Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleEnhancing photocatalytic water splitting over nitrogen-rich BaTaO2N with Zr doping†
Hongfei Suna,
Jiuyang Xionga,
Xia Ha*b,
Qian Yuana,
Xin Maoa,
Liyan Zhua,
Hui Xua and
Xuecheng Liu *a
*a
aChongqing Key Laboratory of Catalysis and New Environmental Materials, Engineering Research Center for Waste Oil Recovery Technology and Equipment, College of Environment and Resources, Chongqing Technology and Business University, Chongqing 400067, China. E-mail: liuxc@ctbu.edu.cn
bSichuan Vocational College of Chemical Technology, Luzhou 646300, China. E-mail: xia_hanzhong9305@163.com
First published on 11th June 2025
Abstract
Photocatalytic hydrogen production offers a promising solution for the energy crisis and environmental pollution, and the performance of the photocatalyst is crucial for enhancing the efficiency of hydrogen production. Achieving the intricate structure of metal-doped perovskite oxynitride as photocatalysts responsive to visible light continues to pose a significant challenge. BaTaO2N demonstrates excellent hydrogen evolution activity under visible light irradiation, and its absorption edge exceeds 600 nm. In this study, a N-rich BaTaO2N with Zr doping photocatalyst (1 wt% Zr) was successfully synthesized via a flux method, thereby enhancing its activity for photocatalytic water splitting. The apparent quantum efficiency (AQE) at 420 nm is measured to be 1.73%. Doping with Zr results in a narrower band gap in BaTaO2N and extends the electron lifetime. N-rich BaTaO2N significantly enhances the separation efficiency of photogenerated electrons and holes, thereby elevating the catalytic activity of the photocatalyst.
Introduction
Amidst the surging global demand for energy and the increasingly dire environmental challenges we face, identifying sustainable and clean energy solutions has emerged as an urgent priority in contemporary society.1–3 Due to its high energy density and environmental sustainability, hydrogen is increasingly being recognized as a crucial component of the future energy system.4–6 In the field of electrocatalytic hydrogen production, the rational design of heterostructured electrocatalysts via strategies such as metal doping, interfacial bridge bonding, or strong electron coupling effects represents a highly promising approach for achieving energy-efficient electrocatalytic co-production of hydrogen and high-value chemicals.7–11In the future, the generation of hydrogen through water splitting reactions using photocatalytic technology is expected to be one of the most effective approaches for realizing the hydrogen energy economy.12,13 The light absorption spectrum of numerous conventional photocatalysts is predominantly confined to the ultraviolet region, leading to inadequate catalytic efficiency under visible light conditions.14 In addition, the stability and selectivity of the catalyst are critical for its practical application. Consequently, the advancement of novel photocatalytic semiconductor materials and the optimization of reaction conditions have emerged as central themes in contemporary research.15–17
BaTaO2N is categorized as a perovskite-type nitrogen oxide, exhibiting visible light absorption wavelengths that exceed 600 nm.18–20 It has been demonstrated to be a novel and efficient photocatalytic semiconductor material. However, the photocatalytic performance of BaTaO2N requires enhancement. It has been reported that the enrichment of nitrogen can enhance the capture and recombination of photoelectrons, thereby improving performance.21–24 Narrow bandgap semiconductors demonstrate enhanced activity for hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) in aqueous solutions when electron donors or acceptors are present. Doping with zirconium (Zr) can extend the lifetime of electrons in BaTaO2N.25,26 Li et al. doped BaTaO2N with narrow-band gap Zr and observed that its hydrogen evolution activity surpassed that of undoped BaTaO2N.27
In the synthesis of BaTaO2N, the flux method offers multiple advantages, including facilitating ion diffusion, refining the particle size of the product, and simplifying the post-treatment process. This approach not only enhances the mass transfer efficiency during the reaction but also enables precise control over the morphology and dimensions of BaTaO2N nanoparticles, thereby optimizing their physicochemical properties for applications in photocatalysis and related fields.28
In this study, N-rich BaTaO2N compounds were synthesized using the flux method. Additionally, zirconium (Zr) was doped to modify the surface properties of BaTaO2N, thereby promoting the formation of excess electron compensation in the Ta–O–N bond. This modification ultimately enhanced the performance in photocatalytic water splitting tests. The catalyst exhibited remarkable hydrogen evolution activity when tested in an aqueous solution of methanol.
