids resulting in higher catalytic activity and lower temperatures. Additionally, Seo et al.227 synthesized protonated beta zeolites with similar Si/Al ratios but different crystal sizes. They found that zeolites with the lowest Si/Al ratio (10.7) and a small crystallite size (10 nm) had the highest catalytic activity in HDPE degradation yielding 80% liquid products. This shows the importance of the high specific surface area and strong acidity of zeolites in plastic cracking.
In summary, we have studied different zeolite catalysts used in plastic waste pyrolysis and studied how their structure and catalytic activity are related. While zeolites have high catalytic activity in plastic pyrolysis, there are still limitations for further enhancement of activity and selectivity based on acidity, pores and morphology changes. Zeolite catalysts, whose acidity is the main active center, are hard to selectively form products due to the intense cracking activity of the sites. The strong acidity often leads to lower selectivity and frequent formation of by-products. High cracking activity also leads to product accumulation in pores, pore blockage and consequently deactivation of the catalyst. These issues limit the efficiency of the catalyst and increase product separation, purification and catalyst regeneration costs. The following sections will introduce metal/zeolite composite catalysts, aiming to improve the catalytic performance and overcome the limitations observed in pure zeolite catalysts for plastic waste pyrolysis by adding other metal active sites and structural modification of the zeolite framework.
5.2 Metal/zeolite catalysts in plastic cracking
Metal/zeolite catalysts are of interest to researchers due to their excellent catalytic activity and product selectivity. In other critical heterogeneous reactions, they have also been used extensively. For plastic waste pyrolysis, they are also essential. Firstly, metal loading on zeolites allows precise tuning of the acid sites, which improves both the conversion rate and selectivity. Metals like Pt, Pd and Ni boost the yield of targeted products like BTX and are essential for high selectivity towards desired compounds. Additionally, active metal clusters or nanoparticles supported on zeolites are highly hydrogen active. Metal/zeolites are also suitable for hydrocracking plastic waste. In summary, plastic waste pyrolysis becomes efficient through the synergistic interaction between metal sites and zeolitic acid sites that enables feedstock conversion and product distribution. This synergy provides a new avenue for the valorization of plastic waste resources.Metal/zeolite catalysts have shown potential in enhancing the catalytic activity for pyrolyzing plastic waste. Current research predominantly utilizes non-noble metals for impregnation, including Ga, Ce, Fe, Ni, and Zr. In a study by Miskolczi et al.,228 Ce, Cu, Fe(III), Fe(II), Mg, Ni, Sn, and Zn were loaded onto ZSM-5 and Y zeolites. This investigation revealed that metal loadings significantly lowered the Ea of plastic pyrolysis, with a consistent reduction sequence across both ZSM-5 and Y zeolites: Cu < Ce < Mg < Ni < Fe(III) < Fe(II) < Zn < Sn. In another study, Kokuryo et al.229 demonstrated that synthesized Zr-β zeolite exhibited superior activity in LDPE pyrolysis compared to conventional β zeolites, attributable to the Lewis acidity introduced by Zr. Further, Miskolczi et al.230 used Ca, Ce, La, and Mn promoters in Ni/ZSM-5 catalysts to enhance syngas yields in the pyrolysis of PE, PP, and PET, with Ce and La promoted catalysts significantly increasing syngas production. Similarly, Pyo et al.231 found that Ga-ZSM-5 exhibited the lowest apparent activation energy of 110 kJ mol−1 compared to 122–172 kJ mol−1 in HUSY and other HZSM-5 catalysts, accounting for its high activity in PP cracking.
Metal/zeolite catalysts also contribute to product selectivity. Some studies have shown that metal/zeolite catalysts yield products with specific chain lengths or enhance selectivity toward aromatic products such as BTX. MFI zeolite is especially suited for aromatic compounds because hydrocarbon pools in specific channels and Diels–Alder cyclization reactions enable aromatic ring formation, making MFI zeolite an ideal support for metal/zeolite catalysts targeting aromatic production. In a study by Park et al.,232 the catalytic performance of ZSM-5 with a Si/Al ratio of 200 was compared to that of its Co-loaded variant for plastic waste pyrolysis of straw. Co slightly reduced the light olefin yield while increasing MAH production and increasing propylene selectivity. In another study, Fu et al.233 evaluated catalysts with Fe, Ni and FeNi supported on β, Y, MOR and Socony Mobil-5 zeolites. Y obtained a high oil yield of 64.0 wt%, rich in paraffins (38.21%) and monocyclic aromatics (35.40%), with low olefin content (13.12%). Interestingly, FeNi catalytic effects differ significantly from single metal Fe or Ni catalysts because FeNi promoted cyclization and olefin hydrogenation, while Fe and Ni primarily facilitated dealkylation of monocyclic and polycyclic aromatics. This difference was due to the unique hydrogen extraction capability of single elements, which FeNi lacks. In a recent study, Chen et al.9 utilized a design combining β zeolite with multistage porous TS-1 loaded with Pt. The acidic sites on β zeolite activated and cleaved C–C bonds to generate olefins, while Pt@Hie-TS-1 adjusted the C5–C7 shape selectivity and hydrogenated them into paraffinic products. As shown in Fig. 8(a), the β + Pt@Hie-TS-1 catalyst significantly outperformed existing metal-loaded zeolite catalysts in terms of the C5–C7 yield. Additionally, Zhao et al.234 developed an efficient zeolite–metal oxide catalyst (HZSM-5 + CuZnZrOx) for conversion of PE and CO2 into aromatics and CO. Fig. 8(b) shows that hydrogen radicals are generated during aromatization and diffuse from the BAS of zeolite to adjacent CuZnZrOx, reacting with CO2 to form bicarbonates, which hydrogenate to CO. The presence of hydrogen inhibits further hydrogenation and secondary hydrogenolysis of aromatic products, ultimately achieving a 62.5 wt% aromatic yield.
 | ||
| Fig. 8 (a) The C5–C7 yield over β + Pt@Hie-TS-1 in comparison with catalysts in ref. 9. Adapted with permission from Wiley, copyright 2024. (b) Proposed reaction pathway for the co-conversion of PE and CO2 to aromatics and CO. m/z, mass/charge ratio; distribution of the carbon number in products from LDPE conversion; aromatic yield. Product analysis for the 13CO2 isotope-labeled experiment.234 Adapted with permission from AAAS, copyright 2022. (c) Product distribution of polyethylene hydrocracking catalyzed by various metals supported on ZSM-5_H. Reaction conditions: T = 375 °C, time = 2 h, and H2 pressure = 45 bar (ref. 235) (open access). | ||
Unlike the active sites for catalytic cracking of plastic waste, which involve acidic sites, hydrocracking requires synergistic interaction at metal sites and acidic centers in zeolites. As illustrated in Fig. 9, the typical hydrocracking process of C–C bonds in plastics over metal/zeolite catalysts comprises three sequential steps: (1) dehydrogenation of alkanes at metal sites; (2) isomerization/cracking of the resulting olefins at acidic sites; (3) hydrogenation of olefins at metal sites.236 In plastic waste hydrocracking, noble metals such as Pt, Pd and Ru are often used, due to their superior catalytic activity that accelerates hydrogenation reactions and their ability to adsorb hydrogen effectively, enhancing the reactivity of hydrogen with plastic molecules. For example, in the work of Tang et al.,236 Pt nanoparticles were anchored onto the external surface of USY zeolite using a colloidal fixation method, achieving over 90% selectivity for gasoline range fractions in PE cracking, with catalytic activity exceeding 450% compared to non-anchored catalysts. As shown in Fig. 8(c), Dyson et al.235 compared the hydrogenation activity of Co, Ni, and Ru on HZSM-5, finding that Ru/HZSM-5 achieved nearly 100% conversion of PE into CH4. In light hydrocarbon hydrocracking reactions, the presence of metals contributes to a higher yield of saturated products and enhances the isomerization of n-alkanes.237–239 This phenomenon also applies to the cracking of plastic waste. In a study by Góra-Marek et al.,240 Pd/beta and beta catalysts were compared for the hydrocracking of LDPE. When comparing catalytic cracking and thermal cracking, both catalytic and hydrocracking exhibited lower T50 values (the temperature value obtained at 50% LDPE conversion) than pyrolysis alone, with hydrocracking on Pd/beta showing the lowest T50 value, indicating that the addition of Pd significantly enhanced the cracking efficiency. Due to its higher cracking efficiency, Pd/beta catalysis yielded more C2–C5 products, while C6+ products were less prevalent than with beta alone. Moreover, the Pd/beta catalyst increased the proportion of branched isomers (the CISO/Cn ratio increased from 0.45 to 0.65), attributed to the strong isomerization activity of the cooperative metal sites and acid sites.
 | ||
| Fig. 9 Synergistic strategies for catalyzing PE hydrocracking using metal-loaded zeolite catalysts.7,8,236 | ||
Furthermore, the metal loading and the proximity between metal and zeolite acidic sites can significantly impact hydrocracking performance. Yuan et al.241 loaded Ru on MOR zeolites, designing a gradient of 0.7, 1.2, and 1.7 wt% Ru, and prepared MOR fragments through ball milling to enhance the accessibility of LDPE to both Ru and acidic sites. Experimental results indicated that LDPE was converted into gaseous alkanes and liquid fuels within a short reaction time, with 0.7Ru/mMOR20 displaying superior performance for liquid fuel production, achieving a 31.7% yield of C5–C21 hydrocarbons. Conversely, as the Ru loading increased, the yield of gaseous products rose progressively, with methane production on 1.7Ru/mMOR20 being threefold higher than on 0.7Ru/mMOR20. Higher metal loading increases the Ru particle size, which hinders the desorption of olefinic intermediates during hydrocracking. This promotes the persistent adsorption at the alkane chain terminus, leading to cascade hydrogenolysis of terminal C–C bonds and resulting in the excessive production of low value alkanes. Another study by Tang et al.236 has modulated the distance between Pt and acid by gluing Pt nanoparticles to USY zeolite by colloidal fixation. The researchers found that catalysts with Pt NPs on USY pores exhibit high intrinsic catalytic activity although only Pt NPs are readily available and thus are not able to convert large polymer molecules. On the other hand, excessive distance between Pt and USY zeolite can also affect catalytic performance due to long diffusion paths between metal Pt and acidic sites. Pt NPs exclusively anchored on the catalyst surface facilitate reactant access to active sites and reduce diffusion resistance between metal and acidic sites. High-branched gasoline fuel yields over 80% were obtained for LDPE, HDPE, PP and PS.
