 Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleLeveraging solvent affinity for phase-selective doping to enhance doping efficiency in a DPP-based n-type conjugated polymer†
Soyeong
Jang
 a,
Osnat
Zapata-Arteaga
*a,
Diego Rosas
Villalva
a,
Osnat
Zapata-Arteaga
*a,
Diego Rosas
Villalva
 a,
Guorong
Ma
a,
Guorong
Ma
 b,
Andrew
Bates
b,
Anirudh
Sharma
b,
Andrew
Bates
b,
Anirudh
Sharma
 a,
Abdul-Hamid
Emwas
c,
Yongcao
Zhang
a,
Jianhua
Han
a,
Xiaodan
Gu
a,
Abdul-Hamid
Emwas
c,
Yongcao
Zhang
a,
Jianhua
Han
a,
Xiaodan
Gu
 b and
Derya
Baran
b and
Derya
Baran
 *a
*a
aMaterial Science and Engineering Program (MSE), Physical Sciences and Engineering Division, King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST), Thuwal, 23955-6900, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. E-mail: derya.baran@kaust.edu.sa
bSchool of Polymer Science and Engineering, The University of Southern Mississippi, Hattiesburg, MS 39406, USA
cKAUST Core Laboratories, King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST), Thuwal, 23955-6900, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
First published on 19th May 2025
Abstract
Phase-selective doping holds promise for optimizing the electronic properties of conjugated polymers. This approach has been observed on a selection of polymer hosts and dopants, but it is unclear how to translate such an effect to other materials. In our study, we show that in coprocessing techniques, the affinity of the solvent to the polymer host, determined by Hansen solubility parameters, influences whether a dopant is primarily located within the amorphous phase or distributed across both the crystalline and amorphous phases. We used tetrabutylammonium fluoride (TBAF) as the dopant, an n-type DPP-based polymer host (2PyDPP-2CNTVT), and five common solvents. Optical, electrical, and structural characterizations reveal that solvents with high polymer affinity lead to low solid-state order and high Seebeck coefficients S but exhibit low electrical conductivity σ. Alternatively, solvents with partial affinity for both polymer and dopant produce films with mixed phases, where the dopant concentrates in amorphous regions. These films retain a higher structural order at elevated doping levels, achieving electrical conductivity σ, an order of magnitude higher than high-affinity solvents at similar doping concentrations. Our findings propose a solvent-centric strategy for phase-selective doping, potentially fine-tuning the electronic properties for various applications.
New conceptsThis study introduces a solvent-guided strategy for phase-selective doping in conjugated polymers, leveraging Hansen solubility parameters (HSP) as a predictive tool. Unlike existing phase-selective doping methodologies constrained to specific polymer–dopant combinations, this approach strategically utilizes solvent affinity to tailor the microstructure and regulate the phase-specific dopant distribution in n-type polymers. Our finding reveals that solvents positioned at the periphery of the polymer's solubility sphere that have high affinity for the dopant enable optimal doping efficiency by localizing dopant within amorphous regions while preserving the crystalline order. This conceptual advance provides a practical method to enhance doping efficiency without extensive experimentation with different dopant and polymers, potentially accelerating advancements in organic electronics. |
Introduction
Molecular doping of conjugated polymers is crucial for tuning the electronic and optical properties in various optical and energy-harvesting applications, such as organic photovoltaics,1 organic field-effect transistors,2 and organic thermoelectrics (OTEs).3 Within the field of OTE, modulating the carrier concentration is a key to optimizing the Seebeck coefficient S, electrical σ, and thermal conductivity κ – parameters that govern the thermoelectric figure of merit ZT = Sσ2/κT. Nonetheless, optimizing these parameters concurrently is challenging because they are interrelated.4 While σ and S are often tuned via the carrier concentration, the S is not determined by carrier concentration alone – it also depends on the electronic density of states (DOS) near the Fermi level.5 In particular, the shape of the DOS influenced by the material's dimensionality and the presence of energetic disorder.6 This inverse S–σ relationship underpins a long-standing challenge in thermoelectrics.There are three approaches to partially overcome such an issue; the first relies on the engineering of DOS using polymer mixtures7—by mixing two different materials with varying DOS landscapes, it is possible to tune the gap between the transport and Fermi energies, and thus of the S. In optimal compositions, there is a substantial increase in the S that outperforms that of a single material.8–10 The second approach exploits anisotropy in polymer structures through high-temperature rubbing, inducing significant alignment and enhancing σ along the orientation direction.11,12 Such anisotropy increases the localization length in the rubbing direction, resulting in a higher power factor.13
A more recent approach involves phase-selective doping, in which the dopant preferentially populates the amorphous domains while leaving the crystalline phase unaltered.14 Using this approach, Dash et al. and then Zhong et al. reached PF in the range of 160–170 μW m−1 K−2 (ref. 14–16) due to the undisturbed (high mobility) crystalline phase. Furthermore, they could discern different dedoping kinetics related to whether the dopant was located in the crystalline, amorphous, or mixed phases. However, so far, the extensibility of this approach appears limited to a given combination of polymer host/dopant and doping methodology.