Experimental section
Synthesis of BaTaO2N
A certain amount of solid BaCO3 and Ta2O5 was weighed according to the molar ratio of Ba![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Ta
Ta![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) KCl being 1.1
KCl being 1.1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10, and then they were ground in an agate mortar for 20 minutes. Subsequently, a certain amount of KCl was added and the grinding was continued for 10 minutes, so as to make the raw materials mix uniformly while ensuring that the total mass of the raw materials remained at 1.5 g. The sample was heated in a tube furnace at a rate of 10 °C min−1 and subsequently maintained at 950 °C under an ammonia flow of 100 mL min−1 for 6 hours. After this process, the sample was washed and dried to obtain barium tantalum oxynitride (BaTaO2N), abbreviated as BTON.
10, and then they were ground in an agate mortar for 20 minutes. Subsequently, a certain amount of KCl was added and the grinding was continued for 10 minutes, so as to make the raw materials mix uniformly while ensuring that the total mass of the raw materials remained at 1.5 g. The sample was heated in a tube furnace at a rate of 10 °C min−1 and subsequently maintained at 950 °C under an ammonia flow of 100 mL min−1 for 6 hours. After this process, the sample was washed and dried to obtain barium tantalum oxynitride (BaTaO2N), abbreviated as BTON.
Synthesis of N-rich BaTaO2N
Ta2O5, TaCl5, KCl, and BaCO3 were accurately weighed and mixed in a molar ratio of Ba![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Ta
Ta![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) KCl = 1.1
KCl = 1.1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10. Then, the mixture was thoroughly ground in an agate mortar for 30 minutes. Subsequently, the mixture was heated in a tube furnace at a rate of 10 °C min−1 to 950 °C and was maintained at this temperature for 6 hours under an NH3 flow rate of 100 mL min−1. During the synthesis process, Ta2O5 and TaCl5 were rapidly stirred for 5 minutes at a mass ratio of 9
10. Then, the mixture was thoroughly ground in an agate mortar for 30 minutes. Subsequently, the mixture was heated in a tube furnace at a rate of 10 °C min−1 to 950 °C and was maintained at this temperature for 6 hours under an NH3 flow rate of 100 mL min−1. During the synthesis process, Ta2O5 and TaCl5 were rapidly stirred for 5 minutes at a mass ratio of 9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1. Afterward, the samples were washed, filtered, and dried to obtain nitrogen-rich barium tantalum oxynitride (N-rich BaTaO2N), which is referred to as NBTON.
1. Afterward, the samples were washed, filtered, and dried to obtain nitrogen-rich barium tantalum oxynitride (N-rich BaTaO2N), which is referred to as NBTON.
Synthesis of N-rich BaTaO2N with Zr doping
N-rich BaTaO2N with Zr doping (Zr-BNTON) was synthesized using Ta2O5 (99.9%, analytically pure), TaCl5 (99.9%, analytically pure), KCl (99.9%, analytically pure), ZrO(NO3)2 (99.9%, analytically pure), and BaCO3 (99.9%, analytically pure) as the raw materials. These chemicals are utilized directly and do not necessitate further purification. During the synthesis process, Ta2O5 and TaCl5 were rapidly stirred for 5 minutes at a mass ratio of 9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1. A specific amount of the mixture (Zr
1. A specific amount of the mixture (Zr![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Ba
Ba![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Ta = 0.01
Ta = 0.01![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1.1
1.1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) was thoroughly combined with KCl, ensuring that the solute concentration in the KCl flux reached 10 mol%. At the same time, both the total solute mass and the flux of KCl were maintained at 1.5 g. The sample was subjected to heating in a muffle furnace at a rate of 10 °C per minute. The material is subsequently heated at 950 °C in an NH3 atmosphere for 6 hours, with an NH3 flow rate maintained at 100 mL min−1. Following washing, filtration, and drying processes, the final product Zr-BNTON is obtained.