5.3 Other catalysts in plastic cracking
Zeolites are commonly used catalysts for the cracking of plastics, and other catalysts have also been investigated and have shown good catalytic performance. FCC catalysts consist of crystalline zeolites, acidic SiO2–Al2O3 and binding agents, and form fluid catalytic cracking systems.138 Due to their weak acidity, FCC catalysts have less catalytic activity than zeolites but their cost allows them to increase catalytic activity by using more catalyst materials. This makes FCC catalysts very useful for industrial applications. Recently, some researchers have studied FCC catalysts for catalytic cracking of plastic waste. Weckhuysen et al.138 studied conversion of PP using FCC catalysts. Fe, Ni and V metals were deposited on catalysts which improved aromatization and pre-cracking activity. Moreover, metal deposition reduced coke formation by blocking zeolitic domains, indicating that the strong acidity and microporous channels of zeolites are not essential for the aromatization of PP. The authors also suggested that PP is thermally pre-cracked and products interact with the catalyst. Higher transport allows product evolution at lower temperatures, due to direct interactions between PP and the catalyst particle surface, than radical reactions on the plastic. To meet the energy requirements of catalytic conversion, the contact area of the polymer/catalyst should be increased as much as possible. In another study, Sedran et al.242 used three commercial FCC catalysts to crack LDPE and all three showed similar results; products were concentrated in gasoline fractions and high aromatic products were yielded. The researchers suggested that employing the FCC catalytic process, a proven and cost-effective technology, to address environmental issues represents an intriguing approach that requires no additional technological development.Another class of catalysts similar to zeolites used for plastic waste pyrolysis are clays. The acidity of natural clays comes from Brønsted acids formed by dissociation of water and interlayer cations. This acidity is influenced by the type of interlayer cation, as the higher the cation's polarization strength, the greater the water dissociation and resultant acidity.243,244 Additionally, Brønsted acidity can emerge from the creation of silanol groups at layer edges, resulting from the disruption of terminal Si–O–Si bonds. Moreover, acidity is also dependent on the presence of LAS, attributed to Al3+, Mg2+, and Fe3+ ions at crystal edges and exchangeable acidic cations.244 Through acid activation, involving modification with sulfuric acid or other inorganic acids, the structural edges of clay crystals are opened, and octahedral sheet cations such as Al3+, Mg2+, and Fe ions are leached. This process enlarges internal cavities and increases pore size, facilitating access to internal acid sites.245 These features endow clay with acid sites, high surface area, and mesoporosity, enabling its application in catalytic plastic pyrolysis reactions. Clay catalysts are highly attractive for industrial applications due to their abundance and low cost. Typically, the acidity of clay is lower than that of zeolites but higher than that of SiO2. At 600 K, their activity is inferior to USY zeolite. However, raising the reaction temperature enables the complete decomposition of PE, achieving liquid product yields of up to 70%. In comparison, USY zeolite yields less than 50% liquid products while generating more coke. The liquid products from clay catalysis are heavier and fall within the gasoline range due to the milder acidity of clay, which mitigates excessive cracking of plastics.246 A comparative study evaluated the performance of Al and Al/Fe pillared clays derived from stevensite, montmorillonite, and beidellite minerals, alongside acid-treated structured clays (K10®, HMO, HSA, and HBe), in the pyrolysis of medium density polyethylene (MDPE).247 Pyrolysis was carried out for 4 h in a fixed bed microreactor at 300 °C under a N2 flow. All Fe and Al containing pillared clays were more selective in producing liquid yields over 5% than reference HZSM-5 zeolite which yielded 50%. Restructured clay HMO yielded the primary yield in the diesel range. Other restructured clays (K10®) were less active than HZSM-5. Pillared and restructured clays were selective for producing aromatics, except for HSA favouring aromatic production, similar to HZSM-5 zeolite. The higher yield of aliphatic hydrocarbons in gasoline and diesel ranges is mainly due to the relatively lower acidity of clay catalysts. Catalysts with higher acid site densities, such as HZSM-5 zeolite, favor the production of gases and light olefins due to strong Brønsted acidity, which promotes over-cracking reactions.
The multivalent states and acid–base properties of metal oxides have allowed them to be used extensively in heterogeneous catalysis. In the pyrolysis of plastics, several metal oxides have been investigated. Table 7 summarizes the application of a selected portion of metal oxides in plastic pyrolysis, highlighting their dual functionality in catalyzing the thermal degradation of polymers and converting volatile intermediates into more stable products. In catalytic applications, Al2O3 is a commonly used catalyst support, due to its large pore volume and high specific surface area, which facilitate the accommodation of bulky polymer molecules and significantly enhance diffusion efficiency. Furthermore, the Lewis acidity of Al2O3 imparts additional functionality for the degradation of plastics. Jiang et al.248 synthesized Fe–Ce@Al2O3 for catalytic conversion of PC waste into aromatics. The catalyst was prepared using co-precipitation, impregnation, and physical mixing methods. Experimental results showed that the catalyst synthesized by co-precipitation yielded the highest monocyclic aromatics due to its weak acidity, larger pores, higher specific surface area, and uniform metal oxide dispersion. In another study, Pt catalysts supported on Al2O3 were used to convert PE at a reaction temperature of 280 °C. Exothermic hydrogenolysis and endothermic aromatization were combined to convert PE into long chain alkyl aromatics and cycloalkanes.249 This one step reaction significantly reduced complexity and improved industrial feasibility. Notably, no organic solvents were used in the reaction system. Moreover, over 80 wt.% of low molecular liquids and waxes were produced. The stability of the catalyst was investigated through three consecutive 6 h reaction cycles. The liquid/wax yield decreased by 15 wt% in the second cycle but stabilized in the third cycle due to the reduced Pt surface area over repeated reactions. The turnover frequency remained constant over cycles. This reaction has strong industrial potential; however, it is limited by the extended reaction time of 24 h.
| Catalysts | Feedstock | Reaction conditions | Liquid yield (wt%) | Product distribution | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MgO | HDPE | Pyrolysis temperature of 500 °C, catalytic temperature of 450 °C, HDPE![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) MgO of 15 MgO of 15![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
37.0 | 36% C5–C12 aromatics, 38% C5–C12 alkenes, 11% C5–C12 alkanes | 250 |
| Ni/CuO | PS | Pyrolysis temperature of 390 °C, reaction time of 90 min | 93.5 | 68.9% aromatics, 21.29% olefins, 2.2% oxygenates | 251 |
| ZnO | LDPE | 10% ZnO addition, 50 kPa pressure | 72.0 | 56.2% C7–C36 alkanes, 30% C9–C18 alkenes, mainly composed of diesel range hydrocarbons | 252 |
| Sulphated ZrO2 | PET | Pyrolysis temperature of 450 °C, residence time of 20 s, catalyst to plastic mass ratio of 3 wt% | 41.4 | 27.5 wt% of benzoic acid, 13.9 wt% of other aromatic compounds | 253 |
| Ni/Al2O3 | HDPE | Pyrolysis temperature of 400 °C, reaction time of 120 min, 1 MPa H2 pressure, HDPE![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Ni/Al2O3 of 50 Ni/Al2O3 of 50![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
78.1 | 78.88 wt% of n-alkanes, 10.92 wt% of alkenes, and other products | 142 |
| Cu@TiO2 | LDPE | Pyrolysis temperature of 300 °C, reaction time of 30 min, LDPE![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Cu@TiO2 of 19 Cu@TiO2 of 19![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
86.4 | C13–C19 liquid oil | 146 |
| Pb–Co/BaTiO3 | HDPE | Pyrolysis temperature of 350 °C, reaction time of 30 min, HDPE![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Pb–Co/BaTiO3 of 19 Pb–Co/BaTiO3 of 19![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1 |
86.0 | 18.55% C6–C12, 31.34% C13–C16, 25.71% C17–C20, 16.02% C20–C30 | 41 |
In addition, transition metal oxides are a class of widely used materials in catalysis, which exhibit varied effects on chemical reactions due to differences in their chemical properties. Kumagai et al.57 employed a tandem microreactor system to study the pyrolysis of PET over various metal oxides, including ZnO, MgO, TiO2, and ZrO2. The study revealed that ZnO, possessing the highest basic strength among the tested oxides, selectively promoted the decarboxylation of benzoic acid and terephthalic acid (TPA) at relatively low temperatures. Benzene accounted for 88.8% of the oil-phase products. In contrast, MgO, TiO2, and ZrO2, with lower basic strengths, exhibited significantly reduced decarboxylation capabilities for benzoic acid and TPA, requiring reaction temperatures 50–70 °C higher than ZnO. Huang et al.154 designed a system where crystalline zirconia nanoparticles were precisely localized between two mesoporous silica slabs. Macromolecules were transferred radially through the mesopores to the highly active zirconia particles, where the chains were selectively hydrogenolyzed into hydrocarbons centered around C18−. By covalently embedding amorphous zirconia nanoparticles into the mesoporous silica walls, catalytic sites with unsaturated coordination required for the reaction were stabilized. Computational studies showed that this catalyst achieved catalytic activity comparable to Pt/C. Wang et al.254 synthesized two FeNi catalysts via sol–gel and impregnation methods to produce carbon materials from PP. The catalysts were able to produce CNTs at 700–800 °C. At 800 °C, high purity multi-walled CNTs with outer diameters of 20–30 nm and lengths of several micrometers were obtained. A comparative analysis showed that the superior dispersion properties of the catalyst synthesized by the sol–gel method resulted in higher catalytic activity. These results highlight the dual utility of transition metal oxide catalysts—both for high activity in plastic pyrolysis and for value added carbon. In HDPE pyrolysis, CuCO3 catalysts were used to convert plastics into liquid hydrocarbons.255 The collected liquid hydrocarbon fuels predominantly consisted of paraffins, olefins, and aromatics. Impressively, they were used to power a gasoline engine on a car, and may be used in gasoline and diesel engines.
The above catalysts are suitable for plastic pyrolysis. Zeolites are the most commonly used catalysts since they are highly selective for gasoline and diesel fractions. Other catalysts have good catalytic performance and potent selectivity for particular products, but often require high temperatures for plastic pyrolysis. Hierarchical materials with larger specific surface area and combination of mesopores and macropores have more potential for plastic pyrolysis, which mitigate mass transfer limitation due to the large molecular size of plastics and reduce coke deposits for longer term operation. One challenge for the current catalyst development is the balance between active catalytic sites and pore design for producing hydrocarbons with specific chain lengths while prolonging catalyst life.