To address this gap, we argue that a solvent-guided approach based on the Hansen solubility parameters (HSP) offers a promising strategy for phase selective doping. Moreover, upon optimization, it could also be a tool for controlling the microstructure in conjugated polymers.17 The HSP builds on the Hildebrand solubility parameter by providing a systematic and predictive framework for solvent screening. This considers contributions from dispersion forces (δD), polar interactions (δP), and hydrogen bonding (δH) within a three-dimensional solubility space. A relative energy distance (RED) value differentiates between a good solvent (RED < 1) and a poor one (RED > 1), making it a valuable tool for achieving the desired morphology in co-processing doping methods.18,19
We expect this solvent centric method can also mitigate challenges remain for sequential doping. Dopant molecules often have limited penetration into tightly packed crystalline domains, meaning a significant fraction of the polymer in the crystalline regions can remain undoped.20 As a results, many sequential doping protocols rely on polymer swelling or repeated doping steps to drive dopants into these ordered regions.21 This difficulty becomes especially pronounced in thick or densely packed polymer films, where dopant diffusion is slow and incomplete.22 By contrast, our solvent affinity directed co-process strategy incorporates the dopant during film formation in a single step, using a careful chosen solvent to ensure uniform dopant distribution without disturbing the polymer's morphology.
Here, we show that the solubility-centric methodology using HSP as a predictive tool can effectively guide solvent selection to control the solid-state order and enhance the doping efficiency of the n-type conjugated polymers. As a testbed for our experiments, we employed an in-house designed DPP (diketopyrrolopyrrole)-based n-type polymer, 2PyDPP-2CNTVT, co-processed with tetrabutylammonium fluoride (TBAF), and chemical structures are depicted in Fig. 1(a) and (b). UV-Vis-NIR measurements demonstrated that a solvent such as tetrahydrofuran (THF), located on the periphery of the solubility sphere of the polymer, promotes a higher solid-state order, while a solvent with a higher affinity for the polymer, such as chloroform (CF), results in a more amorphous state. This variation in morphology significantly affects σ, where CF-induced amorphous films show a σ of 0.12 S cm−1, while THF-induced films achieve a σ of 7.43 S cm−1. Grazing incidence wide-angle X-ray scattering (GIWAXS) analysis further revealed that the enhanced σ in ordered films is due to the preferential location of the dopant in the amorphous regions, preserving the stacking order π–π and -thus maintaining a high crystalline phase even at high doping levels. Overall, this study demonstrates that a solubility-guided solvent selection strategy enables phase-selective doping, thereby optimizing the solid-state order and electrical properties, providing a streamlined path to achieving optimal doping efficiency without extensive exploration of different dopants or host polymers.
Results and discussion
Solvent screening system using HSP
As a first approximation, we calculated the HSP parameters for two solutes, the polymer 2PyDPP-2CNTVT and the dopant TBAF. Then, we calculated the solvent affinity between these solutes against a battery of solvents in a database. For this, we used a commercially available database and software (HSPiP),23 along with a methodology previously described in the literature.19 In brief, the solvent–solute interactions are divided into three contributions: dispersive (D), polar (P), and hydrogen-bonding (H) forces. The square root of these components is expressing HSP, i.e. δi (i = D, P, H) following eqn (1).| δ2 = δD2 + δP2 + δH2 | (1) |
| Ra2 = 4(δD1 − δD2)2 + (δP1 − δP2)2 + (δH1 − δH2)2 | (2) |
For the particular case of “polymer–dopant combinations”, we should consider a multisphere system that accounts for the polymer and dopant solutes, each with a defined R0 at a given concentration and temperature. However, for ionic materials, such as the dopant studied in this work, R0 is not easily defined.26 Regardless, as a simple approximation, we expect that the solvent affinity towards a given polymer–dopant combination will be skewed toward the center of the dopant. Specifically, in an imaginary vector line between the polymer and the dopant, we can expect to find a suitable solvent for the polymer–dopant combination somewhere in the middle. Building on this concept, we hypothesized that solvents on the edge of the HSP sphere and in the vector path towards the dopant should allow both (i) the formation of polymer films with higher structural order and (ii) higher dopant diffusion with lower penalty on the structural order as polymer swelling will be predominant over solvation. Using this framework, we selected a subset of solvents that we expect provide a solvent gradient in solvent affinity towards the polymer–dopant composition: chloroform (CF), chlorobenzene (CB), dichlorobenzene (DCB), trichlorobenzene (TCB) and tetrahydrofuran (THF).
We highlight that this approach does not capture a complete picture of solute–solvent interactions. Other methodologies like COSMO-RS (conductor-like screening model for realistic solvents) and combined HSP/COSMO-RS27,28 provide a more accurate description of the physics that govern solute–solvent interactions. However, they are computationally expensive and impractical when screening a large pool of solvents. Our approach provides a quick hand-check over a large pool of materials.
Partial solvents lead to lower localization energies
In a subsequent step, we fabricated TBAF-doped polymer film layers with nominal TBAF contents that ranged from 5–45 mol% (i.e., dopant added in the polymer solution). We measured σ and S and plotted these parameters in the form of a log–log S–σ (Fig. 2(a)), as it provides additional information via the semi-localized transport (SLoT) model introduced by Gregory et al.29,30 following eqn (3) | (3) |
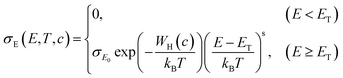 | (4) |
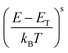 accounts for the increase in electrical conductivity with carrier concentration, while
accounts for the increase in electrical conductivity with carrier concentration, while  captures the transition between localized and delocalized charge transport through WH(c) – a term that scales inversely with carrier concentration and the degree of structural order through the interchain electronic wavefunction overlap. Therefore, fitting our data with this model provides a representative picture of the effects that carrier concentration and solid-state order exert on carrier localization and, consequently, on electronic properties.
captures the transition between localized and delocalized charge transport through WH(c) – a term that scales inversely with carrier concentration and the degree of structural order through the interchain electronic wavefunction overlap. Therefore, fitting our data with this model provides a representative picture of the effects that carrier concentration and solid-state order exert on carrier localization and, consequently, on electronic properties.