1) was thoroughly combined with KCl, ensuring that the solute concentration in the KCl flux reached 10 mol%. At the same time, both the total solute mass and the flux of KCl were maintained at 1.5 g. The sample was subjected to heating in a muffle furnace at a rate of 10 °C per minute. The material is subsequently heated at 950 °C in an NH3 atmosphere for 6 hours, with an NH3 flow rate maintained at 100 mL min−1. Following washing, filtration, and drying processes, the final product Zr-BNTON is obtained.
Characterizations of photocatalysts
Powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis was performed using the Rigaku RU-200b X-ray powder diffractometer, which was carefully calibrated to emit Cu Kα radiation (λ = 1.5406 Å). The instrument operated at a voltage of 45 kV and a current of 250 mA. Ultraviolet-visible light spectra (UV-vis, DRS, UV-2450) were obtained utilizing advanced UV-vis spectrometers equipped with integrating sphere assemblies. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images were acquired using the JEOL JEM-2100 (RH) instrument, operating at an accelerated voltage of 200 kV to provide high-resolution insights into the morphology of the samples. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) data were collected employing the Thermo ESCALAB 250 instrument—one of the most sophisticated XPS spectrometers available in the United States which utilizes Al Kα X-ray radiation for precise elemental analysis. Photoluminescence spectra (PL) were recorded using a xenon lamp fluorescence spectrometer (FS-2500), facilitating a detailed investigation into the luminescent properties of the materials under study.Photocatalytic water splitting testing
150 mg of the sample was added to 150 mL of a water solution containing 10 vol% methanol (Guo yao Group). The material was in situ doped with a platinum cocatalyst using a 0.3 wt% H2PtCl6 precursor. The experiment was conducted in a Pyrex reaction vessel connected to a closed gas circulation system (CEL-SPH2N, AG, CEAULIGHT, Beijing). The temperature inside the reactor was maintained at approximately 283 K using a circulating water cooling system. Before irradiation, the mixture containing the photocatalyst was subjected to a 15-minute vacuum treatment to remove dissolved gases, followed by irradiation with a 300 W Xe lamp (λ ≥ 420 nm). The total amount of hydrogen released during the reaction was quantified using a GC7920 gas chromatograph (Beijing) equipped with a thermal conductivity detector. The reaction system was periodically evacuated every 30 minutes, and the hydrogen produced during each irradiation cycle was analyzed using the CEL-SPH2N system. To evaluate the photocatalytic oxygen evolution performance of the sample powder, the release of oxygen in water under visible light conditions was monitored. Additionally, 0.1 g of La2O3 was added to a solution containing a cobalt catalyst (0.5 wt%) and 10 mM AgNO3, and the oxygen evolution performance of the sample was assessed according to the established procedure.Results and discussions
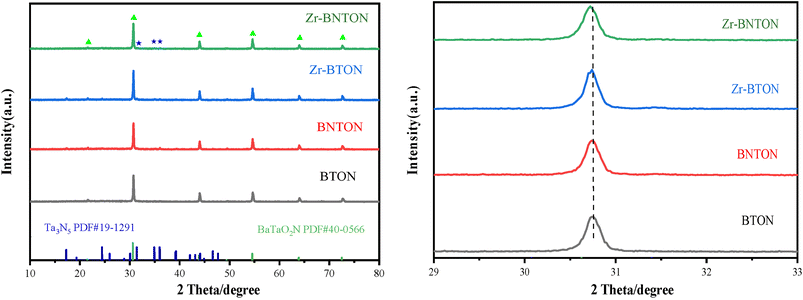