5.4 Catalyst deactivation and regeneration
Catalyst deactivation is a common problem in catalytic plastic waste pyrolysis, which is a very complex process that poses a significant barrier. In this chapter we will summarize the reasons for catalyst deactivation. Catalysts undergo several physicochemical processes during the reaction phase that result in rapid and severe deactivation. These include coke deposition, thermal degradation of the support and metal sintering. The reasons for catalyst deactivation depends on the composition, structure and operation of the reaction.Coke deposition results from the physical deposition of carbon-containing species from the fluid phase onto the catalyst surface, leading to the blockage of active sites and pores and consequently loss of activity.256 Due to the low thermal conductivity and high viscosity of plastics, as well as impurities commonly found in plastic waste, such as Ca, Ti, Fe, Cu, Zn, and Pb, which often exist as oxides—these impurities exhibit high stability and strong fouling tendencies on the catalyst surface, making them difficult to remove. As a result, coke deposition in the catalytic pyrolysis of plastics is nearly inevitable.257 For supported catalysts, deactivation caused by coke deposition can be illustrated in Fig. 10(a): (i) as a monolayer of strong chemisorption or multilayer physical adsorption, it obstructs access to active sites; (ii) complete encapsulation of active sites prevents the reactants from approaching them; (iii) blockage of micropores and mesopores impedes pathways to internal active sites; (iv) during advanced coke growth stages, structural changes and decomposition of the catalyst occur, potentially leading to reactor blockage.258 Some studies distinguished two types of coke formation: (i) carbon formed via CO disproportionation and (ii) coke formed through condensation or decomposition of hydrocarbons, typically comprising heavy hydrocarbons.259
 | ||
| Fig. 10 (a) Deactivation pathways by coke deposition on a supported metal catalyst.258 Adapted with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2020. (b) Reaction scheme of pyrolysis-cracking of polyethylene and deactivation mechanisms of HZSM-5, Hβ, and HY catalysts with examples of coke molecules.260 Adapted with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2011. | ||
During plastic pyrolysis, excessive acidic sites on zeolite promote coke formation. Coke precursors such as olefins and aromatics are initially adsorbed into the acidic sites of the catalyst. As the reaction progresses, these precursors further react with other molecules to form coke.261 Due to the high temperatures of plastic pyrolysis reactions, coke precursors undergo hydrogen transfer and dehydrogenation reactions leading to formation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Consequently, coke exhibits high stability and large dimensions, accumulating within the pores, leading to pore blockage and catalyst deactivation.262 Coke formation depends heavily on the catalyst topological structure and operational parameters. As the temperature increases, the coke formation rate accelerates, since the conditions favor the formation of coke precursors. At elevated temperatures, coke formation proceeds through the oligomerization of olefinic products, followed by the cyclization of these oligomers. Subsequent hydrogen transfer converts them to monoaromatics. These monoaromatics are then alkylated, and finally undergo cyclization and further hydrogen transfer to yield coke precursors such as diaromatics and triaromatics.263 In one study, researchers analyzed the coke formed in HZSM-5, Hβ, and HY zeolites with different topological structures. As shown in Fig. 10(b), the coke structure showed that the coke in ZSM-5 zeolite consists of benzene molecules connected by long and numerous aliphatic chains. In contrast, the coke in β zeolites contains polyaromatic compounds with 3 to 4 aromatic rings and higher olefin content in the aliphatic chains. The coke accumulated in Y zeolite after the reaction primarily consists of condensed aromatic structures with 4–5 rings, extending up to 7 aromatic rings in some cases, and features relatively few and shorter aliphatic chains. The relatively low coke accumulation in MFI zeolite and β zeolite is due to curved pores which suppress coke deposition. However, the supercage structure of Y zeolite promotes undesirable bimolecular condensation reactions leading to higher coke formation.264,265 Marcilla et al.266 found that higher cracking temperatures instead reduced coke deposition on HZSM-5 and HUSY zeolites. This was attributed to rapid reactant cracking into smaller molecules, which escaped the pores and inhibited coke accumulation. The coke content was 15% on HUSY versus 5% on HZSM-5, due to the latter's smaller pore size, restricting coke formation. Chen et al.267 studied the effects of coke deposition on active sites and catalytic performance during catalytic cracking over Y zeolite. They observed that external coke accumulated at a faster rate, and the coke species evolved from tricyclic aromatics to hexacyclic alkyl aromatics. The study concluded that strong acidic sites and micropores facilitated coke deposition, leading to a gradual decrease in catalyst acidity as coke accumulation progressed.
Coke deposition depends on the topology. Magnoux et al.268 studied the effect of coke deposition on 3 protonated zeolites: FAU (Si/Al = 3.0), MOR (Si/Al = 7.7) and MFI (Si/Al = 46). Both MFI and FAU zeolites have three-dimensional channels and MOR has one-dimensional channels. After reacting with propylene at 623 K for 12 h, coke deposition was compared across the three topologies. The highest coke content (14.4 wt%) was observed on FAU zeolite with the largest internal cavities. Coke deposition was reduced by a factor of four on MFI zeolite which had the highest coke resistance. On the one-dimensional MOR zeolite, the coke content was 10.3 wt%. Coke oxidation on MFI zeolites was slower than on FAU and MOR zeolites, suggesting that coke oxidation is shape selective.
Thermal degradation is also a major cause of catalyst deactivation. Thermal degradation typically occurs as follows: (i) the catalyst framework structure is destroyed (pores collapse, active sites are lost); (ii) the catalyst support can be thermally decomposed or structurally decomposed at high temperatures. These changes may have a significant effect on physical properties, such as specific surface area, porosity, and mechanical strength.256 Zeolites have high thermal stability and can generally maintain their framework structure at temperatures up to 600 °C.269 Therefore, thermally decomposition affects non-zeolite-based catalyst supports, such as Al2O3, MgO, SiO2, ZrO2 and TiO2. Studies have shown that supports undergo phase transitions at high temperatures. For example, Al2O3 forms δ-Al2O3 at 100 °C, turns into γ-Al2O3 at 300–450 °C and further transitions to other crystalline forms at higher temperatures.270 Furthermore, research shows that addition of elements such as La, Si, and Ba to Al2O3 supports can significantly improve thermal stability.271 Similarly, halogens may promote sintering catalyst supports. For example, in MgO or TiO2 supports, Cl and steam can cause mobile surface hydroxides, which can then volatilize and condense into agglomerates.
Metal sintering is another common deactivation mechanism for metal catalysts under high temperature reactions. Sintering refers to the aggregation and growth of metal particles at elevated temperatures, resulting in a significant reduction in active surface area and a decline in catalytic performance. For supported metal catalysts, the sintering mechanism consists of: (i) Ostwald ripening: atomic migration from smaller to larger metal particles; (ii) Brownian motion: coalescence and growth of individual crystallites through surface migration. These processes reduce the total surface area, decreasing free energy and enhancing thermodynamic stability.256,258 Sintering reduces the number of active sites accessible and leads to a significant decrease of catalytic activity. In structure-insensitive reactions (e.g. CO hydrogenation), sintering has little effect on the turnover frequency (TOF) of each exposed active site. In structure-sensitive reactions (e.g. hydrogenolysis or steam reforming), sintering reduces TOF, leading to a significant decrease in overall catalytic activity. Temperature is the main influence of metal sintering. Metal atom mobility increases near Tamman temperature (approximately 1/3 of the melting point).256,272 For example, in an O2 atmosphere, Pt catalysts supported on Al2O3, SiO2, or Al2O3–SiO2 show sintering above 600 °C, while Ru and Ir catalysts start sintering at approximately 400 °C. Studies have shown that treating Pt/γ-Al2O3 systems at ≤600 °C in an O2 atmosphere improves metal dispersion.273–275 Despite their superior sintering resistance due to higher Tamman temperatures, noble metals are costly, driving research interest toward transition metals. Among these, Ni has received attention due to its excellent performance in hydrogenation,276 dehydrogenation,277 and coupling reactions.278 However, Ni is more susceptible to sintering due to its low Tamman temperature (590 °C). Remiro et al. compared Ni and Rh catalysts in steam reforming of bio-oil and found that Ni catalysts are significantly deactivated at higher temperatures due to sintering.279 Different strategies have been proposed to reduce metal sintering. For example, adding elements like K or Cu to Ni catalysts reduces sintering.280,281 Other strategies include using porous supports to promote metal dispersion and strengthen strong metal–support interactions to suppress particle aggregation.282
Catalyst deactivation can severely reduce or even terminate the catalytic activity in plastic pyrolysis, representing a critical bottleneck hindering its industrialization. During the reaction, the loss or blockage of active sites due to coking, poisoning, sintering, and other reasons prevents reactants from accessing these active sites, leading to a sharp decline in the conversion rate of the plastic pyrolysis reaction. Furthermore, some studies indicate that partial coking of the catalyst can alter the reaction pathway, causing significant changes in product selectivity and promoting the formation of undesirable by-products.283,284 As the catalyst gradually deactivates, maintaining conversion rates often necessitates more severe reaction conditions, which can trigger excessive cracking. This reduces the yield of high-value chemicals or liquid fuels and increases the production of non-condensable gases and coke. In industrial operations, the loss of catalyst activity forces frequent shutdowns for catalyst regeneration or replacement, directly reducing effective production time and output, thereby significantly increasing operating costs. In summary, catalyst deactivation leads to direct losses at both the microscopic level of active site performance and the macroscopic economic level. Extending the catalyst lifespan is central to enhancing the efficiency and economic viability of plastic pyrolysis.
Catalyst deactivation is inevitable during catalytic plastic waste pyrolysis. Regeneration can reduce the cost of replacement of catalysts and thus production costs. The feasibility of catalyst regeneration depends on the deactivation mechanism. For example, structural damage of catalysts due to high temperature is often difficult or expensive to correct. Consequently, “regeneration” refers to addressing deactivation due to coke deposition on catalysts, particularly porous materials.285 For coke deposition, strategies include reducing coke formation and regenerating catalysts affected by coke accumulation. Since coke deposition starts at openings of catalyst pores, catalysts with high surface areas can tolerate more coke, thus prolonging their life.286 Reducing the diffusion path length of reactants can promote diffusion of reactants and products, minimize the residence time of coke precursors in pores and decrease the likelihood of coke formation.287,288 Surface passivation techniques that remove external strong acids while preserving internal acid sites are also shown to reduce coke formation. Catalytically activated catalysts that are activated by coke removal are usually reversible and the deposited carbonaceous compounds can be removed by oxidation or gasification.289 A common industrial approach is to calcinate catalyst in oxygen or air.256 However, oxidation regeneration with air or oxygen is highly exothermic. It releases large amounts of heat which can lead to local overheating and structural damage to the catalyst. Water vapor produced during oxidation can also leak Al atoms out of the zeolite, decreasing the catalyst activity. Therefore, balance should be maintained between structural damage prevention and effective removal of coke during catalyst regeneration. Kassargy et al.290 showed that burning coke at 500 °C for 3 h effectively removed coke deposited during the cracking of PE. The regenerated USY zeolite retained catalytic activity similar to that of fresh catalysts after eight cycles. This suggests that regeneration at 500 °C is feasible for zeolite catalysts with high thermal stability.