Within this concept, we highlight two distinct trends in the TE performance of the thin films: (i) the first set of fitting parameters σ(T, c) includes CF-, CB-, and DCB-based films. In this group, the measured thermally generated voltages remain within the non-degenerate regime, reaching values of several hundreds of μV K−1, and σ are generally below ∼1 S cm−1. (ii) The second trend pertains to THF-based films, which exhibit a downward-vertical offset across the non-degenerate and near-degenerate regions. Despite having the same nominal doping level, these films display significantly higher σ values than those in the first set, resulting in a maximum electrical conductivity (σmax) that is approximately ten times greater than the CF-, CB-, and DCB-based films. These observations suggest a lower localization energy WH(c) in THF-based films compared to the other series, potentially arising from enhanced structural order or differences between the ‘nominal’ and ‘real’ doping levels (i.e., the actual number of generated charge carriers). As discussed in the following sections, our results indicate that both effects contribute to the properties of THF-based films.
Examining the σmax of individual compositions provides insights into the variations between ‘real’ and ‘nominal’ doping levels across each set. In particular, σmax consistently plateaus around 20–35 mol% in all cases, but its magnitude varies and appears to increase with the RED value, particularly for solvents closer in affinity to the dopant. This observation is partially expected; solvents with a higher affinity for the polymer than the dopant tends to have poor polymer–dopant interactions and hinder dopant diffusion through different pre-aggregates in the solution state. In contrast, increasing the solvent's affinity toward that of the dopant can improve dopant diffusion and, therefore, σmax until a trade-off point is reached, either due to poor solubility of the polymer fraction or excessive pre-aggregation of the doped fraction that crashes out of the solution state.20,31
Regarding TE performance, DCB-based films outperform the other materials, achieving a PF of 16.88 μW m−1 K−2 and a ZT of 0.005 at room temperature, assuming a thermal conductivity of 0.3 W m−1 K−1 value, whereas THF-based films, despite their higher σmax of 7.43 S cm−1, only reach a PF of 4.00 μW m−1 K−2 and a ZT of 0.001. This lower ZT and PF value in THF-based materials can be attributed to the penalty on the Seebeck voltage, which is a direct consequence of the seemingly higher carrier concentration at similar dopant loadings but also on a lower degree of disorder within the conjugated polymer.32 In brief, as carrier density within the organic semiconductor increases, a more significant fraction of carriers share the same entropy at a given temperature, decreasing the S.
Optical and electronic characterization
For more accurate quantification of the doping level, we fitted the UV-Vis-NIR spectral features and used the polaron (P2) and transition bands (A0−0 to A0–5) to calculate the polaron mole fraction (θ). It is noteworthy that the lowest-energy polaron (P1) band is absent in our studied cases due to a high localization of the doped species33 or to most doped species are in the form of charge transfer complexes (CTCs). As a reference, we applied the method developed by Spano et al.,34 which assumes that each polymer contains a fixed number of doping sites, with site occupation determined from the integrated area of the absorbance, as described by eqn (5). | (5) |
Fig. 3 shows the UV-Vis spectra and fitting analysis for pristine and doped polymer films deposited from CF, CB, DCB, and THF, while those corresponding to TCB and toluene-based material are available in Fig. S2a and b of the ESI.† Here, three characteristic bands are observed at approximately 1.8 eV, 1.9 eV, & 2.7 eV, typical of DPP-based copolymers. In the doped films, an additional band appears at 1.16 eV, which, based on its position and shape, is attributed to a highly localized polaron or CTC.33,38 From the spectral fitting presented in Fig. 3e, two distinct trends emerge: (i) for films processed with CF, CB, and DCB, the ratio  increases with θ compared to the pristine material and then decreases after reaching a doping threshold. Such threshold differs within each set but scales for solvents near the periphery of the polymer's HSP sphere, that is, θ = 0.11 for CF-, 0.24 for CB-, and 0.21 for DCB-based films, respectively. (ii) THF seems to be near a limit between partial and non-solvent conditions, given that the trend changes entirely and there is virtually no change in the
increases with θ compared to the pristine material and then decreases after reaching a doping threshold. Such threshold differs within each set but scales for solvents near the periphery of the polymer's HSP sphere, that is, θ = 0.11 for CF-, 0.24 for CB-, and 0.21 for DCB-based films, respectively. (ii) THF seems to be near a limit between partial and non-solvent conditions, given that the trend changes entirely and there is virtually no change in the  with added dopant until reaching θ values of 0.27.
with added dopant until reaching θ values of 0.27.