Fig. 1 presents the X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of Zr-BNTON, Zr-BTON, BNTON, and BTON. Distinct diffraction peaks were observed at 2θ positions of 21.5°, 30.6°, 43.9°, 54.6°, 64.1°, and 72.5° corresponding to BaTaO2N (PDF#40-0566), indicating the presence of the ilmenite phase of BaTaO2N within the sample matrix. Additionally, diffraction peaks associated with Ta3N5 (PDF#19-1291) were detected at angles of 31.6°, 34.8°, and 36.1°, suggesting a small quantity of crystalline Ta3N5 is present in the sample matrix. It is noteworthy that during the incorporation of zirconium, a byproduct Ta3N5 is generated as a result of the substitution of Zr4+ for Ta5+.29 In the magnified XRD pattern at 30.6°, a slight peak shift was observed for Zr-BNTON and Zr-BTON, which can be ascribed to the incorporation of Zr. This process leads to an equal separation of Ta2O5 and its subsequent nitridation into Ta3N5. Furthermore, Ta3N5 can also be detected in N-rich samples, which may be attributed to barium loss occurring during the high-temperature nitridation process.Fig. 2(a) and (b) display the transmission electron microscope (TEM) and high-resolution transmission electron microscope (HR-TEM) images of Zr-BNTON, emphasizing its structural features. The results demonstrate that the rod-like structure of Ta3N4 has been successfully deposited onto the surface of Zr-BNTON using the assisted solvent method. In Fig. 2(b), the interplanar spacings of 0.18 nm and 0.19 nm observed in the Zr-BNTON material correspond to the (210) plane of BaTaO2N and the (025) plane of Ta3N4, respectively. During the nitridation process, a highly reducing atmosphere effectively inhibits the formation of undesirable reduced Ta species and associated anionic defects. Furthermore, the TEM image of the pristine BTON in Fig. 2(c) shows no evidence of Ta3N5, indicating that Ta3N5 only appears in Zr-doped and N-rich materials. Supplementary Fig. 3(a) presents a scanning electron microscope (SEM) image of Zr-BNTON at a magnification of 500 nm, revealing its irregular particle morphology. Supplementary Fig. 3(b) depicts the elemental distribution within the material. Notably, despite the low zirconium content, it is uniformly distributed throughout the sample.
 | ||
| Fig. 2 (a) TEM images of the Zr-BNTON at 50 nm; (b) HR-TEM images of the Zr-BNTON at 5 nm. (c) TEM image of the pristine BTON sample. | ||
Ultraviolet-visible spectral analysis was conducted in the wavelength range of 250–800 nm to assess the light absorption capacity and bandgap energy (Eg) of BTON, Zr-BTON, BNTON, and Zr-BNTON. Fig. 3(a) illustrates that the absorption edge of BTON is situated at approximately 650 nm. The light absorption patterns of Zr-BTON, BNTON, and Zr-BNTON exhibit a gradual shift towards longer wavelengths. The results demonstrate that the BTON semiconductor material with high nitrogen content exhibits a significant absorption coefficient in the ultraviolet region. Fig. 4(b) presents the Eg values for these samples, which were determined using the eqn (αhn) 1/n = A (hv-Eg), where α represents the absorption coefficient, hv denotes photon energy, and A is Planck's constant. Concurrently, with Zr doping, there is a slight narrowing of the band gap. This analysis indicates that doping Zr into BTON results in a decrease in the Eg value, which is advantageous for enhancing photocatalytic hydrogen production.