To address the structural damage to catalysts caused by high temperatures, researchers have been exploring alternative methods for coke removal. Current approaches include the use of ozone,291 non-thermal plasma,292 and Fenton reagents,293 all of which operate at low temperatures. Ozone, with its stronger oxidizing ability compared to oxygen, can more easily convert carbon into carbon dioxide at lower temperatures, thereby minimizing structural damage to the catalyst. Parera et al.294 used oxygen and ozone to remove coke deposits from Pt–Sn/Al2O3 catalysts, whose required temperatures for complete removal were 450 °C and 125 °C, respectively. Nonthermal plasma is used to decompose and oxidize coke deposits on the catalyst or material surface, enabling regeneration. Astafan et al.295 showed that highly alkylated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon coke in FAU zeolites could be removed at 800 K using combustion. However, using low energy nonthermal plasma, the natural acidity and microporosity of the zeolites could be restored at 293 K. Fenton reagents are strong oxidizing systems composed of H2O2 and Fe2+ which generate highly active hydroxyl radicals by catalytic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide by iron ions. Recently, this method has been applied to coke removal. Morales et al.296 tested Fenton reagents for coke removal on microporous ZSM-5 catalysts, and successfully reactivated the porous catalysts below 100 °C. These three methods have minimal structural damage to catalysts and are promising for industrial use. Longer catalyst life can significantly reduce preparation costs, making these techniques highly useful for industrial applications.
6 Conclusion and outlook
In the past decade, much work has been done in plastic pyrolysis, and this review summarizes recent work on catalytic pyrolysis of plastic waste. Since governments and the public are increasingly aware of plastic pollution, plastic waste pyrolysis has been increasingly studied. While investigations have expanded into various approaches, including thermocatalysis, photocatalysis, electrocatalysis, and biocatalysis, catalytic cracking aimed at producing liquid fuels stands out as the most promising pathway toward industrialization due to its sustainability and economic viability. However, the chemical heterogeneity of mixed plastic waste presents a significant challenge, as it impedes complete decomposition under uniform reaction conditions. Achieving long term development of a circular economy for plastic waste requires a profound understanding of the chemical properties of different plastics and the mechanisms underpinning their thermal decomposition. Catalytic reaction conditions exert a huge influence on the distribution of pyrolysis products. Consequently, research efforts have increasingly focused on catalytic pyrolysis at relatively lower temperatures. Large amounts of work on catalyst development have been conducted, yielding zeolites, metal/zeolite composites, FCC catalysts, clays and metal oxides. This review discusses the performance of catalysts, focusing on zeolites, their unique pore topology and acidity, which are very efficient in plastic pyrolysis. However, there is no good knowledge of catalyst longevity and the coke deposition mechanism, a major barrier to catalyst optimization and industrial adoption. Addressing these problems requires analyses of product distribution.Realizing a circular economy through waste plastic pyrolysis technology is a complex and comprehensive engineering challenge, involving waste plastic treatment, catalyst design, reactor and reaction condition optimization, and economic feasibility assessment. During the laboratory development stage, significant emphasis has been placed on the analysis of pyrolysis products. Current research trends focus on converting pyrolysis products into liquid fuels such as gasoline and diesel, high-value olefins, and aromatic products like BTX. Some researchers are also exploring alternative applications for plastic pyrolysis products, such as hydrogen storage materials.297 Therefore, the value of the products should be the primary consideration when implementing plastic pyrolysis. Feedstock treatment is a current research challenge. Mixed plastics contain impurity elements like Cl and O, which complicate plastic treatment, potentially lead to catalyst poisoning, and generate toxic by-products. Addressing this issue can be approached from multiple angles: developing new catalytic technologies and catalysts tolerant of complex feedstocks, such as the “chemical scissor” strategy capable of processing PVC-containing mixed plastics under mild conditions,298 or alternatively, directing impurity elements towards transformation into valuable chemicals within the catalytic system. Plastic sorting technology presents another feasible pretreatment approach. Sorting plastics into different categories allows for the design of catalytic cracking technologies tailored to specific plastics, significantly reducing catalyst development complexity. Currently developing plastic sorting technologies include AI intelligent sorting combining optical sensor cameras and AI algorithms,299 high-precision spectroscopic analysis techniques like Raman spectroscopy and infrared spectroscopy for classification,300,301 and chemical recycling pretreatment methods analyzing plastic structures via techniques like NMR for sorting.300,302 However, current plastic sorting technologies still fall short in terms of performance or economic viability for real industrial application.
Although various reactors have been developed, existing research still cannot directly compare their performances. To assess heat and mass transfer limitations, establishing precise kinetic models is necessary. These models can effectively simulate actual temperatures and product distributions, thereby more accurately describing the three-phase characteristics of the pyrolysis process. The design and development of catalytic pyrolysis reactors should progress towards greater feedstock adaptability, simplified pretreatment, and optimized energy utilization, aiming for more efficient and energy-saving pyrolysis processes. Furthermore, long-term operational stability, economic feasibility, and performance at larger scales require validation through practical industrial projects.
The development of catalysts or tandem processes for the co-pyrolysis of complex mixed plastics remains a mainstream research focus. This heavily relies on researchers' understanding of the pyrolysis mechanisms of different plastics. Consequently, elucidating reaction mechanisms and pathways under various conditions will remain a critical challenge to be overcome for the foreseeable future. Research on pyrolysis mechanisms strongly depends on experiments and modern characterization techniques. Given the complexity of plastic molecule pyrolysis, using model compounds like tetracosane to decipher reaction mechanisms is an important approach. In situ characterization techniques can capture intermediates during the reaction process, providing crucial information to aid in deducing reaction pathways. Combining molecular dynamics calculations can enhance the understanding of the reaction process. In one research direction, using polyolefins and PS as reaction intermediates or bridges can be considered, converting other plastics like PVC, PET, etc., into resins or other components containing only C and H elements via the removal of Cl, O, and other atoms. This is feasible because the pyrolysis mechanisms and product compositions of these two types of plastics are well-understood. Target products can be designed as naphtha, light olefins, and aromatic monomers, which is viable both in terms of pyrolysis difficulty and economics. Moreover, for oxygen-containing plastics like PET, directing the pyrolysis products toward CO and coupling them with the Fischer–Tropsch process using H2 to produce liquid hydrocarbons may be a feasible treatment pathway for oxygen-containing plastics.
Author contributions
All authors contributed to the conceptualization, writing and editing of this article.Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.Data availability
No primary research results, software or code have been included and no new data were generated or analysed as part of this review. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D5CY01132A.Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the Central Guidance on Local Science and Technology Development Fund of Shanxi Province (No. YDZJSX2025D017), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. U19B2003, 21975174), and China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation (121014-2).Notes and references
- J. M. García, Chem, 2016, 1, 813–815 Search PubMed.
- M. Deeney, J. Yates, J. Banner and S. Kadiyala, BMJ, 2025, 388, r71 CrossRef PubMed.
- C. Horejs, Nat. Rev. Mater., 2020, 5, 641–641 CrossRef.
- N. Kiran, E. Ekinci and C. E. Snape, Resour., Conserv. Recycl., 2000, 29, 273–283 CrossRef.
- J.-C. Castella, J. Lu, C. Friis, T. B. Bruun, R. Cole, V. Junquera, M. Kenney-Lazar, S. Mahanty, C. Ornetsmüller, P. Pravalprukskul and I. Vagneron, Glob. Environ. Chang., 2023, 80, 102651 CrossRef.
- N. Singh, D. Hui, R. Singh, I. P. S. Ahuja, L. Feo and F. Fraternali, Composites, Part B, 2017, 115, 409–422 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Dong, W. Chen, K. Xu, Y. Liu, J. Wu and F. Zhang, ACS Catal., 2022, 12, 14882–14901 CrossRef CAS.
- J. E. Rorrer, A. M. Ebrahim, Y. Questell-Santiago, J. Zhu, C. Troyano-Valls, A. S. Asundi, A. E. Brenner, S. R. Bare, C. J. Tassone, G. T. Beckham and Y. Román-Leshkov, ACS Catal., 2022, 12, 13969–13979 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Wang, W. Wang, M. Chu, D. Gao, Y. Wang, Y. Lv, R. Wang, L. Song, H. Zhao, J. Chen and G. Chen, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2024, 63, e202409288 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Prajapati, K. Kohli, S. K. Maity and B. K. Sharma, Molecules, 2021, 26, 3175 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Chen, Y. Wang and L. Zhang, ChemSusChem, 2021, 14, 4137–4151 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Qin, F. Wu, Y. Dou, D. Zhao, C. Hélix-Nielsen and W. Zhang, Adv. Mater., 2025, 37, 2418138 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. H. Chang, Sci. Total Environ., 2023, 877, 162719 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Zhang, Z. Chu, R. Cao, X. Wu and K. Han, Fuel, 2026, 404, 136319 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Mandviwala, R. Forero Franco, T. Berdugo Vilches, I. Gogolev, J. González-Arias, I. Cañete Vela, H. Thunman and M. Seemann, Chem. Eng. J., 2024, 500, 156892 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Kusenberg, S. De Langhe, B. Parvizi, A. J. Abdulrahman, R. J. Varghese, S. U. Aravindakshan, A. Kurkijärvi, A. M. Gandarillas, J. Jamieson, S. De Meester and K. M. Van Geem, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 2024, 181, 106571 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Rahman, H. Jahromi, P. Roy, A. Bhattarai, M. Ammar, J. Baltrusaitis and S. Adhikari, Energy Fuels, 2023, 37, 13202–13217 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Steel, C. Barnett, A. K. L. Yuen, A. F. Masters, A. Montoya, T. Maschmeyer and T. M. Aida, ChemSusChem, 2025, 18, e202501269 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Angyal, N. Miskolczi, L. Bartha, A. Tungler, L. Nagy, L. Vida and G. Nagy, Fuel Process. Technol., 2010, 91, 1717–1724 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Han, S. Shin, H. Jung, W. Cho and Y. Baek, Energies, 2023, 16, 2656 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Zhang, N. Zhou, L. Ke, Y. Zeng, Q. Wu, J. Zhang, R. Liao, L. Fan, K. Cobb, R. Ruan, Y. Liu and Y. Wang, Chem. Eng. J., 2025, 514, 163194 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Moustafa, K. Abdelrahman, A. Abdelhaleem and I. S. Fahim, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 2025, 189, 107112 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Han, Y. Yan, X. Pang, B. Wang and D. Sun, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2023, 323, 124505 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Wang, S. Huang and S. C. E. Tsang, Chem. Commun., 2025, 61, 1496–1508 RSC.
- S. R. Ivanova, E. F. Gumerova, K. S. Minsker, G. E. Zaikov and A. A. Berlin, Prog. Polym. Sci., 1990, 15, 193–215 CrossRef CAS.
- D. P. Serrano, J. Aguado, J. M. Escola, E. Garagorri, J. M. Rodriguez, L. Morselli, G. Palazzi and R. Orsi, Appl. Catal., B, 2004, 49, 257–265 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Zhong, J. Liu, L. Gao, J. Chen, X. Wang, Y. Zhang, Y. A. Wu, M. Shakeri, X. Zhang and B. Zhang, Nano Res., 2024, 17, 10088–10098 CrossRef CAS.
- D. P. Serrano, J. M. Escola, L. Briones, S. Medina and A. Martínez, Fuel, 2015, 144, 287–294 CrossRef CAS.