From these observations, we argue that doping first affects the amorphous fraction, leading to a partial ordering of the polymer backbone and a more pronounced J-character, as found in other references.36,39–43 Upon reaching the doping threshold, any additional dopant deteriorates the solid-state order, as seen by the decrease in  after reaching doping threshold. Alternatively, the doping threshold is a more complex parameter to decipher, as it seems to scale with the availability of sites with H-like character and the solvent affinity now toward the dopant. For example, CF- and THF-based seem to start with the same degree of H-and J-like character as probed by the
after reaching doping threshold. Alternatively, the doping threshold is a more complex parameter to decipher, as it seems to scale with the availability of sites with H-like character and the solvent affinity now toward the dopant. For example, CF- and THF-based seem to start with the same degree of H-and J-like character as probed by the  . However, in THF-based films, θ increases more gradually as seen in Fig. 3(f) rather than saturating at a fixed doping level like CF-based films, which seems to be the case for selected samples at equal nominal doping levels probed by electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) (see Fig. S4(d), ESI†)44,45
. However, in THF-based films, θ increases more gradually as seen in Fig. 3(f) rather than saturating at a fixed doping level like CF-based films, which seems to be the case for selected samples at equal nominal doping levels probed by electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) (see Fig. S4(d), ESI†)44,45
Overall, for CF-, CB- and DCB-solvents, dopant seems to infiltrate within the H-like aggregates at low nominal dopant loadings and then into the more ordered J-aggregates. Meanwhile, in THF-based films, the dopant interacts mainly with the H-aggregates even at higher nominal dopant loading, leaving the solid-state order largely unperturbed.
Ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy (UPS) and low energy inverse photoemission spectroscopy (LE-IPES) were conducted to probe the energy-level of pristine and doped 2PyDPP-2CNTVT polymer films. The work function (WF) of pristine 2PyDPP-2CNTVT was determined to be 4.43 eV, whereas the IE and EA was measured to be 6.1 eV and 3.89 eV, respectively. As shown in Fig. 4(a) and (b), the Fermi level (EF) distinctly shifts upwards by 0.48 eV towards the LUMO upon doping with TBAF, as observed by a significant reduction in WF from 4.43 eV to 3.95 eV providing evidence for electron doping in the polymer host. UPS and LE-IPES spectra for different solvent conditions are provide in the Fig. S3 in ESI.† Furthermore, EPR measurements shown in Fig. 4(c) revealed the emergence of free radical via TBAF doping. The EPR spectra measured in other solvents are shown in Fig. S4 in ESI.†
 | ||
| Fig. 4 Energy-level diagram of (a) pristine and (b) TBAF-doped (40 mol%) 2PyDPP-2CNTVT polymer films. (c) EPR spectra of pristine (black line, magnified 5 times) and doped (red line) polymer films. | ||
Surface morphology and crystalline structure
To investigate the impact of solvent selection on the crystalline structure of the polymer films, we collected Grazing Incidence Wide Angle X-ray Scattering (GIWAXS) patterns for both pristine and doped films using the same solvents described in previous sections. All films were prepared under identical deposition conditions and thermal annealing protocols to minimize the influence of film processing on microstructure across each set. The nominal doping level for all series was 35 mol%. The 2D GIWAXS patterns shown in Fig. 5(a)–(h) reveal a bimodal distribution of crystallites for all solvent choices, with a notable predominance of crystallites oriented in a face-on configuration, regardless of the solvent used.Fig. 5(i) and (j) present the variations in lamellar stacking distance, derived from the (100) peak, and the π–π stacking distance, derived from the (010) peak, thereby capturing changes in lattice dimensions for both face-on and edge-on orientations. Under THF conditions, the π–π stacking distance exhibits negligible change upon doping with TBAF, unlike under other solvent conditions. Only a slight expansion in the (100) d-spacing is observed, suggesting minimal incorporation of dopant molecules within the lattice for the crystallites probed through GIWAXS. In contrast, TBAF-doped polymer films prepared using CF, CB, and DCB exhibit significant expansion in the π–π stacking direction, indicative of dopant intercalation between the backbone regions, although intercalation within the lamella cannot be discarded. Given that GIWAXS primarily probes the crystalline fraction, and such changes are absent in THF-based films, we infer that dopant infiltration occurs predominantly within the amorphous regions, as observed in other studies.14–16 It is possible that the space within the polymer network is sufficient to accommodate the dopant, as argued for other DPP-based materials.46 Nonetheless, even in those scenarios, changes in the fitted parameters of the π–π stacking distance are expected due to the effect of polaron delocalization on the surrounding lattice. Detailed fitting information is shown in Fig. S5 in ESI.†
Our observations show that for THF-based films, the crystal lattice remains unchanged, suggesting that the dopant intercalates mostly within the amorphous and less organized phases of the polymer network, as indicated by our optical analysis in Fig. 3. In contrast, for polymer films made from solvents of higher affinity, the dopant induces a distortion in the π–π stacking direction and a partial deterioration of the structural order at the studied dopant loading, cf. Tables S4 and S5 from the ESI.† Further morphology and surface chemical analysis using Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) and AFM-IR provides additional insight into morphology changes upon doping. Moreover, it provides a preview of the dopant distribution homogeneity on the surface and thus miscibility between the host and dopant species in a given solvent. Fig. 6(a)–(h) shows representative examples of the topography on pristine and doped CF-, CB-, DCB-, and THF-based films; additional examples are available in Fig. S6 of the ESI.† AMF-IR measurement was taken at a wavenumber of 1380 cm−1, corresponding to C–N stretching mode of TBAF, to detect its presence on the surface of polymer film. Noteworthy, the doping mechanism of TBAF is still under scrutiny,47–49 and thus the probed frequency might not offer a one-to-one comparison of doped regions on the film's surface. Nonetheless, we assume that at fraction of the overall TBAF-clusters are responsible for doping their vicinity and assess how well these clusters are distributed. The IR mapping images in Fig. 6(i)–(l) reveal that a more homogenous distribution of TBAF molecules was achieved from film fabricated by THF. The corresponding FTIR spectra of TBAF and 2PyDPP-2CNTVT are shown in Fig. S8 in ESI.† The dopant cluster size was calculated from the AFM-IR images and compared in the Table S6 in ESI.† The detail process of calculating dopant area from AFM-IR images are shown in Fig. S9 in ESI.†
Here, we highlight that the domain size, as probed from the height correlation length (cf. Fig. S7, ESI†), ranges from 180–250 nm for the pristine materials. We attribute the differences in the pristine state to the varying drying kinetics resulting from the boiling points of distinct solvents. More striking changes occur upon doping. For CF-based films, the domain size increases in comparison to the pristine state, and large regions of the dopant seem to segregate onto the surface of the film-probably because of saturation and poor miscibility of the dopant within the polymer network, as suggested from our previous discussions. In contrast, for the other solvent systems, we observed a decrease in domain size, dropping by about half to values between 100–50 nm compared to their pristine counterparts and likely due to the better mobility of the dopant in the solution-state arising from the higher dopant solvent affinity.