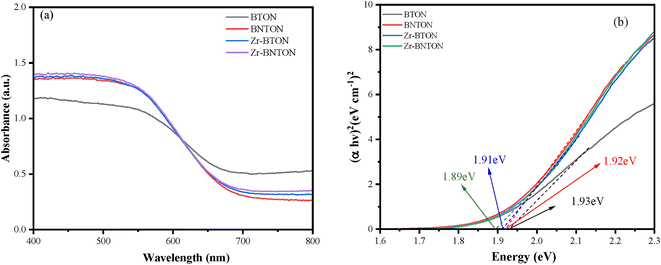 | ||
| Fig. 3 (a) Ultraviolet-visible absorption spectra of BTON, BNTON, Zr-BTON, and Zr-BNTON; (b) bandgaps of BTON, BNTON, Zr-BTON, and Zr-BNTON. | ||
 | ||
| Fig. 4 XPS survey spectra of BTON, Zr-BTON, and Zr-BNTON: (a) the complete band spectra (b) N 1s state; (c) Ba 3d state; (d) O 1s state; (e) Zr 3d state. | ||
Fig. 4 employs X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) to analyze the surface chemical composition of BTON, Zr-BTON, and Zr-BNTON. The full spectrum reveals that BTON is primarily composed of tantalum (Ta), barium (Ba), nitrogen (N), and oxygen (O), whereas both Zr-BTON and Zr-BNTON contain zirconium (Zr). The atomic content of the samples was quantified using the XPS method, as detailed in Table S1.† The peak observed around 395 eV in Fig. 5(b) corresponds to the N3− ion within the crystal lattice, indicating the presence of Ta–N bonds. Notably, this peak exhibits greater intensity in the spectra for Zr-BTON and Zr-BNTON, suggesting an increase in Ta–N bond formation attributed to the substitution of N atoms for O atoms during nitridation.30 In BTON, the Ba 3d5/2 spectrum displays two sub-peaks at 777.9 eV and 779.2 eV, which are respectively assigned to BaO and BaO2. As illustrated in Fig. 5(d), the O 1s spectrum presents two overlapping peaks at 529.2 eV and 531.1 eV; these correspond to lattice oxygen (O2−) and surface hydroxyl groups (OH−). For zirconium compounds depicted in Fig. 5(e), a peak at 176.2 eV is identified as corresponding to Zr from its 3d3/2 state, while a peak at 182.8 eV is associated with ZrO2 from its 3d5/2 state, thereby confirming successful zirconium doping. Additionally, the intensity of the Zr–O peak in the Zr-BNTON spectrum was found to be significantly lower than that observed in the Zr-BTON spectrum. This reduction may be attributed to a partial loss of zirconium, which reacts with TaCl5 during doping to form ZrCl4. The characteristic peaks of the Ta 4f spectrum presented in ESI Fig. 1† can be categorized into two groups of double peaks located at 23.8/25.8 eV and 25.1/27.1 eV, corresponding respectively to Ta–O and Ta–N bonds. To further investigate the surface chemical composition of the samples, peak deconvolution was conducted on the XPS full spectra. The atomic percentages of various elements were determined based on the XPS peak areas (Table S1 in the ESI†).
Fig. 5 presents the photoluminescence (PL) spectrum obtained at an excitation wavelength of 520 nm, highlighting the fluorescence band. A comparative analysis of the PL spectra for BTON, BNTON, Zr-BTON, and Zr-BNTON reveals a gradual decrease in their fluorescence signals. This observation indicates that the formation of a heterogeneous structure comprising Ta3N4 nanorods and BaTaO2N nanoparticles enhances photoionization charge separation. The ionic radius of Zr4+ is larger than that of Ta5+. The substitution of Ta5+ by Zr4+ induces lattice distortion, thereby increasing the formation of lattice defects. These defects can serve as charge trapping centers, which suppress electron-hole recombination and consequently enhance charge separation efficiency. This ultimately boosts the photocatalytic activity.
Fig. 6(a) presents the impedance spectra recorded under open-circuit voltage conditions. Analysis indicates that Zr-BNTON demonstrates a significantly lower interfacial charge transfer resistance in comparison to BTON. Furthermore, the band edge positions of both BTON and Zr-BNTON were determined through Mott–Schottky (MS) analysis. Fig. 6(b) illustrates the mass spectrum curves for the two samples. The positive slope observed in the mass spectrum curve suggests N-type semiconducting characteristics for both materials. By extrapolating the linear segment of the mass spectrum curve to intersect with the potential axis, the values for BTON and Zr-BNTON, relative to NHE, are −0.69 V and −0.51 V, respectively. The values of BNTON and Zr-BTON versus NHE are −0.67 V and −0.55 V, respectively (ESI Fig. 4†).