- I.-H. Choi, H.-J. Lee, G.-B. Rhim, D.-H. Chun, K.-H. Lee and K.-R. Hwang, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 2022, 161, 105424 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Hao, Z. Yang, B. Wu, J. Zhu, Z. Li, J. Liu and L. Ma, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 2022, 168, 105789 CrossRef CAS.
- J. E. Rorrer, C. Troyano-Valls, G. T. Beckham and Y. Román-Leshkov, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2021, 9, 11661–11666 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Wu, W.-T. Lee, R. C. Turnell-Ritson, P. C. L. Delannoi, K.-H. Lin and P. J. Dyson, Nat. Commun., 2023, 14, 6524 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Li, H. Luo, Z. Shao, H. Zhou, J. Lu, J. Chen, C. Huang, S. Zhang, X. Liu, L. Xia, J. Li, H. Wang and Y. Sun, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2023, 145, 1847–1854 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Jing, Y. Wang, S. Furukawa, J. Xia, C. Sun, M. J. Hülsey, H. Wang, Y. Guo, X. Liu and N. Yan, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2021, 60, 5527–5535 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Wei, M. Zhu, B. Liu, N. Wang, J. Liu, K. Tomishige, S. Liu and G. Liu, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2023, 62, e202310505 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Liu, W. Dai, J. Zheng, Y. Du, Q. Wang, N. Hedin, B. Qin and R. Li, Adv. Sci., 2024, 11, 2404426 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. D. Anuar Sharuddin, F. Abnisa, W. M. A. Wan Daud and M. K. Aroua, Energy Convers. Manage., 2016, 115, 308–326 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Abnisa and W. M. A. Wan Daud, Energy Convers. Manage., 2014, 87, 71–85 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Zannikos, S. Kalligeros, G. Anastopoulos, E. Lois and J. Renew, Energy, 2013, 2013, 360368 Search PubMed.
- J. M. Heikkinen, J. C. Hordijk, W. de Jong and H. Spliethoff, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 2004, 71, 883–900 CrossRef CAS.
- I. Ahmad, M. Ismail Khan, M. Ishaq, H. Khan, K. Gul and W. Ahmad, Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2013, 98, 2512–2519 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Hong, S. Oh, H. Lee, H. Kim and K. Yoo, Materials Science, 1999, 37, 515–521 CAS.
- S. S. Park, D. K. Seo, S. H. Lee, T.-U. Yu and J. Hwang, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 2012, 97, 29–38 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Aboulkas, K. El Harfi and A. El Bouadili, Energy Convers. Manage., 2010, 51, 1363–1369 CrossRef CAS.
- S.-H. Jung, M.-H. Cho, B.-S. Kang and J.-S. Kim, Fuel Process. Technol., 2010, 91, 277–284 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Abnisa, W. M. A. W. Daud and J. N. Sahu, Environ. Prog. Sustainable Energy, 2014, 33, 1026–1033 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Othman, L. M. Sidek, N. E. A. Basri, M. N. M. Yunus and N. A. Othman, ICEES, 2009, p. 5398623.
- O. Alfernando, F. D. A. Nugraha, I. G. Prabasari, M. Haviz and Nazarudin, J. Phys.:Conf. Ser., 2020, 1567, 022023 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Song, Y. Li, F. Huo, J. Liu, W. Hou, N. Wang, Q. Zhou, J. Xu and X. Lu, Can. J. Chem. Eng., 2023, 101, 4395–4408 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Grause, T. Handa, T. Kameda, T. Mizoguchi and T. Yoshioka, Chem. Eng. J., 2011, 166, 523–528 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Yoshioka, G. Grause, C. Eger, W. Kaminsky and A. Okuwaki, Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2004, 86, 499–504 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Artetxe, G. Lopez, M. Amutio, G. Elordi, M. Olazar and J. Bilbao, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2010, 49, 2064–2069 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Wang, J. Zhang, B. H. Shanks and R. C. Brown, Green Chem., 2015, 17, 557–564 RSC.
- S. Du, J. A. Valla, R. S. Parnas and G. M. Bollas, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2016, 4, 2852–2860 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Masuda, T. Kushino, T. Matsuda, S. R. Mukai, K. Hashimoto and S.-I. Yoshida, Chem. Eng. J., 2001, 82, 173–181 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Kumagai, R. Yamasaki, T. Kameda, Y. Saito, A. Watanabe, C. Watanabe, N. Teramae and T. Yoshioka, Chem. Eng. J., 2018, 332, 169–173 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Kumagai, R. Yamasaki, T. Kameda, Y. Saito, A. Watanabe, C. Watanabe, N. Teramae and T. Yoshioka, Energy Fuels, 2020, 34, 2492–2500 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Masuda, Y. Miwa, K. Hashimoto and Y. Ikeda, Polym. Degrad. Stab., 1998, 61, 217–224 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Cao, W. Chen, W. Jiang, X. Li, P. Sun, S. Fu and Q. Zhang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2025, 64, e202504743 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Kawecki, P. R. W. Scheeder and B. Nowack, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2018, 52, 9874–9888 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Artetxe, G. Lopez, M. Amutio, G. Elordi, J. Bilbao and M. Olazar, Chem. Eng. J., 2012, 207–208, 27–34 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Qian, W. Tian, L. Yin, Z. Yang, F. Tian and D. Chen, Appl. Catal., B, 2023, 339, 123159 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Yang, Q. Dong, C. Zhang, W. Zhang, J. Miscall, A. H. Brozena, J. Chen, N. Liu, T. Li, F. Liu, C. A. Nascimento, B. Dantas, B. Zhang, F. Mumtaz, Z. Liu, S. Liu, Y. Du, Z. Wang, Z. Pang, D. Liu, J. Huang, F. V. Lima, X. Pan, Y. Ju, K. Fu, S. Hu, G. T. Beckham and L. Hu, Nat. Chem. Eng., 2025, 2, 424–435 CrossRef.
- T. Bi, Y. Chen, L. Lin and X. Han, Nat. Chem. Eng., 2025, 2, 650–661 CrossRef.
- W. H. Starnes and X. Ge, Macromolecules, 2004, 37, 352–359 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Lewandowski and K. Skórczewska, Polymer, 2022, 14, 3035 CAS.
- P. E. Sánchez-Jiménez, A. Perejón, J. M. Criado, M. J. Diánez and L. A. Pérez-Maqueda, Polymer, 2010, 51, 3998–4007 CrossRef.
- S. Zhang, H. Han, M. Cao, Y. Xie and J. Chen, Interdiscip. Mater., 2025, 4, 5–23 CAS.
- A. López, I. de Marco, B. M. Caballero, M. F. Laresgoiti and A. Adrados, Fuel Process. Technol., 2011, 92, 253–260 CrossRef.
- W. Cai, X. Wang, Z. Zhu, R. Kumar, P. Nana Amaniampong, J. Zhao and Z.-T. Hu, Fuel, 2023, 353, 129210 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Li, Y. Niu, L. Yi, Y. Li, J. Fu, F. Tang, K. Li and Y. Zou, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 2025, 187, 107022 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Zhang, S. Kim, L. Wahl, R. Khare, L. Hale, J. Hu, D. M. Camaioni, O. Y. Gutiérrez, Y. Liu and J. A. Lercher, Science, 2023, 379, 807–811 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Wang, X. Feng, D. Lin, Y. Li, J. Shang, J. Zhang, S. Li, Y. Liu, H. Zhao, Z. Ma, X. Chen, X. Zhang and C. Yang, Chem. Eng. J., 2024, 485, 149737 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Tanaka, S. Mitsuoka, R. Nakajima, S. Matsuura, T. Hashimoto and A. Ishihara, Appl. Catal., A, 2026, 709, 120644 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Tian, R. Bai, Z. Gao, Z. Chen, M. Wang, H. Tang, S. Lin, B. Xu, X. Liu, J. Yu and D. Ma, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2025, 147, 30268–30276 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Seidi, E. Movahedifar, G. Naderi, V. Akbari, F. Ducos, R. Shamsi, H. Vahabi and M. R. Saeb, Polymer, 2020, 12, 1701 CAS.
- N. Dutta and A. Gupta, Clean Technol. Environ. Policy, 2021, 23, 2213–2220 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Rodríguez Lamar, J. Noboa, A. S. Torres Miranda and D. A. Streitwieser, J. Polym. Environ., 2021, 29, 3842–3853 CrossRef.
- D. Jiraroj, A. Chaipurimat, N. Kerdsa, S. Hannongbua and D. N. Tungasmita, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 2016, 120, 529–539 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Kasar, L. S. Songachan and M. Ahmaruzzaman, J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym., 2025, 35, 1640–1661 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. He, N. Li, M. Dong, S. Wei, W. Zhao, Y. Gao, H. Liu, W. Wang, T. Wang, K. Wang, S. Wang and D. Liu, Appl. Catal., B, 2026, 382, 125917 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Zhang, L. Cheng, R. Chen, J. Gu, J. Zheng, H. Yuan and Y. Chen, Chem. Eng. J., 2025, 517, 164273 CrossRef CAS.
- H. S. Wang and A. Anastasaki, ACS Cent. Sci., 2025, 11, 19–21 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Zeng, Y. Su, J. Jiang and Z. Huang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2025, 147, 2737–2746 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Shah, M. R. Jan and Adnan, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 2014, 31, 1389–1398 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Artetxe, G. Lopez, M. Amutio, I. Barbarias, A. Arregi, R. Aguado, J. Bilbao and M. Olazar, Waste Manage., 2015, 45, 126–133 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. S. Chauhan, S. Gopinath, P. Razdan, C. Delattre, G. S. Nirmala and R. Natarajan, Waste Manage., 2008, 28, 2140–2145 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Zayoud, H. Dao Thi, M. Kusenberg, A. Eschenbacher, U. Kresovic, N. Alderweireldt, M. Djokic and K. M. Van Geem, Waste Manage., 2022, 139, 85–95 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Niu, T. Chen, H. Zong, H. Sun, B. Chen, X. Li, J. Yan and C. Sun, Chem. Eng. J., 2025, 524, 169769 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Hopewell, R. Dvorak and E. Kosior, Philos. Trans. R. Soc., B, 2009, 364, 2115–2126 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. T. Williams and E. A. Williams, Energy Fuels, 1999, 13, 188–196 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Grause, S. Matsumoto, T. Kameda and T. Yoshioka, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2011, 50, 5459–5466 CrossRef CAS.
- M. N. Siddiqui and H. H. Redhwi, Fuel Process. Technol., 2009, 90, 545–552 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Kaminsky, B. Schlesselmann and C. M. Simon, Polym. Degrad. Stab., 1996, 53, 189–197 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Cao, M. Zhang, Y. Jiao, Y. Li, B. Sun, D. Xiao, M. Wang and D. Ma, Nat. Sustain., 2023, 6, 1685–1692 CrossRef.