Discussion on mobility
In Fig. 2, we argue that the enhanced σ in THF-based films is due to increased mobility arising from undisturbed structural order. Following this rationale, we extracted the electron mobility (μe) from OFETs,50 using pristine and TBAF-doped films with nominal dopant concentrations of 0.6 mol%, as seen in Fig. 7. Fig. S10 (ESI†) presents representative raw transfer curves with their fitting parameters, containing both linear and saturation mobilities for doped polymer across the different solvents. Notably, this material exhibits a high electron mobility, which tentatively ascribe to a high degree of structural anisotropy when processed via spin-coating or blade-coating conditions (as seen on Fig. S11 of the ESI†). Here, for CF-, CB- and DCB-based films, there is an increase in mobility compared to the pristine state, probably attributed to the filling and deactivation of the trap and tail states – and also to a partial dopant-induced ordering as indicated in our UV-Vis-NIR analysis (cf.Fig. 3).36,39–43 In contrast, in THF-based films, there is a smaller change in μe, from 0.77–0.57 cm2 V−1 s−1 compared to other solvent systems – likely due to a more homogeneous energy landscape and limited availability of sites with H-like character. Although μe is lower in THF-based films compared to the rest of the solvent systems, we highlight that the activation energy (Ea), extracted from the Arrhenius equation in temperature-dependent σ measurements decreases from 200 meV, 47 meV, 77 meV, & 11 meV for CF, CB, DCB, and THF-based doped polymer film, thus indicating a lower carrier hopping barrier and also a higher crystallinity in THF-based samples.51–53
in temperature-dependent σ measurements decreases from 200 meV, 47 meV, 77 meV, & 11 meV for CF, CB, DCB, and THF-based doped polymer film, thus indicating a lower carrier hopping barrier and also a higher crystallinity in THF-based samples.51–53
Conclusion
In summary, we have presented a solvent-guided strategy for phase selective doping on a high-mobility n-type conjugated polymer 2PyDPP-2CNTVT using TBAF as dopant. Using the HSP, we demonstrated that solvent affinity can be critical information to adjust not only the doping efficiency but also the ratio between crystalline and amorphous phases to improve σ, S, or both. We have demonstrated that solvents on the periphery of the polymer's HSP sphere and partially soluble toward the chosen dopant achieved an efficient doping without disturbing molecular ordering, and lead to a more homogeneous microstructure and a smaller domain size, which we ascribe to a better miscibility between the host-dopant species on the solution state.Experimental
Materials
The synthesis of 2PyDPP-2CNTVT, was commissioned to 1-Material. The NMR spectra confirming its chemical structure are shown in Fig. S13 and S14 (ESI†). The results of the DFT calculations are presented in Fig. S15 (ESI†). The NMR spectra of tetra-n-butylammonium fluoride (TBAF) to confirm the water content are shown in Fig. S16 (ESI†). TBAF and solvents CF, CB, and DCB were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich.HSP evaluation
The HSP values of the polymer and the dopant were determined according to the binary solvent gradient methodology, using several solvents. The solubility of the material for each solvent was determined in the HSPiP software, indicating a value of 1 for all gradient compositions that reached a concentration of 10 mg mL−1 without forming visible aggregates and a value of 0 for those that did not. The solubility test for the polymer and dopant was conducted under room temperature. The HSP values for solvents used in this study were calculated from the HSPiP software database.We dissolved 2PyDPP-2CNTVT and TBAF in each solvent and determined the solubility by direct observation. The experimental observation was then used to perform calculations with the HSPiP software. Based on the solubility data, we obtained the HSPs for 2PyDPP-2CNTVT and TBAF, as shown in Table S3 (ESI†). The HSPs for 2PyDPP-2CNTVT are (δD, δP, δH) = (18.1, 3.4, 4.8) with an HSP sphere radius (R0) of 5.5 and for TBAF (δD, δP, δH) = (23.5, 11.6, 14.5) with an R0 of 19.5.