Fig. 7(a) illustrates the capability of four catalysts, each incorporated with a cocatalyst, to facilitate hydrogen release from water under visible light (λ ≥ 420 nm) over three hours. The results demonstrated that the Zr-BNTON catalyst exhibited the highest hydrogen evolution rate. Specifically, its average hydrogen production rate reached 110 μmolh−1g, marking an approximately 60% enhancement relative to the pristine BTON catalyst. Fig. 7(b) illustrates the oxygen production rates of the four catalysts over 3 hours, revealing that the Zr-BNTON material exhibits the highest activity, achieving an average oxygen production rate of 320 μmolh−1g, which is more than double that of BTON. It is noteworthy that this material not only exhibits high efficiency in hydrogen production but also demonstrates high activity in oxygen generation. The AQE value of Zr-BNTON at 420 nm is 1.73% (ESI Fig. 2†).
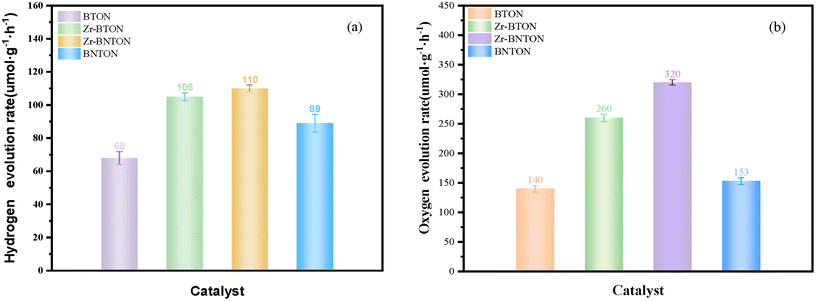 | ||
| Fig. 7 (a) The amount of hydrogen gas evolved over 3 hours for BTON, Zr-BTON, Zr-BNTON, and BTON. (b) The amount of oxygen gas evolved over 3 hours for BTON, Zr-BTON, Zr-BNTON, and BNTON. | ||
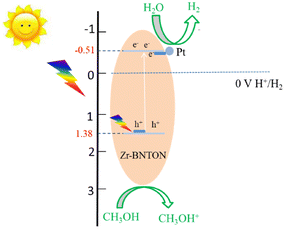
Based on the above results and characterization analysis, a reasonable mechanism of the photocatalytic water decomposition activity exhibited by Zr-BNTON can be assumed. The potential of the valence band (VB) of BTON is −0.51 V. Zr doping leads to a slight increase in the conduction band (CB) potential, with the CB potential of BTON being 1.38 V. Meanwhile, the compensating charge defects from N enrichment cause a slight decrease in the VB potential, thereby reducing the bandgap of the material. As shown in Fig. 8, after the electrons and holes in Zr-BNTON are photoexcited, the accumulated electrons in the Zr-BNTON conduction band can be transferred to the Pt co-catalyst, where water is reduced to produce H2.
Conclusion
In this investigation, N-rich BaTaO2N with Zr doping was synthesized through the flux method to augment the photocatalytic water decomposition performance. The hydrogen evolution rate of photocatalytic water decomposition reaches 110 μmol/gh. Zr-BNTON presents an apparent quantum efficiency (AQE) of 1.73% at a wavelength of 420 nm, and its STH conversion efficiency is 1.3%. The structure of the photocatalyst can be effectively modified to inhibit the recombination of photogenerated carriers, thereby enhancing its photocatalytic performance. We decidedly believe that this research will serve as a promising starting point for modifying the structural aspects of photocatalysts to expedite the decomposition of water.Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.Conflicts of interest
The contributing authors have no interests to declare.Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Science and Technology Innovation Foundation of Chongqing (grant no. CSTB2023NSCQ-MSX0511), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 22202025), the Science and Technology Research Program of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission (grant no. KJQN202200818), the Scientific Research Foundation for Advanced Talents, Chongqing Technology and Business University (No. 1956055).References
- N. P. Brandon and Z. Kurban, Clean energy and the hydrogen economy, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci., 2017, 375, 20160400–20160416, DOI:10.1098/rsta.2016.0400.