- Z. Zhang, J. Wang, X. Ge, S. Wang, A. Li, R. Li, J. Shen, X. Liang, T. Gan, X. Han, X. Zheng, X. Duan, D. Wang, J. Jiang and Y. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2023, 145, 22836–22844 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Xuan, S. Yan and Y. Dong, Process, 2023, 11, 2764 CrossRef CAS.
- I. Muhammad and G. Manos, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2022, 10, 15824–15837 CrossRef CAS.
- J. P. Hittinger and D. F. Shantz, Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2022, 343, 112170 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Quesada, M. Calero, M. Á. Martín-Lara, A. Pérez and G. Blázquez, Energy Fuels, 2020, 34, 1781–1790 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Li, Y. Jia, D. Chen, G. Yuan, K. Qian, L. Yin, K. Wang, L. Hong and Y. Hu, Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2025, 233, 111175 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Miandad, M. A. Barakat, A. S. Aburiazaiza, M. Rehan, I. M. I. Ismail and A. S. Nizami, Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 2017, 119, 239–252 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Kassargy, S. Awad, G. Burnens, K. Kahine and M. Tazerout, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 2017, 127, 31–37 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Rahimi and J. M. García, Nat. Rev. Chem., 2017, 1, 0046 CrossRef.
- G. Lopez, M. Artetxe, M. Amutio, J. Bilbao and M. Olazar, Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev., 2017, 73, 346–368 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Botla, P. Barmavatu, M. Pohorely, M. Jeremias and V. S. Sikarwar, Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog., 2024, 50, 102514 CrossRef CAS.
- S. B. Rasul, U. Som, M. S. Hossain and M. W. Rahman, Sci. Rep., 2021, 11, 17048 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Verma, S. Sharma and H. Pramanik, Waste Manage., 2021, 120, 330–339 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. K. Singh, B. Ruj, A. K. Sadhukhan and P. Gupta, J. Energy Inst., 2019, 92, 1647–1657 CrossRef CAS.
- R. J. de Korte, M. N. Dunkle, R. van Belzen, A. Battistella and G. Bellos, Fuel Process. Technol., 2025, 267, 108148 CrossRef CAS.
- I. Kalargaris, G. Tian and S. Gu, Energy, 2017, 131, 179–185 CrossRef CAS.
- J. M. Riesco-Avila, J. R. Vera-Rozo, D. A. Rodríguez-Valderrama, D. M. Pardo-Cely and B. Ramón-Valencia, Sustainability, 2022, 14, 9026 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Jaafar, L. Abdelouahed, A. El Samrani, R. El Hage and B. Taouk, Renewable Energy, 2023, 218, 119252 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Sorino, P. de Vizia, M. Baldelli, L. Bartolucci, S. Cordiner, A. Falsetti, F. Lombardi and V. Mulone, Waste Manage., 2025, 201, 114793 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. A. Wall and S. Straus, J. Polym. Sci., 1960, 44, 313–323 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Chen, X. Zhang, L. Che, H. Peng, S. Zhu, F. Yang and X. Zhang, Fuel, 2020, 271, 117308 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Ding, S. Liu, Y. Huang, S. Liu, N. Zhou, P. Peng, Y. Wang, P. Chen and R. Ruan, Energy Convers. Manage., 2019, 196, 1316–1325 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Zhang, Z. Fu, W. Wang, G. Ji, M. Zhao and A. Li, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2022, 10, 91–103 CrossRef CAS.
- J. H. Chan and S. T. Balke, Polym. Degrad. Stab., 1997, 57, 113–125 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Corma and A. V. Orchillés, Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2000, 35-36, 21–30 CrossRef CAS.
- S. M. Lomakin, S. Z. Rogovina, A. V. Grachev, E. V. Prut and C. V. Alexanyan, Thermochim. Acta, 2011, 521, 66–73 CrossRef CAS.
- V. Mortezaeikia, O. Tavakoli and M. S. Khodaparasti, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 2021, 160, 105340 CrossRef CAS.
- A. R. Auxilio, W.-L. Choo, I. Kohli, S. Chakravartula Srivatsa and S. Bhattacharya, Waste Manage., 2017, 67, 143–154 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. E. Levine and L. J. Broadbelt, Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2009, 94, 810–822 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Fan, L. Liu, Z. Xiao, Z. Su, P. Huang, H. Peng, S. Lv, H. Jiang, R. Ruan, P. Chen and W. Zhou, Energy, 2021, 228, 120612 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Fan, Z. Su, J. Wu, Z. Xiao, P. Huang, L. Liu, H. Jiang, W. Zhou, S. Liu and R. Ruan, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 2021, 157, 105213 CrossRef CAS.
- A. López, I. de Marco, B. M. Caballero, M. F. Laresgoiti, A. Adrados and A. Aranzabal, Appl. Catal., B, 2011, 104, 211–219 CrossRef.
- N. Miskolczi, L. Bartha, G. Deák, B. Jóver and D. Kalló, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 2004, 72, 235–242 CrossRef CAS.
- A. López, I. de Marco, B. M. Caballero, A. Adrados and M. F. Laresgoiti, Waste Manage., 2011, 31, 1852–1858 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. F. Anene, S. B. Fredriksen, K. A. Sætre and L.-A. Tokheim, Sustainability, 2018, 10, 3979 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Berrueco, F. J. Mastral, E. Esperanza and J. Ceamanos, Energy Fuels, 2002, 16, 1148–1153 CrossRef CAS.
- Ö. Çepelioğullar and A. E. Pütün, Journal of Selcuk University Natural and Applied Science, 2013, 2, 694–706 Search PubMed.
- J. A. Onwudili, N. Insura and P. T. Williams, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 2009, 86, 293–303 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Miandad, M. A. Barakat, M. Rehan, A. S. Aburiazaiza, I. M. I. Ismail and A. S. Nizami, Waste Manage., 2017, 69, 66–78 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. P. S. Caldeira, A. Peral, M. Linares, A. S. Araujo, R. A. Garcia-Muñoz and D. P. Serrano, Appl. Catal., A, 2017, 531, 187–196 CrossRef CAS.
- Adnan, J. Shah and M. R. Jan, J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng., 2015, 51, 96–102 CrossRef CAS.
- E. Borsella, R. Aguado, A. De Stefanis and M. Olazar, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 2018, 130, 320–331 CrossRef CAS.
- I. Vollmer, M. J. F. Jenks, R. Mayorga González, F. Meirer and B. M. Weckhuysen, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2021, 60, 16101–16108 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Li, S. W. Lee, G. Yuan, J. Lei, S. Lin, P. Weerachanchai, Y. Yang and J.-Y. Wang, Energies, 2016, 9, 431 CrossRef.
- M. R. Jan, J. Shah and H. Gulab, Fuel Process. Technol., 2010, 91, 1428–1437 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Han, Y. Zhou, S. Chen, H. Chen, J. Zhang, Z. Qu, F. Zeng, T. Ji, H. Jiang, W. Cao, Z. Tang and R. Chen, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2025, 64, e202505518 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Pan, X. Xue, C. Zhang, D. Wang, Y. Xie and R. Zhang, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 2018, 136, 146–152 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Fekhar, L. Gombor and N. Miskolczi, J. Energy Inst., 2019, 92, 1270–1283 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Zhang, H. Yao, R. Khare, P. Zhang, B. Yang, W. Hu, D. Ray, J. Hu, D. M. Camaioni, H. Wang, S. Kim, M.-S. Lee, M. L. Sarazen, J. G. Chen and J. A. Lercher, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2024, 63, e202319580 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. López, I. de Marco, B. M. Caballero, M. F. Laresgoiti and A. Adrados, Chem. Eng. J., 2011, 173, 62–71 CrossRef.
- T. M. Ukarde and H. S. Pawar, Fuel, 2021, 285, 119155 CrossRef CAS.
- J. F. Mastral, C. Berrueco, M. Gea and J. Ceamanos, Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2006, 91, 3330–3338 CrossRef CAS.
- R. van Grieken, D. P. Serrano, J. Aguado, R. García and C. Rojo, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 2001, 58–59, 127–142 CrossRef CAS.
- D. S. Achilias, C. Roupakias, P. Megalokonomos, A. A. Lappas and E. V. Antonakou, J. Hazard. Mater., 2007, 149, 536–542 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Vasile, H. Pakdel, B. Mihai, P. Onu, H. Darie and S. Ciocâlteu, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 2001, 57, 287–303 CrossRef CAS.
- S. C. Cardona and A. Corma, Appl. Catal., B, 2000, 25, 151–162 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Yan, G. Li, Z. Lei, X. Yuan, J. Li, X. Wang, B. Wang, F. Tian, T. Hu, L. Huang, Y. Ding, X. Xi, F. Zhu, S. Zhang, J. Li, Y. Chen, R. Cao and X. Wang, Nat. Commun., 2025, 16, 2800 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Liu, P. A. Kots, B. C. Vance, A. Danielson and D. G. Vlachos, Sci. Adv., 2021, 7, eabf8283 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Chen, A. Tennakoon, K.-E. You, A. L. Paterson, R. Yappert, S. Alayoglu, L. Fang, X. Wu, T. Y. Zhao, M. P. Lapak, M. Saravanan, R. A. Hackler, Y.-Y. Wang, L. Qi, M. Delferro, T. Li, B. Lee, B. Peters, K. R. Poeppelmeier, S. C. Ammal, C. R. Bowers, F. A. Perras, A. Heyden, A. D. Sadow and W. Huang, Nat. Catal., 2023, 6, 161–173 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Cen, X. Han, L. Lin, S. Yang, W. Han, W. Wen, W. Yuan, M. Dong, Z. Ma, F. Li, Y. Ke, J. Dong, J. Zhang, S. Liu, J. Li, Q. Li, N. Wu, J. Xiang, H. Wu, L. Cai, Y. Hou, Y. Cheng, L. L. Daemen, A. J. Ramirez-Cuesta, P. Ferrer, D. C. Grinter, G. Held, Y. Liu and B. Han, Nat. Chem., 2024, 16, 871–880 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Sun, C. Wu, Y. Zhou, J. Zhang, Z. Qu, F. Zeng, Z. Tang, W. Xing and R. Chen, Chem. Eng. J., 2024, 500, 156988 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Duan, W. Chen, C. Wang, L. Wang, Z. Liu, X. Yi, W. Fang, H. Wang, H. Wei, S. Xu, Y. Yang, Q. Yang, Z. Bao, Z. Zhang, Q. Ren, H. Zhou, X. Qin, A. Zheng and F.-S. Xiao, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144, 14269–14277 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. A. Abdullah, A. Novianti, I. I. Hakim, N. Putra and R. A. Koestoer, IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci., 2018, 105, 012033 CrossRef.
- N. Hamidi, F. Tebyanian, R. Massoudi and L. Whitesides, Curr. J. Appl. Sci. Technol., 2013, 3, 417–439 Search PubMed.
- S. Papari, H. Bamdad and F. Berruti, Materials, 2021, 14, 2586 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. H. Lin and M. H. Yang, Appl. Catal., B, 2007, 69, 145–153 CrossRef CAS.