OTE device fabrication and characterization
Doped films were prepared by spin-coating a polymer solution (10 mg mL−1 in CF, CB, DCB, TCB, THF and toluene) mixed with different amounts of TBAF solution (20 mg mL−1 in CF, CB, DCB, TCB, THF and toluene) in a glove box under nitrogen atmosphere. The molar concentration is calculated considering the molecular weight of TBAF and the molecular weight of the repeating unit in each polymer. The film was spin-cast on cleaned glass substrates with thermally sputtered Au electrodes at 1000 rpm for 1.5 min. After that, the films are annealed on a hotplate at 120 °C for 30 min. Measurements were performed using a probe station in an N2-filled glovebox. The σ was calculated according to the formula σ = (I/V) × L/(w × d). The thickness of the film was acquired through a Tensor profiler. The device configuration is shown in Fig. S12 (ESI†).OFET device fabrication
Devices were fabricated in a bottom-contact top-gate configuration by evaporating 50 nm of gold on a glass substrate through a shadow mask to define source and drain contacts. The channel lengths ranged from 50 μm to 100 μm. CYTOP was spin-coated at 2500 rpm and dried at 90 °C for 20 minutes, yielding a dielectric layer of 1 μm. Lastly, a 40 nm Ag contact was deposited by thermal evaporation. Pristine and TBAF-doped polymer were spin-coated at 1000 rpm and annealed on a hotplate at 125 °C for 30 minutes. The examples of curve fitting details are shown in Fig. S10 of ESI.†UV-vis absorbance spectroscopy
A F20-UVX spectrometer (Filmetrics), equipped with tungsten halogen and deuterium light sources (Filmetrics), was used to measure the absorbance of the films over the 350–1600 nm.Atomic force microscopy (AFM) and infrared spectroscopy combined AFM (AFM-IR)
AFM images were captured using the scanning probe microscope (NT-MDT) in tapping mode. AFM-IR was performed using nanoIR3 from Bruker Instrument, coupled to a MIRcat-QT quantum cascade, mid-infrared laser. The AFM-IR data was collected in tapping mode using a gold-coated AFM probe. The pulse mid-IR laser was tuned to frequencies unique to each component as determined by FTIR characterization. The detail of calculating dopant cluster size is shown in Fig. S9 (ESI†).Grazing-Incidence Wide Angle X-ray Scattering
Grazing-Incidence Wide Angle X-ray Scattering (GIWAXS) of polymeric thin films were performed on a laboratory beamline system (Xenocs Inc. Xeuss 3.0) with an X-ray wavelength of 1.54 Å and sample to detector distance of 15 cm and an incidence angle of 0.2°. Samples were kept under vacuum to minimize air scattering. The diffraction images were recorded on a Pilatus 1M detector (Dectris Inc.) with an exposure time of 1.5 h using Xenocs software.Ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy (UPS)
UPS measurement was carried out in an ultrahigh vacuum chamber manufactured by Omincron, using a low intensity UV light (He I line) with an excitation energy of 21.21 eV. The spectra of photo emitted electrons were at a pass energy of 2 eV using an ARGUS-CU analyzer equipped with a 128 channel stripped anode detector (ScientaOmicron) calibrated using clean polycrystalline silver. All measurement were performed with the base pressure of 10−10 mbar in the UHV chamber.Low-energy inverse photoelectron spectroscopy (LE-IPES)
LE-IPES measurement was conducted in isochromatic mode utilizing an home-built ultra-high vacuum setup performed with the base pressure of 10−9 mbar. Photon emitted during this spectroscopic process were captured using a solid-state photomultiplier tube (PMT) detector (Hamamatsu R585), positioned external to the vacuum. The detector was installed with a Semrock 280 nm bandpass filter, which allowed a narrow wavelength window of 10 nm.Density of functional theory (DFT) calculation
DFT calculations were performed on the ORCA 6.0.1 package with a B3LYP correlation functional and def2-TZVP basis set. The ionization potential of TBAF was calculated based on equation-of-motion coupled-cluster theory and using cc-pVDZ basis set.Author contributions
S. Jang planned the study and carried out OTE and OFET device fabrication/characterization, optical and AFM image analysis. She also prepared the original draft of the manuscript and contributed to visualization. O. Z. Arteaga supervised the project, performed data curation and analysis of OTE device, optical measurement and GIWAXS, provided review and editing of the manuscript. D. R. Villalva designed the polymer. G. Ma conducted GIWAXS measurements. A. Bates performed AFM-IR measurements. A. Sharma conducted and analysed UPS measurements. A. H. Emwas investigated EPR and NMR data, and Y. Zhang assisted AFM measurements. J. Han carried out DFT calculations. X. Gu supervised GIWAXS and AFM-IR investigation and providing resources and guidance. D. Baran supervised the project, reviewed and edited the manuscript and provided funding acquisition. All authors read and commented on the manuscript.Data availability
Data for this article, including GIWAXS results of edf format, 2D pattern images and line-cut fitting parameters are available at KAUST Repository at https://doi.org/10.25781/KAUST-898M9.Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.Acknowledgements
This publication is based upon work supported by the King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) and Office of Research Administration (ORA) under award no. ORA-CRG2022-4668. A. S. acknowledges KAUST support under award no: OSR-CARF/CCF-3079.Notes and references
- Q. Zhang, Z. Chen, W. Ma, Z. Xie and Y. Han, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2019, 7, 12560–12571 Search PubMed
.
- D. Rawlings, E. M. Thomas, R. A. Segalman and M. L. Chabinyc, Chem. Mater., 2019, 31, 8820–8829 CrossRef CAS
.
- M. A. Haque, D. Rosas Villalva, L. H. Hernandez, R. Tounesi, S. Jang and D. Baran, Chem. Mater., 2021, 33, 8147–8172 CrossRef CAS
.