- B. N. Iyke, Climate change, energy security risk, and clean energy investment, Energy Econ., 2024, 129, 107225–107241, DOI:10.1016/j.eneco.2023.107225.
- J. Xiao, et al., Sub-50 nm perovskite-type tantalum-based oxynitride single crystals with enhanced photoactivity for water splitting, Nat. Commun., 2023, 14, 8030–8038, DOI:10.1038/s41467-023-43838-3.
- M. M. Aba, I. L. Sauer and N. B. Amado, Comparative review of hydrogen and electricity as energy carriers for the energy transition, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 57, 660–678, DOI:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2024.01.034.
- C. Tarhan and M. A. Çil, A study on hydrogen, the clean energy of the future: Hydrogen storage methods, J. Energy Storage, 2021, 40, 102676–102685, DOI:10.1016/j.est.2021.102676.
- H. Zhou, J. Xue, H. Gao and N. Ma, Hydrogen-fueled gas turbines in future energy system, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 64, 569–582, DOI:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2024.03.327.
- G. Zhou, et al., Efficient paired electrolysis of glycerol upgrading with hydrogen fuel over heterostructured Fe-Co2Mo3O8@Co electrocatalyst, Chem. Eng. J., 2025, 503, 158619–158628, DOI:10.1016/j.cej.2024.158619.
- Y. Wu, et al., Interfacial Bridge Bonds Induced Strong Electronic Coupling of Co@V-WOx Catalyst for Enhanced Concurrent Co-Electrolysis Performance, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2025, 2502104–2502112, DOI:10.1002/adfm.202502104.
- C. Lin, et al., Long-term efficient electrosynthesis of adipic acid and hydrogen by heterostructural molybdenum-nickel alloy electrode, Chem. Eng. J., 2025, 509, 161475–161483, DOI:10.1016/j.cej.2025.161475.
- Y. Guo, Z. Yu, B. He and P. Chen, Metallic cobalt mediated molybdenum nitride for efficient glycerol upgrading with water electrolysis, Chin. Chem. Lett., 2025, 111010, DOI:10.1016/j.cclet.2025.111010.
- X. Ren, et al., Pt-decorated spinel MnCo2O4 nanosheets enable ampere-level hydrazine assisted water electrolysis, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2024, 676, 13–21, DOI:10.1016/j.jcis.2024.07.097.
- S. Nishioka, F. E. Osterloh, X. Wang, T. E. Mallouk and K. Maeda, Photocatalytic water splitting, Nat. Rev. Methods Primers, 2023, 3, 42–56, DOI:10.1038/s43586-023-00226-x.
- Y. Zhao, et al., A Hydrogen Farm Strategy for Scalable Solar Hydrogen Production with Particulate Photocatalysts, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 9653–9658, DOI:10.1002/anie.202001438.
- G. Veréb, et al., Wavelength Dependence of the Photocatalytic Performance of Pure and Doped TiO2 Photocatalysts—A Reflection on the Importance of UV Excitability, Catalysts, 2022, 12, 1492–1501, DOI:10.3390/catal12121492.
- S. Chang, et al., Boosted Z-scheme photocatalytic overall water splitting with faceted Bi4TaO8Cl crystals as water oxidation photocatalyst, Appl. Catal. B Environ., 2023, 328, 122541–122550, DOI:10.1016/j.apcatb.2023.122541.
- J. Yu, et al., Fluorine-expedited nitridation of layered perovskite Sr2TiO4 for visible-light-driven photocatalytic overall water splitting, Nat. Commun., 2025, 16, 361–370, DOI:10.1038/s41467-024-55748-z.