- P. A. Owusu, N. Banadda, A. Zziwa, J. Seay and N. Kiggundu, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 2018, 130, 285–293 CrossRef CAS.
- V. L. Mangesh, T. Perumal, S. Subramanian and S. Padmanabhan, Energy Fuels, 2020, 34, 8824–8836 CrossRef CAS.
- S. H. Shah, Z. M. Khan, I. A. Raja, Q. Mahmood, Z. A. Bhatti, J. Khan, A. Farooq, N. Rashid and D. Wu, J. Hazard. Mater., 2010, 179, 15–20 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Das and P. Tiwari, Resour., Conserv. Recycl., 2018, 128, 69–77 CrossRef.
- Y. Choi, S. Wang, Y. M. Yoon, J. J. Jang, D. Kim, H.-J. Ryu, D. Lee, Y. Won, H. Nam and B. Hwang, Energy, 2024, 286, 129564 CrossRef CAS.
- Ö. Çepelioğullar and A. E. Pütün, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 2014, 110, 363–374 CrossRef.
- A. Inayat, L. Rocha-Meneses, C. Ghenai, M. Abdallah, A. Shanableh, K. Al-Ali, A. Alghfeli and R. Alsuwaidi, Case Stud. Therm. Eng., 2022, 31, 101841 CrossRef.
- Y. Xue, S. Zhou, R. C. Brown, A. Kelkar and X. Bai, Fuel, 2015, 156, 40–46 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Zhang, J. Nie, R. Xiao, B. Jin, C. Dong and G. Xiao, Energy Fuels, 2014, 28, 1940–1947 CrossRef CAS.
- B. J. Milne, L. A. Behie and F. Berruti, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 1999, 51, 157–166 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Elordi, M. Olazar, G. Lopez, M. Amutio, M. Artetxe, R. Aguado and J. Bilbao, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 2009, 85, 345–351 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Arabiourrutia, G. Elordi, G. Lopez, E. Borsella, J. Bilbao and M. Olazar, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 2012, 94, 230–237 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Zhang, G. Ji, C. Chen, Y. Wang, W. Wang and A. Li, Fuel Process. Technol., 2020, 206, 106455 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Zhang, A. Li, Y. S. Zhang, W. Xie, C. Liu, Y. Peng, H. Zhang, Y. Kang, B. Qu and G. Ji, Fuel, 2024, 371, 131950 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Irfan, R. Saleem, B. Shoukat, H. Hussain, S. Shukrullah, M. Y. Naz, S. Rahman, A. A. J. Ghanim, G. Nawalany and T. Jakubowski, Sci. Rep., 2023, 13, 9057 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Cui, Y. Zhang, L. Cui, Y. Liu, B. Li and W. Liu, J. Cleaner Prod., 2023, 411, 137303 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Zhou, L. Dai, Y. Lv, H. Li, W. Deng, F. Guo, P. Chen, H. Lei and R. Ruan, Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 418, 129412 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Wang, J. Jiang, X. Wang, S. Liu, X. Shen, X. Cao, Y. Sun, L. Dong, X. Meng, A. J. Ragauskas and Y. Wang, Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 444, 136360 CrossRef CAS.
- D. K. Ratnasari, M. A. Nahil and P. T. Williams, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 2017, 124, 631–637 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Moorthy Rajendran, V. Chintala, A. Sharma, S. Pal, J. K. Pandey and P. Ghodke, Mater. Today Commun., 2020, 24, 100982 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Elordi, M. Olazar, P. Castaño, M. Artetxe and J. Bilbao, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2012, 51, 14008–14017 CrossRef CAS.
- J. L. V. Neto, C. R. Duarte, V. V. Murata and M. A. S. Barrozo, Drying Technol., 2008, 26, 299–307 CrossRef.
- H. Nagashima, T. Ishikura and M. Ide, Can. J. Chem. Eng., 2009, 87, 228–236 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Elordi, M. Olazar, G. Lopez, M. Artetxe and J. Bilbao, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2011, 50, 6650–6659 CrossRef CAS.
- B.-J. R. Mungyeko Bisulandu and F. Huchet, Appl. Therm. Eng., 2023, 221, 119637 CrossRef.
- M. S. Qureshi, A. Oasmaa, H. Pihkola, I. Deviatkin, A. Tenhunen, J. Mannila, H. Minkkinen, M. Pohjakallio and J. Laine-Ylijoki, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 2020, 152, 104804 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Zhang, G. Ji, D. Ma, C. Chen, Y. Wang, W. Wang and A. Li, Process Saf. Environ. Prot., 2020, 142, 203–211 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Kaminsky and J.-S. Kim, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 1999, 51, 127–134 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Jie, W. Li, D. Slocombe, Y. Gao, I. Banerjee, S. Gonzalez-Cortes, B. Yao, H. AlMegren, S. Alshihri, J. Dilworth, J. Thomas, T. Xiao and P. Edwards, Nat. Catal., 2020, 3, 902–912 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Motasemi and M. T. Afzal, Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev., 2013, 28, 317–330 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Baena-González, A. Santamaria-Echart, J. L. Aguirre and S. González, Waste Manage., 2020, 118, 139–149 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. W. Kim, Y. T. Kim, Y. F. Tsang and J. Lee, Sci. Total Environ., 2023, 903, 166789 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. G. Buekens and H. Huang, Resour., Conserv. Recycl., 1998, 23, 163–181 CrossRef.
- D. P. Serrano, J. Aguado and J. M. Escola, ACS Catal., 2012, 2, 1924–1941 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Liang, J. Chen, Z. Qin, J. Li, P. Wang, S. Wang, G. Wang, M. Dong, W. Fan and J. Wang, ACS Catal., 2016, 6, 7311–7325 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Dai, N. Zhou, Y. Lv, Y. Cheng, Y. Wang, Y. Liu, K. Cobb, P. Chen, H. Lei and R. Ruan, Prog. Energy Combust. Sci., 2022, 93, 101021 CrossRef.
- S. Melendi, M. A. Diez, R. Alvarez and C. Barriocanal, Fuel, 2011, 90, 1431–1438 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Zhang, K. Gora-Marek, J. S. Watson, J. Tian, M. R. Ryder, K. A. Tarach, L. López-Pérez, J. Martínez-Triguero and I. Melián-Cabrera, Nat. Sustain., 2019, 2, 39–42 CrossRef.
- A. Maity, S. Chaudhari, J. J. Titman and V. Polshettiwar, Nat. Commun., 2020, 11, 3828 CrossRef PubMed.
- X. Wang, Y. Ma, Q. Wu, Y. Wen and F.-S. Xiao, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2022, 51, 2431–2443 RSC.
- Z.-P. Hu, J. Han, Y. Wei and Z. Liu, ACS Catal., 2022, 12, 5060–5076 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Bensafi, N. Chouat and F. Djafri, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2023, 496, 215397 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Yan, H. Wang, Y. Liao and C. Wang, Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev., 2023, 178, 113219 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Bai, Y. Song, Y. Li and J. Yu, Trends Chem., 2019, 1, 601–611 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Louis, F. Ocampo, H. S. Yun, J. P. Tessonnier and M. M. Pereira, Chem. Eng. J., 2010, 161, 397–402 CrossRef CAS.
- T. R. Carlson, G. A. Tompsett, W. C. Conner and G. W. Huber, Top. Catal., 2009, 52, 241–252 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Marcilla, M. I. Beltrán, F. Hernández and R. Navarro, Appl. Catal., A, 2004, 278, 37–43 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Marcilla, A. Gómez-Siurana and F. J. Valdés, Appl. Catal., A, 2009, 352, 152–158 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Manos, A. Garforth and J. Dwyer, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2000, 39, 1198–1202 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Manos, A. Garforth and J. Dwyer, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2000, 39, 1203–1208 CrossRef CAS.
- R. C. Mordi, R. Fields and J. Dwyer, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 1994, 29, 45–55 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Smit and T. L. M. Maesen, Nature, 2008, 451, 671–678 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y.-T. Cheng, Z. Wang, C. J. Gilbert, W. Fan and G. W. Huber, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 11097–11100 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Zhang, J. Zhao, L. Zhang, Y. Chen and W. Ma, Energy Convers. Manage., 2024, 312, 118571 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Zhang, Q. Wu, L. Fan, R. Liao, J. Zhang, R. Zou, K. Cobb, R. Ruan and Y. Wang, Chem. Eng. J., 2024, 484, 149777 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Coelho, L. Costa, M. M. Marques, I. M. Fonseca, M. A. N. D. A. Lemos and F. Lemos, Appl. Catal., A, 2012, 413–414, 183–191 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Elordi, M. Olazar, M. Artetxe, P. Castaño and J. Bilbao, Appl. Catal., A, 2012, 415–416, 89–95 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Agullo, N. Kumar, D. Berenguer, D. Kubicka, A. Marcilla, A. Gómez, T. Salmi and D. Y. Murzin, Kinet. Catal., 2007, 48, 535–540 CrossRef CAS.
- A. O. S. Silva, M. J. B. Souza, A. M. G. Pedrosa, A. C. F. Coriolano, V. J. Fernandes and A. S. Araujo, Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2017, 244, 1–6 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Aguado, D. Serrano, M. Romero and J. J. C. C. Escola, J. Mater. Chem., 2008, 18, 4210–4218 RSC.
- J. Aguado, J. L. Sotelo, D. P. Serrano, J. A. Calles and J. M. Escola, Energy Fuels, 1997, 11, 1225–1231 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Socci, A. Osatiashtiani, G. Kyriakou and T. Bridgwater, Appl. Catal., A, 2019, 570, 218–227 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Zhou, X. Han, Z. Qu, J. Zhang, F. Zeng, Z. Tang and R. Chen, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2024, 12, 6013–6022 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Z. Tan, M. Ortega, S. A. Miller, C. W. Hullfish, H. Kim, S. Kim, W. Hu, J. Z. Hu, J. A. Lercher, B. E. Koel and M. L. Sarazen, ACS Catal., 2024, 14, 7536–7552 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Zhang, Y. Ma, K. Song, Y. Zhang and Y. Tang, J. Catal., 2013, 302, 115–125 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. J. Lee, J.-H. Kim, S. H. Kim, S. B. Hong and G. Seo, Appl. Catal., B, 2008, 83, 160–167 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Miskolczi, T. Juzsakova and J. Sója, J. Energy Inst., 2019, 92, 118–127 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Kokuryo, K. Miyake, Y. Uchida, S. Tanaka, M. Miyamoto, Y. Oumi, A. Mizusawa, T. Kubo and N. Nishiyama, ACS Omega, 2022, 7, 12971–12977 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Al-asadi, N. Miskolczi and Z. Eller, J. Cleaner Prod., 2020, 271, 122186 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Pyo, Y.-M. Kim, Y. Park, S. B. Lee, K.-S. Yoo, M. Ali Khan, B.-H. Jeon, Y. J. Choi, G. H. Rhee and Y.-K. Park, J. Ind. Eng. Chem., 2021, 103, 136–141 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Valizadeh, S. Valizadeh, H. Kim, Y. J. Choi, M. W. Seo, K. S. Yoo, K.-Y. A. Lin, M. Hussain and Y.-K. Park, Environ. Res., 2024, 245, 118076 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Fu, Y. W. Cheng, Y. Wang, Y. Zhang and C.-H. Wang, Chem. Eng. J., 2024, 494, 153078 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Liu, B. Ma, J. Tian and C. Zhao, Sci. Adv., 2024, 10, eadn0252 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W.-T. Lee, A. van Muyden, F. D. Bobbink, M. D. Mensi, J. R. Carullo and P. J. Dyson, Nat. Commun., 2022, 13, 4850 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Han, X. Zhou, T. Ji, F. Zeng, W. Deng, Z. Tang and R. Chen, EES Catal., 2024, 2, 300–310 RSC.