- G. Zuo, H. Abdalla and M. Kemerink, Adv. Electron. Mater., 2019, 5, 1800821 Search PubMed
.
- B. Lv, Y. Liu, W. Wu, Y. Xie, J.-L. Zhu, Y. Cao, W. Ma, N. Yang, W. Chu, Y. Jia, J. Wei and J.-L. Sun, Nat. Commun., 2022, 13, 1835 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- G. Zuo, X. Liu, M. Fahlman and M. Kemerink, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28, 1–7 CrossRef
.
- G. Zuo, Z. Li, E. Wang and M. Kemerink, Adv. Electron. Mater., 2018, 4, 1700501 CrossRef
.
- G. D. Mahan and J. O. Sofo, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 1996, 93, 7436–7439 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- Z. Zhu, C. Liu, F. Jiang, J. Xu and E. Liu, Synth. Met., 2017, 225, 31–40 CrossRef CAS
.
- M. Cutler and N. F. Mott, Phys. Rev., 1969, 181, 1336–1340 CrossRef CAS
.
- L. Hartmann, K. Tremel, S. Uttiya, E. Crossland, S. Ludwigs, N. Kayunkid, C. Vergnat and M. Brinkmann, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2011, 21, 4047–4057 Search PubMed
.
- L. Biniek, S. Pouget, D. Djurado, E. Gonthier, K. Tremel, N. Kayunkid, E. Zaborova, N. Crespo-Monteiro, O. Boyron, N. Leclerc, S. Ludwigs and M. Brinkmann, Macromolecules, 2014, 47, 3871–3879 CrossRef CAS
.
- D. Scheunemann, V. Vijayakumar, H. Zeng, P. Durand, N. Leclerc, M. Brinkmann and M. Kemerink, Adv. Electron. Mater., 2020, 6, 2000218 Search PubMed
.
- A. Dash, S. Guchait, D. Scheunemann, V. Vijayakumar, N. Leclerc, M. Brinkmann and M. Kemerink, Adv. Mater., 2024, 36, 2311303 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- Y. Zhong, V. Untilova, D. Muller, S. Guchait, C. Kiefer, L. Herrmann, N. Zimmermann, M. Brosset, T. Heiser and M. Brinkmann, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32, 2202075 CrossRef CAS
.
- S. Guchait, A. Dash, A. Lemaire, L. Herrmann, M. Kemerink and M. Brinkmann, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2024, 39, 2404411 CrossRef
.
- Y. Yao, W. Huang, J. Chen, X. Liu, L. Bai, W. Chen, Y. Cheng, J. Ping, T. J. Marks and A. Facchetti, Adv. Mater., 2023, 35, 2209906 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
-
C. M. Hansen, Hansen Solubility Parameters: A User's Handbook, CRC Press, 2nd edn, 2007 Search PubMed
.
- D. Corzo, D. Rosas-Villalva, A. C, G. Tostado-Blázquez, E. B. Alexandre, L. H. Hernandez, J. Han, H. Xu, M. Babics, S. De Wolf and D. Baran, Nat. Energy, 2022, 8, 62–73 Search PubMed
.
- I. E. Jacobs, E. W. Aasen, J. L. Oliveira, T. N. Fonseca, J. D. Roehling, J. Li, G. Zhang, M. P. Augustine, M. Mascal and A. J. Moulé, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2016, 4, 3454–3466 RSC
.
- V. Untilova, J. Hynynen, A. I. Hofmann, D. Scheunemann, Y. Zhang, S. Barlow, M. Kemerink, S. R. Marder, L. Biniek, C. Müller and M. Brinkmann, Macromolecules, 2020, 53, 6314–6321 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- R. Kroon, J. D. Ryan, D. Kiefer, L. Yu, J. Hynynen, E. Olsson and C. Müller, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2017, 27, 1704183 CrossRef
.
-
S. Abbott, C. M. Hansen and Y. Hiroshi, Hansen Solubility Parameters in Practice, 5th edn, 2008, https://Hansen-solubility.com Search PubMed
.
- G. Jo, S. H. Cho, H. Kim, H. Yoon, S. Han and M. Chang, Org. Electron., 2020, 81, 105688 CrossRef CAS
.
- F. Niefind, S. Karande, F. Frost, B. Abel and A. Kahnt, Nanoscale Adv., 2019, 1, 3883–3886 RSC
.
- Y. Agata and H. Yamamoto, Chem. Phys., 2018, 513, 165–173 CrossRef CAS
.
- C. Loschen and A. Klamt, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2014, 53, 11478–11487 CrossRef CAS
.
- A. Benazzouz, L. Moity, C. Pierlot, V. Molinier and J.-M. Aubry, Colloids Surf., A, 2014, 458, 101–109 Search PubMed
.
- S. A. Gregory, R. Hanus, A. Atassi, J. M. Rinehart, J. P. Wooding, A. K. Menon, M. D. Losego, G. J. Snyder and S. K. Yee, Nat. Mater., 2021, 20, 1414–1421 Search PubMed
.
- S. D. Kang, G. J. Snyder, S. Dongmin Kang and G. Jeffrey Snyder, Nat. Mater., 2017, 16, 252–257 CrossRef PubMed
.
- S. N. Patel, A. M. Glaudell, K. A. Peterson, E. M. Thomas, K. A. O’Hara, E. Lim and M. L. Chabinyc, Sci. Adv., 2017, 3, e1700434 Search PubMed
.