- S. Atri, et al., MXene-Derived Oxide Nanoheterostructures for Photocatalytic Sulfamethoxazole Degradation, ACS Appl. Nano Mater., 2024, 7, 16506–16515, DOI:10.1021/acsanm.4c02523.
- J. W. Seol, J.-S. Lee, M. Avdeev and Y.-I. Kim, Characterizations of structural, optical, and dielectric properties of oxynitride perovskites ACa0.2M0.8O2.6N0.4 (A= Sr, Ba; M = Nb, Ta), Prog. Solid State Chem., 2024, 73, 100439–100448, DOI:10.1016/j.progsolidstchem.2024.100439.
- M. Hojamberdiev, et al., Unfolding the Role of B Site-Selective Doping of Aliovalent Cations on Enhancing Sacrificial Visible Light-Induced Photocatalytic H2 and O2 Evolution over BaTaO2N, ACS Catal., 2022, 12, 1403–1414, DOI:10.1021/acscatal.1c04547.
- B. Dong, et al., Synthesis of BaTaO2N oxynitride from Ba-rich oxide precursor for construction of visible-light-driven Z-scheme overall water splitting, Dalton Trans., 2017, 46, 10707–10713, 10.1039/c7dt00854f.
- X. Liu, et al., Boosting photolytic hydrogen production over N-rich BaTaO2N, J. Photochem. Photobiol. Chem., 2024, 456, 115828–115832, DOI:10.1016/j.jphotochem.2024.115828.
- S. Jadhav, et al., Efficient photocatalytic oxygen evolution using BaTaO2N obtained from nitridation of perovskite-type oxide, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2020, 8, 1127–1130, 10.1039/c9ta10684g.
- X. Jia, et al., All-Solid-State Z-scheme Ta3N5/Bi/CaTaO2N photocatalyst transformed from perovskite CaBi2Ta2O9 for efficient overall water splitting, Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 431, 134041–134050, DOI:10.1016/j.cej.2021.134041.
- Y. Bao, H. Zou, N. Yang, G. Li and F. Zhang, Synthesis of perovskite BaTaO2N with low defect by Zn doping for boosted photocatalytic water reduction, J. Energy Chem., 2021, 63, 358–363, DOI:10.1016/j.jechem.2021.08.010.
- Y. Wang, et al., Simple synthesis of Zr-doped graphitic carbon nitride towards enhanced photocatalytic performance under simulated solar light irradiation, Catal. Commun., 2015, 72, 24–28, DOI:10.1016/j.catcom.2015.08.022.
- Q. Jiang, R. Wan, Z. Zhang, Y. Lei and G. Tian, First-principles calculations to investigate Zr substitution enhanced thermoelectric performance of p-type Zr Hf1−CoBi (x = 0,0.25,0.5,0.75,1) compounds, Phys. Lett. A, 2022, 424, 127839–127847, DOI:10.1016/j.physleta.2021.127839.
- W. Li, et al., Enhanced Z-scheme water splitting at atmospheric pressure with suppression of reverse reactions using Zr-doped BaTaO2N as hydrogen evolution photocatalyst, J. Catal., 2023, 428, 115187–115193, DOI:10.1016/j.jcat.2023.115187.
- Y. Setsuda, Y. Maruyama, C. Izawa and T. Watanabe, Low-temperature Synthesis of BaTaO2N via the Flux Method Using NaNH2, Chem. Lett., 2017, 46, 987–989, DOI:10.1246/cl.170267.
- H. Li, et al., Zr-doped BaTaO2N photocatalyst modified with Na–Pt cocatalyst for efficient hydrogen evolution and Z-scheme water splitting, EES Catal., 2023, 1, 26–35, 10.1039/d2ey00031h.
- K. Lu, et al., N NaTaO3@Ta3N5 Core–Shell Heterojunction with Controlled Interface Boosts Photocatalytic Overall Water Splitting, Adv. Energy Mater., 2023, 13, 2301158–2301166, DOI:10.1002/aenm.202301158.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d5ra01325a |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2025 |