- J. I. Mirena, J. W. Thybaut, G. B. Marin, J. A. Martens and V. V. Galvita, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2021, 60, 6357–6378 CrossRef CAS.
- J. G. Speight, Catal. Today, 2004, 98, 55–60 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Zecevic, G. Vanbutsele, K. P. de Jong and J. A. Martens, Nature, 2015, 528, 245–248 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Pyra, K. A. Tarach, A. Śrębowata, I. Melián-Cabrera and K. Góra-Marek, Appl. Catal., B, 2020, 277, 119070 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Chen, L. Cheng, J. Gu, H. Yuan and Y. Chen, Energy Convers. Manage., 2024, 300, 117983 CrossRef CAS.
- G. de la Puente, C. Klocker and U. Sedran, Appl. Catal., B, 2002, 36, 279–285 CrossRef CAS.
- M. M. Mortland and K. V. Raman, Clays Clay Miner., 1968, 16, 393–398 CrossRef.
- J. F. Lambert and G. Poncelet, Top. Catal., 1997, 4, 43–56 CrossRef.
- A. C. V. Coelho, P. D. S. Santos and H. D. S. Santos, Quim. Nova, 2007, 30, 1282–1294 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Manos, I. Y. Yusof, N. Papayannakos and N. H. Gangas, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2001, 40, 2220–2225 CrossRef CAS.
- A. De Stefanis, P. Cafarelli, F. Gallese, E. Borsella, A. Nana and G. Perez, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 2013, 104, 479–484 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Wang, J. Jiang, X. Meng, M. Li, X. Wang, S. Pang, K. Wang, Y. Sun, Z. Zhong, R. Ruan and A. J. Ragauskas, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2020, 54, 8390–8400 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Zhang, M. Zeng, R. D. Yappert, J. Sun, Y.-H. Lee, A. M. LaPointe, B. Peters, M. M. Abu-Omar and S. L. Scott, Science, 2020, 370, 437–441 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Fan, Y. Zhang, S. Liu, N. Zhou, P. Chen, Y. Liu, Y. Wang, P. Peng, Y. Cheng, M. Addy, H. Lei and R. Ruan, Energy Convers. Manage., 2017, 149, 432–441 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Nisar, G. Ali, A. Shah, M. R. Shah, M. Iqbal, M. N. Ashiq and H. N. Bhatti, Energy Fuels, 2019, 33, 12666–12678 CrossRef CAS.
- S. P. Tekade, P. P. Gugale, M. L. Gohil, S. H. Gharat, T. Patil, P. K. Chaudhari, D. S. Patle and A. N. Sawarkar, Energy Sources, Part A, 2025, 47, 3597–3610 CrossRef CAS.
- L. S. Diaz-Silvarrey, A. McMahon and A. N. Phan, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 2018, 134, 621–631 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Yao, H. Li, Y. Dai and C.-H. Wang, Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 408, 127268 CrossRef CAS.
- M. V. Singh, S. Kumar and M. Sarker, Sustainable Energy Fuels, 2018, 2, 1057–1068 RSC.
- M. D. Argyle and C. H. Bartholomew, Catalysts, 2015, 5, 145–269 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Yuan, C. Li, R. Shan, J. Zhang, Y. Wu and Y. Chen, Fuel Process. Technol., 2022, 238, 107531 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Ochoa, J. Bilbao, A. G. Gayubo and P. Castaño, Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev., 2020, 119, 109600 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Rostrup-Nielsen and D. L. Trimm, J. Catal., 1977, 48, 155–165 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Castaño, G. Elordi, M. Olazar, A. T. Aguayo, B. Pawelec and J. Bilbao, Appl. Catal., B, 2011, 104, 91–100 CrossRef.
- M. Guisnet and P. Magnoux, Appl. Catal., A, 2001, 212, 83–96 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Guisnet, L. Costa and F. R. Ribeiro, J. Mol. Catal. A:Chem., 2009, 305, 69–83 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Guisnet and P. Magnoux, Appl. Catal., 1989, 54, 1–27 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Elordi, M. Olazar, G. Lopez, P. Castaño and J. Bilbao, Appl. Catal., B, 2011, 102, 224–231 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Marcilla, M. I. Beltrán and R. Navarro, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 2006, 76, 222–229 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Marcilla, A. Gómez-Siurana and F. J. Valdés, Appl. Catal., A, 2009, 352, 152–158 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Chen, X. Zhang, F. Yang, H. Peng, X. Zhang, S. Zhu and L. Che, Appl. Catal., A, 2021, 609, 117873 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Magnoux and M. Guisnet, Appl. Catal., 1988, 38, 341–352 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Cruciani, J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 2006, 67, 1973–1994 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Pasel, S. Wohlrab, S. Kreft, M. Rotov, K. Löhken, R. Peters and D. Stolten, J. Power Sources, 2016, 325, 51–63 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Arai and M. Machida, Appl. Catal., A, 1996, 138, 161–176 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Trane, S. Dahl, M. S. Skjøth-Rasmussen and A. D. Jensen, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37, 6447–6472 CrossRef CAS.
- E. Romero-Pascual, A. Larrea, A. Monzón and R. D. González, J. Solid State Chem., 2002, 168, 343–353 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Xu, Y. Liu, B. Singh, S. Yi, G. Qin and S. Li, Surf. Interfaces, 2022, 33, 102276 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Zhao, Z. Chen, Z. Lyu, Z. D. Hood, M. Xie, M. Vara, M. Chi and Y. Xia, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141, 7028–7036 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Li, J. Chen, Z. Zhang, I. D. Gridnev and W. J. A. C. Zhang, Angew. Chem., 2019, 131, 7407–7412 CrossRef.
- G. Wang, S. Zhang, X. Zhu, C. Li and H. Shan, J. Ind. Eng. Chem., 2020, 86, 1–12 CrossRef CAS.
- N. A. Till, L. Tian, Z. Dong, G. D. Scholes and D. W. C. MacMillan, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142, 15830–15841 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Remiro, A. Arandia, J. Bilbao and A. G. Gayubo, Energy Fuels, 2017, 31, 7147–7156 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Frusteri, S. Freni, V. Chiodo, L. Spadaro, G. Bonura and S. Cavallaro, J. Power Sources, 2004, 132, 139–144 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Wang, Y. Li, W. Cai, E. Zhan, X. Mu and W. Shen, Catal. Today, 2009, 146, 31–36 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Xie, H. M. Torres Galvis, A. C. J. Koeken, A. Kirilin, A. I. Dugulan, M. Ruitenbeek and K. P. de Jong, ACS Catal., 2016, 6, 4017–4024 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Yang, C. Wang, L. Zhang, W. Dai, Y. Chu, J. Xu, G. Wu, M. Gao, W. Liu, Z. Xu, P. Wang, N. Guan, M. Dyballa, M. Ye, F. Deng, W. Fan and L. Li, Nat. Commun., 2021, 12, 4661 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Wang, L. Yang, M. Gao, X. Shao, W. Dai, G. Wu, N. Guan, Z. Xu, M. Ye and L. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144, 21408–21416 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. P. Serrano, J. Aguado, J. M. Rodríguez and A. Peral, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 2007, 79, 456–464 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Schmidt, C. Hoffmann, F. Giordanino, S. Bordiga, P. Simon, W. Carrillo-Cabrera and S. Kaskel, J. Catal., 2013, 307, 238–245 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Emdadi, L. Mahoney, I. C. Lee, A. C. Leff, W. Wu, D. Liu, C. K. Nguyen and D. T. Tran, Appl. Catal., A, 2020, 595, 117510 CrossRef CAS.
- E. Al-Shafei and Z. Shakor, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 2024, 183, 106830 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Losch, M. Boltz, C. Bernardon, B. Louis, A. Palčić and V. Valtchev, Appl. Catal., A, 2016, 509, 30–37 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Kassargy, S. Awad, G. Burnens, G. Upreti, K. Kahine and M. Tazerout, Appl. Catal., B, 2019, 244, 704–708 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Zhang, X. Zhu, L. Zhang, Y. Li, J. Li, X. Xia, C. Ma and Y. Dong, ACS Omega, 2021, 6, 13484–13495 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Pinard and C. Batiot-Dupeyrat, Catal. Today, 2024, 426, 114372 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Tyagi, N. Kumari and S. Jagadevan, J. Water Process Eng., 2020, 37, 101475 CrossRef.
- C. L. Pieck, C. R. Vera, C. A. Querini and J. M. Parera, Appl. Catal., A, 2005, 278, 173–180 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Astafan, C. Batiot-Dupeyrat and L. Pinard, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2019, 123, 9168–9175 CrossRef CAS.
- M. V. Morales, K. Góra-Marek, H. Musch, A. Pineda, B. Murray, S. Stefanidis, L. Falco, K. Tarach, E. Ponomareva, J. H. Marsman and I. Melián-Cabrera, Appl. Catal., A, 2018, 562, 215–222 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Soltani and J. E. Rorrer, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2023, 62, e202314530 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Polo-Garzon, Z. Wu, Y. Li, J. Zhang, X. Yu, E. Toups, E. Lopez-Honorato, J. T. Damron, J. C. Foster, Y. Cheng, L. L. Daemen, A. J. Ramirez-Cuesta and H. M. Meyer, Sci. Adv., 2024, 10, eadm9963 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Luo, Q. Wu, J. Cao, H. Fang, C. Xu and D. He, Anal. Methods, 2025, 17, 1236–1251 RSC.
- H. Li, L. Li, F. Yin, F. Zhao and J. W. Sutherland, J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manage., 2023, 25, 1841–1852 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Yang, Y. Xiang, Y. Li, W. Bao, F. Ji, J. Dong, J. Chen, M. Xu and R. Lu, AIP Adv., 2023, 13, 075024 CrossRef CAS.
- M. L. Amin, L. N. M. Dinh, A. Rawal, P. B. Zetterlund and V. Agarwal, Macromol. Mater. Eng., 2025, e00195 CrossRef.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2026 |