- D. Venkateshvaran, M. Nikolka, A. Sadhanala, V. Lemaur, M. Zelazny, M. Kepa, M. Hurhangee, A. J. Kronemeijer, V. Pecunia, I. Nasrallah, I. Romanov, K. Broch, I. McCulloch, D. Emin, Y. Olivier, J. Cornil, D. Beljonne and H. Sirringhaus, Nature, 2014, 515, 384–388 Search PubMed
.
- R. Ghosh, C. K. Luscombe, M. Hambsch, S. C. B. Mannsfeld, A. Salleo and F. C. Spano, Chem. Mater., 2019, 31, 7033–7045 Search PubMed
.
- A. J. Moulé, G. Gonel, T. L. Murrey, R. Ghosh, J. Saska, N. E. Shevchenko, I. Denti, A. S. Fergerson, R. M. Talbot, N. L. Yacoub, M. Mascal, A. Salleo, F. C. Spano, A. J. Moulé, G. Gonel, A. S. Fergerson, R. M. Talbot, N. L. Yacoub, T. L. Murrey, R. Ghosh, F. C. Spano, J. Saska, N. E. Shevchenko, M. Mascal, I. Denti and A. Salleo, Adv. Electron. Mater., 2022, 8, 2100888 CrossRef
.
- J. Clark, J.-F. F. Chang, F. C. Spano, R. H. Friend and C. Silva, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2009, 94, 163306 CrossRef
.
- J. Hynynen, D. Kiefer and C. Müller, RSC Adv., 2018, 8, 1593–1599 RSC
.
- F. C. Spano and C. Silva, Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem., 2014, 65, 477–500 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- R. Ghosh, A. R. Chew, J. Onorato, V. Pakhnyuk, C. K. Luscombe, A. Salleo and F. C. Spano, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2018, 122, 18048–18060 Search PubMed
.
- P. Y. Yee, D. T. Scholes, B. J. Schwartz and S. H. Tolbert, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2019, 10, 4929–4934 Search PubMed
.
- S. Hultmark, M. Craighero, S. Zokaei, D. Kim, E. Järsvall, F. Farooqi, S. Marina, R. Kroon, J. Martin, I. Zozoulenko and C. Müller, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2023, 11, 8091–8099 RSC
.
- J. Guo, P. Chen, S. Yang, H. Wei, Y. Liu, J. Xia, C. Chen, H. Chen, S. Wang, W. Li and Y. Hu, Small Methods, 2024, 2400084 Search PubMed
.
- B. X. Dong, Z. Liu, J. W. Onorato, T. Ma, J. Strzalka, P. Bennington, C. K. Luscombe, C. K. Ober, P. F. Nealey and S. N. Patel, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2021, 31, 2106991 CrossRef CAS
.
- S. R. Jackson, G. W. Collins, R. L. Kingsford, P. W. Martin, J. N. Keller and C. G. Bischak, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2024, 12, 9804–9813 RSC
.
- R. Fujimoto, S. Watanabe, Y. Yamashita, J. Tsurumi, H. Matsui, T. Kushida, C. Mitsui, H. T. Yi, V. Podzorov and J. Takeya, Org. Electron., 2017, 47, 139–146 CrossRef CAS
.
- D. Lungwitz, T. Schultz, C. E. Tait, J. Behrends, S. K. Mohapatra, S. Barlow, S. R. Marder, A. Opitz and N. Koch, Adv. Opt. Mater., 2021, 9, 2002039 CrossRef CAS
.
- X. Yan, M. Xiong, X.-Y. Deng, K.-K. Liu, J.-T. Li, X.-Q. Wang, S. Zhang, N. Prine, Z. Zhang, W. Huang, Y. Wang, J.-Y. Wang, X. Gu, S. K. So, J. Zhu and T. Lei, Nat. Commun., 2021, 12, 5723 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- Y. Han, Z. Fei, Y.-H. Lin, J. Martin, F. Tuna, T. D. Anthopoulos and M. Heeney, npj Flexible Electron., 2018, 2, 11 CrossRef
.
- J. Han, C. Ganley, Q. Hu, X. Zhao, P. Clancy, T. P. Russell and H. E. Katz, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2021, 31, 2010567 Search PubMed
.
- X. Zhao, D. Madan, Y. Cheng, J. Zhou, H. Li, S. M. Thon, A. E. Bragg, M. E. DeCoster, P. E. Hopkins and H. E. Katz, Adv. Mater., 2017, 29, 1606928 Search PubMed
.
- S. Deng, Y. Kuang, L. Liu, X. Liu, J. Liu, J. Li, B. Meng, C. Di, J. Hu and J. Liu, Adv. Mater., 2024, 36, 2309679 Search PubMed
.
- D. Kiefer, A. Giovannitti, H. Sun, T. Biskup, A. Hofmann, M. Koopmans, C. Cendra, S. Weber, L. J. Anton Koster, E. Olsson, J. Rivnay, S. Fabiano, I. McCulloch and C. Müller, ACS Energy Lett., 2018, 3, 278–285 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- L. Wu, H. Li, H. Chai, Q. Xu, Y. Chen and L. Chen, ACS Appl. Electron. Mater., 2021, 3, 1252–1259 CrossRef CAS
.
- F. Zhang and A. Kahn, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28, 1703780 Search PubMed
.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d4mh01805b |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2025 |






