Structure, properties and applications of HfO2-based piezoelectric films
Abstract
Recently, metal element doped HfO2 ultrathin films, i.e. Hf1−xAxO2 (A = Zr, Si, La, Y, Sr, Al, Ta, etc.), have garnered significant attention in the pursuit of developing ferroelectric memory. Hf1−xAxO2 ferroelectric films also exhibit strong piezoelectricity, with direct piezoelectric coefficients (d33) exceeding 37 pC N−1. Moreover, epitaxial strain and polarization switching can modulate the converse piezoelectric coefficient (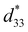 ) from positive to negative values. By utilizing Hf1−xAxO2 piezoelectric films, a wide variety of actuators, resonators, sensors, and other energy conversion devices can be manufactured. Importantly, high-quality, large-size Hf1−xAxO2 films can be grown using atomic layer deposition (ALD) with an annealing temperature of ≤500 °C, which aligns with MEMS fabrication technology at the level of the CMOS backend-of-line (BEOL). Integrating MEMS/NEMS devices with CMOS chips can significantly improve the speed of operation and data collection, opening new possibilities for advanced electronic systems in future.
) from positive to negative values. By utilizing Hf1−xAxO2 piezoelectric films, a wide variety of actuators, resonators, sensors, and other energy conversion devices can be manufactured. Importantly, high-quality, large-size Hf1−xAxO2 films can be grown using atomic layer deposition (ALD) with an annealing temperature of ≤500 °C, which aligns with MEMS fabrication technology at the level of the CMOS backend-of-line (BEOL). Integrating MEMS/NEMS devices with CMOS chips can significantly improve the speed of operation and data collection, opening new possibilities for advanced electronic systems in future.

- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...